Intro
Discover Chinas Self Strengthening Movement, a late Qing reform aiming to modernize through westernization, industrialization, and militarization, driven by key figures and policies to revitalize the nation.
The Self-Strengthening Movement in China was a pivotal period in the country's history, marking a significant shift in its approach to modernization and development. This movement, which took place from the 1860s to the 1890s, was a response to the challenges posed by Western imperialism and the need for China to strengthen its military, economy, and political institutions. The movement's importance lies in its attempts to blend traditional Chinese values with modern Western technologies and practices, aiming to create a stronger, more resilient China.
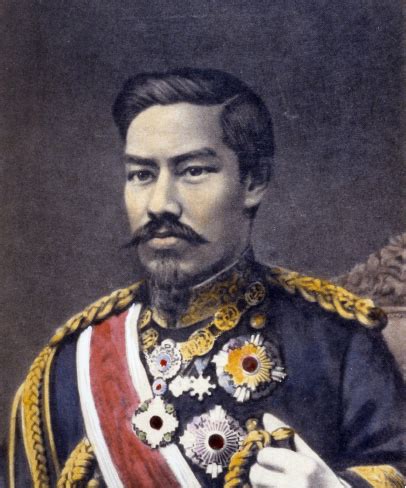
The background to the Self-Strengthening Movement is rooted in the Opium Wars, which exposed China's vulnerability to foreign powers. The Treaty of Nanjing in 1842, following the First Opium War, forced China to open up its ports to British trade and cede Hong Kong, marking the beginning of a series of unequal treaties that eroded Chinese sovereignty. These events highlighted the need for reform and modernization to counter the military superiority of Western nations. The movement was led by high-ranking officials such as Prince Gong, Li Hongzhang, and Zhang Zhidong, who recognized the necessity of adopting Western technology and practices to strengthen China.
The movement's focus was on strengthening China's military capabilities, promoting economic development, and reforming its educational and political systems. The introduction of Western technology, particularly in the fields of weaponry, transportation, and communication, was seen as crucial. The establishment of modern arsenals, shipyards, and telegraph lines were among the key projects undertaken during this period. Additionally, there was an emphasis on promoting foreign trade and encouraging the development of modern industries, such as textiles and mining, to stimulate economic growth.
Introduction to the Self-Strengthening Movement

The Self-Strengthening Movement also led to significant developments in education. Traditional Confucian education was seen as insufficient for the needs of a modernizing China. As a result, modern schools and universities were established, offering courses in Western sciences, mathematics, and languages. This educational reform aimed to produce a new generation of Chinese leaders who were knowledgeable about Western technology and practices, yet still grounded in traditional Chinese values.
Key Figures of the Movement

One of the most notable aspects of the Self-Strengthening Movement was the establishment of the Jiangnan Arsenal in Shanghai, which became a symbol of China's efforts to modernize its military capabilities. The arsenal was equipped with advanced machinery and technology from Europe and was responsible for the production of modern artillery, small arms, and ammunition. Similar efforts were made in other parts of the country, including the establishment of the Foochow Navy Yard, which was designed to produce modern warships.
Economic Reforms and Modernization
Despite its ambitious goals, the Self-Strengthening Movement faced significant challenges and criticisms. Many conservatives within the Qing dynasty saw the adoption of Western practices as a threat to traditional Chinese values and institutions. This resistance limited the scope and depth of the reforms, often resulting in a superficial adoption of Western technology without accompanying institutional and cultural changes.
Criticism and Challenges

The movement's limitations were starkly exposed by China's defeat in the First Sino-Japanese War in 1895. The war highlighted the significant gap between China's modernization efforts and those of Japan, which had undergone a more comprehensive and radical transformation through the Meiji Restoration. The defeat led to a reevaluation of the Self-Strengthening Movement's strategies and a recognition of the need for more profound reforms.
Legacy of the Self-Strengthening Movement

The Self-Strengthening Movement played a crucial role in laying the groundwork for China's future development. It introduced modern technologies, encouraged economic development, and paved the way for further educational and political reforms. Although it faced significant challenges and ultimately failed to achieve its goal of making China a strong, modern state by the end of the 19th century, its legacy can be seen in the subsequent reform movements and China's eventual emergence as a major world power.
Conclusion and Reflection

In reflection, the Self-Strengthening Movement in China represents an important chapter in the country's pursuit of modernization and its complex engagement with Western technologies and values. The movement's emphasis on blending tradition with modernity, although imperfectly executed, reflects the broader challenges faced by many countries in the non-Western world as they navigate the process of modernization.
Gallery of Self-Strengthening Movement
Self-Strengthening Movement Image Gallery










As we reflect on the Self-Strengthening Movement, it is clear that its impact extends beyond the historical period in which it occurred. The challenges it faced and the lessons it offers continue to be relevant for countries undergoing modernization and development. The movement's story serves as a reminder of the complexities and nuances involved in adopting foreign technologies and practices while preserving traditional values and institutions. We invite readers to share their thoughts on the significance of the Self-Strengthening Movement and its relevance to contemporary issues of development and modernization. Your comments and insights are invaluable in continuing the conversation about this pivotal moment in Chinese history.
