Explore the pivotal 18 years that reshaped the world. Discover how significant events, technological advancements, and cultural shifts transformed society, politics, and economies. Learn about the rise of globalization, digital revolution, and shifting world orders that defined this era, shaping the course of modern history forever.
The world has witnessed numerous events that have significantly altered the course of history. Some of these events have been sudden and unexpected, while others have been the result of years of struggle and perseverance. In this article, we will explore 18 years that changed history, highlighting the key events, people, and circumstances that have shaped the world we live in today.

1762: The Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War was a global conflict that lasted from 1756 to 1763. However, 1762 was a pivotal year in the war, as the British gained control of Canada and India, marking the beginning of the British Empire. This war had far-reaching consequences, including the eventual American Revolutionary War and the reorganization of the European continent.
The Rise of British Power
The British victory in the Seven Years' War marked the beginning of their rise to global dominance. Their control of Canada and India provided them with vast resources and territories, setting the stage for the British Empire's expansion.
1776: The American Declaration of Independence
The American Declaration of Independence, signed in 1776, was a document that formally declared the 13 American colonies' independence from Great Britain. This document, written by Thomas Jefferson, laid the foundation for the United States of America and its commitment to democracy and individual rights.

The Birth of American Democracy
The American Declaration of Independence has become a symbol of American democracy, inspiring similar movements around the world. Its emphasis on individual rights, liberty, and democracy has shaped American politics and society.
1789: The French Revolution
The French Revolution, which began in 1789, was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France. The revolution's Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, adopted in 1789, enshrined the principles of liberty, equality, and fraternity, influencing European politics and society for centuries.
The End of Absolute Monarchy
The French Revolution marked the end of absolute monarchy in France, as the people rose up against the aristocracy and the clergy. This revolution had far-reaching consequences, including the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte and the reorganization of Europe.
1803: The Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase, signed in 1803, was a land deal between the United States and France, in which the U.S. acquired approximately 828,000 square miles of land west of the Mississippi River. This purchase doubled the size of the United States, setting the stage for the country's westward expansion.
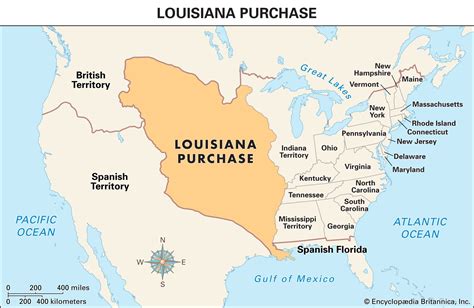
Westward Expansion
The Louisiana Purchase marked the beginning of the United States' westward expansion, as the country sought to expand its territory and resources. This expansion would lead to conflicts with Native American tribes and the eventual annexation of Texas, Oregon, and California.
1815: The Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo, fought in 1815, was a decisive defeat for Napoleon Bonaparte and the French Empire. This battle marked the end of Napoleon's reign and the restoration of the Bourbon monarchy in France.
The Congress of Vienna
The Battle of Waterloo led to the Congress of Vienna, a meeting of European powers that aimed to reorganize Europe and prevent future conflicts. This congress marked the beginning of the Concert of Europe, a system of diplomacy and collective security that would shape European politics for centuries.
1833: The Slavery Abolition Act
The Slavery Abolition Act, passed in 1833, abolished slavery throughout the British Empire. This act marked a significant milestone in the fight against slavery and paved the way for the eventual abolition of slavery in the United States.

The Fight Against Slavery
The Slavery Abolition Act marked a significant step forward in the fight against slavery, inspiring abolitionist movements around the world. This act paved the way for the eventual abolition of slavery in the United States and other countries.
1848: The Revolutions of 1848
The Revolutions of 1848, also known as the Spring of Nations, were a wave of revolutions that swept across Europe, demanding liberal reforms and national independence. These revolutions marked a significant turning point in European politics, as the old order began to crumble.
The Rise of Nationalism
The Revolutions of 1848 marked the rise of nationalism in Europe, as people began to demand greater autonomy and self-determination. This movement would shape European politics for centuries, leading to the unification of Italy and Germany and the eventual collapse of the Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman empires.
1861: The American Civil War
The American Civil War, fought from 1861 to 1865, was a brutal conflict between the Union (the Northern states) and the Confederacy (the Southern states) over issues of slavery and states' rights. This war marked a significant turning point in American history, as the country was reborn and slavery was abolished.

The End of Slavery
The American Civil War marked the end of slavery in the United States, as the Emancipation Proclamation, issued by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863, declared all slaves in Confederate territory to be free. This marked a significant milestone in the fight against slavery and paved the way for the eventual abolition of slavery in the United States.
1871: The Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War, fought in 1871, was a decisive conflict between France and Prussia, resulting in the unification of Germany under Prussian leadership. This war marked the beginning of a new era in European politics, as the German Empire emerged as a major power.
The Rise of Germany
The Franco-Prussian War marked the rise of Germany as a major power in Europe, as the country unified under Prussian leadership. This marked the beginning of a new era in European politics, as Germany emerged as a significant player in international affairs.
1886: The Haymarket Affair
The Haymarket Affair, which took place in 1886, was a labor protest in Chicago that turned violent, resulting in the deaths of several police officers and civilians. This event marked a significant turning point in the labor movement, as workers demanded greater rights and protections.

The Labor Movement
The Haymarket Affair marked a significant turning point in the labor movement, as workers demanded greater rights and protections. This event inspired the creation of Labor Day and the eventual passage of labor laws, protecting workers' rights and improving working conditions.
1898: The Spanish-American War
The Spanish-American War, fought in 1898, was a conflict between the United States and Spain, resulting in the U.S. gaining control of Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. This war marked the beginning of the United States' emergence as a global power.
The Rise of the United States
The Spanish-American War marked the rise of the United States as a global power, as the country expanded its territory and influence. This marked the beginning of a new era in American foreign policy, as the U.S. emerged as a significant player in international affairs.
1903: The Wright Brothers' Flight
The Wright Brothers' Flight, which took place in 1903, marked a significant milestone in aviation history, as Orville and Wilbur Wright successfully flew the first powered, heavier-than-air aircraft. This invention revolutionized transportation and transformed the world.

The Age of Aviation
The Wright Brothers' Flight marked the beginning of the age of aviation, as people began to explore the skies. This invention revolutionized transportation, transforming the world and paving the way for modern air travel.
1914: The Outbreak of World War I
The outbreak of World War I in 1914 marked a significant turning point in world history, as the complex system of alliances and rivalries between European powers led to a global conflict. This war would last four years, resulting in unprecedented loss of life and destruction.
The Great War
The outbreak of World War I marked the beginning of the Great War, a global conflict that would result in unprecedented loss of life and destruction. This war would shape the world for decades to come, leading to the rise of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers.
1917: The Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution, which took place in 1917, was a pair of revolutions that overthrew the Russian Empire and established the Soviet Union. This revolution marked a significant turning point in world history, as the world's first socialist state was established.

The Rise of the Soviet Union
The Russian Revolution marked the rise of the Soviet Union, as the world's first socialist state was established. This marked the beginning of a new era in world politics, as the Soviet Union emerged as a superpower and a rival to the United States.
1929: The Stock Market Crash
The Stock Market Crash of 1929 marked a significant turning point in economic history, as the global economy collapsed and the Great Depression began. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to widespread poverty and unemployment.
The Great Depression
The Stock Market Crash of 1929 marked the beginning of the Great Depression, a global economic downturn that would last for over a decade. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to widespread poverty and unemployment.
1939: The Outbreak of World War II
The outbreak of World War II in 1939 marked a significant turning point in world history, as the complex system of alliances and rivalries between European powers led to a global conflict. This war would last six years, resulting in unprecedented loss of life and destruction.

The Second Great War
The outbreak of World War II marked the beginning of the Second Great War, a global conflict that would result in unprecedented loss of life and destruction. This war would shape the world for decades to come, leading to the rise of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers.
1945: The Atomic Bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, which took place in 1945, marked a significant turning point in world history, as the world entered the nuclear age. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of international relations and global politics.
The Nuclear Age
The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki marked the beginning of the nuclear age, as the world entered a new era of international relations and global politics. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of diplomacy and international cooperation.
1955: The Montgomery Bus Boycott
The Montgomery Bus Boycott, which took place in 1955, was a pivotal event in the Civil Rights Movement, as African Americans in Montgomery, Alabama, boycotted the city's buses to protest segregation. This event marked a significant turning point in the struggle for civil rights in the United States.

The Civil Rights Movement
The Montgomery Bus Boycott marked a significant turning point in the Civil Rights Movement, as African Americans in the United States demanded greater rights and protections. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to the passage of landmark civil rights legislation and the eventual election of Barack Obama as President.
1963: The Assassination of John F. Kennedy
The assassination of John F. Kennedy, which took place in 1963, marked a significant turning point in American history, as the country was plunged into shock and grief. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of American politics and foreign policy.
The Kennedy Legacy
The assassination of John F. Kennedy marked the end of an era in American politics, as the country was plunged into shock and grief. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of American politics and foreign policy.
1969: The First Moon Landing
The first moon landing, which took place in 1969, marked a significant milestone in space exploration, as NASA's Apollo 11 mission successfully landed astronauts on the moon. This event marked a significant turning point in the space age, as humanity expanded its presence in space.
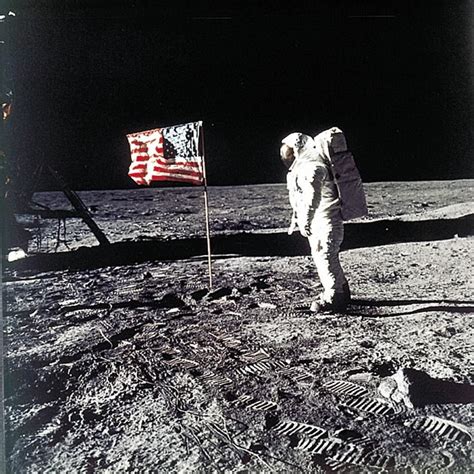

The Space Age
The first moon landing marked a significant turning point in the space age, as humanity expanded its presence in space. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of space exploration and discovery.
1989: The Fall of the Berlin Wall
The fall of the Berlin Wall, which took place in 1989, marked a significant turning point in world history, as the division between East and West Germany was ended. This event marked the beginning of a new era in international relations, as the Soviet Union's grip on Eastern Europe began to loosen.
The End of the Cold War
The fall of the Berlin Wall marked the beginning of the end of the Cold War, as the Soviet Union's grip on Eastern Europe began to loosen. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of international relations and global politics.
1991: The Dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, which took place in 1991, marked a significant turning point in world history, as the world's first socialist state was dissolved. This event marked the beginning of a new era in international relations, as the United States emerged as the world's sole superpower.
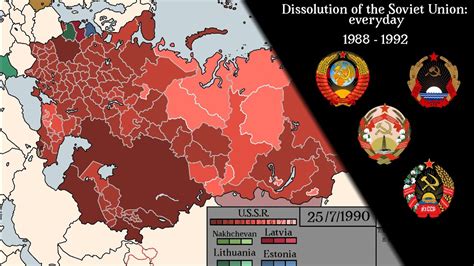
The Post-Cold War Era
The dissolution of the Soviet Union marked the beginning of a new era in international relations, as the United States emerged as the world's sole superpower. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of global politics and international relations.
2001: The September 11 Attacks
The September 11 attacks, which took place in 2001, marked a significant turning point in world history, as the world entered a new era of terrorism and global conflict. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of international relations and global politics.
The War on Terror
The September 11 attacks marked the beginning of the War on Terror, a global conflict that would last for decades. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of international relations and global politics.
2008: The Global Financial Crisis
The global financial crisis, which began in 2008, marked a significant turning point in economic history, as the world entered a new era of economic uncertainty. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to widespread economic downturn and a new era of economic policy.

The New Economic Order
The global financial crisis marked the beginning of a new economic order, as the world entered a new era of economic uncertainty. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to widespread economic downturn and a new era of economic policy.
2011: The Arab Spring
The Arab Spring, which began in 2011, marked a significant turning point in Middle Eastern history, as a wave of protests and uprisings swept across the region. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of Middle Eastern politics and international relations.
The New Middle East
The Arab Spring marked the beginning of a new era in Middle Eastern politics, as a wave of protests and uprisings swept across the region. This event would have far-reaching consequences, leading to a new era of Middle Eastern politics and international relations.
