Intro
Explore the evolution of Marine Corps pay with our in-depth look at 5 key dates in its history. From humble beginnings to modern-day compensations, discover how legislative changes, wartime efforts, and economic shifts have shaped military pay scales, allowances, and benefits for US Marines.
The United States Marine Corps has a rich history of sacrifice, honor, and courage. One crucial aspect of being a Marine is receiving fair compensation for their service. Over the years, Marine Corps pay has undergone significant changes, reflecting the nation's economic conditions, technological advancements, and shifting societal values. In this article, we'll delve into five key dates in Marine Corps pay history, exploring the milestones that have shaped the compensation packages of Marines.
Early Years: 1775-1865

The Continental Congress established the Continental Marines on November 10, 1775, with a monthly pay of $6.67 for privates. This amount was relatively modest compared to other branches of the military. As the American Revolution progressed, Marine pay remained stagnant, with occasional increases to account for inflation. During the War of 1812, Marine pay rose to $8 per month for privates. The Mexican-American War saw another increase, with privates earning $11 per month.
Pay Reform and the Civil War
The mid-19th century brought significant changes to Marine Corps pay. In 1861, the pay scale was reformed, and Marines received a significant increase in compensation. Privates' monthly pay rose to $16, while non-commissioned officers saw substantial boosts in their earnings. This reform aimed to attract and retain qualified personnel during the American Civil War.
The Great War and Interwar Period: 1917-1941

During World War I, Marine Corps pay increased to reflect the rising cost of living. In 1917, privates earned $30 per month, while non-commissioned officers saw significant increases in their pay. The interwar period saw few changes to Marine Corps pay, with the Great Depression forcing reductions in military spending.
World War II and the Post-War Era
World War II brought another wave of pay reforms. In 1942, the Marine Corps implemented a new pay scale, which provided significant increases for all ranks. Privates earned $50 per month, while officers saw substantial boosts in their compensation. The post-war era saw continued growth in Marine Corps pay, with the 1949 Career Compensation Act providing a 15% increase in military pay across the board.
Modernization and Current Developments: 1970s-Present

The 1970s saw significant changes in Marine Corps pay, with the introduction of the All-Volunteer Force (AVF) in 1973. The AVF led to increased competition for recruits, driving up pay and benefits to attract qualified personnel. The 1980s and 1990s saw continued growth in Marine Corps pay, with the 1999 Military Pay Reform Act providing a 4.8% increase in military pay.
Today, Marine Corps pay remains competitive with the civilian sector, reflecting the Corps' commitment to attracting and retaining top talent. The 2020 National Defense Authorization Act provided a 3.1% pay increase for military personnel, ensuring that Marines continue to receive fair compensation for their service.
Gallery of Marine Corps Pay Images
Marine Corps Pay Image Gallery

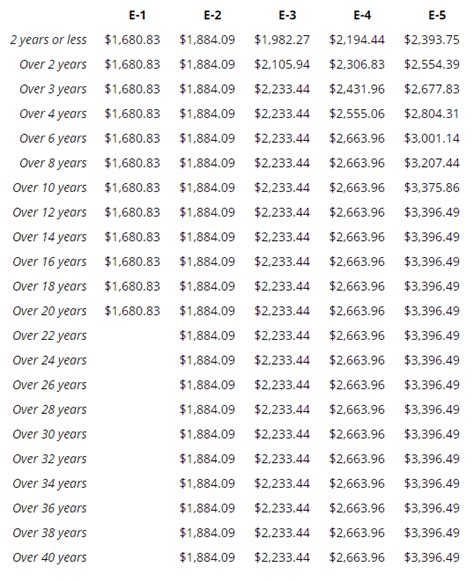





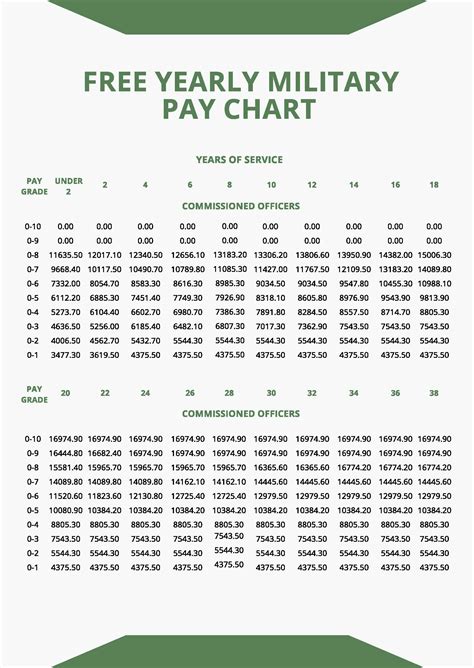
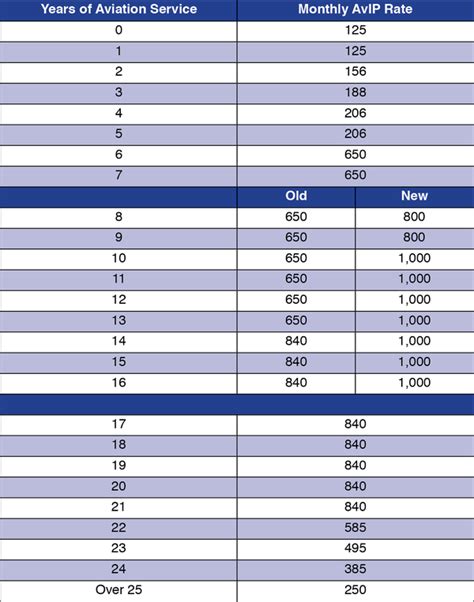
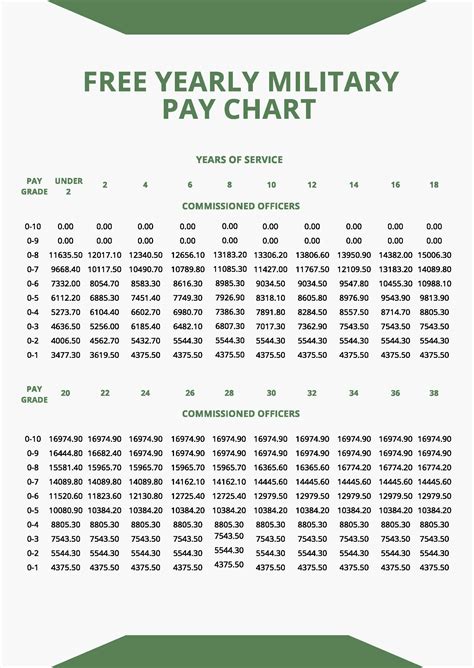
In conclusion, the history of Marine Corps pay is a rich and complex one, reflecting the nation's values, economic conditions, and technological advancements. From the Continental Marines to the present day, Marine Corps pay has evolved to ensure that Marines receive fair compensation for their service. As the Corps continues to modernize and adapt to an ever-changing world, its commitment to providing competitive pay and benefits remains unwavering.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the history of Marine Corps pay. What do you think are the most significant milestones in Marine Corps pay history? How do you think the Corps can continue to attract and retain top talent in the future? Share your comments below, and let's keep the conversation going!
