Intro
Unlock the secrets of Excel formulas! Discover 5 powerful formulas you can type in cell D92 to boost your productivity. Learn how to use SUMIFS, INDEX/MATCH, and more to analyze data, perform calculations, and automate tasks. Master these formulas to become an Excel pro and simplify your workflow with ease.
Excel formulas can be incredibly powerful tools for data analysis and manipulation. Here are five formulas you can type in cell D92, each with a unique purpose and application.
Formula 1: SUMIFS
Summing Data Based on Multiple Criteria
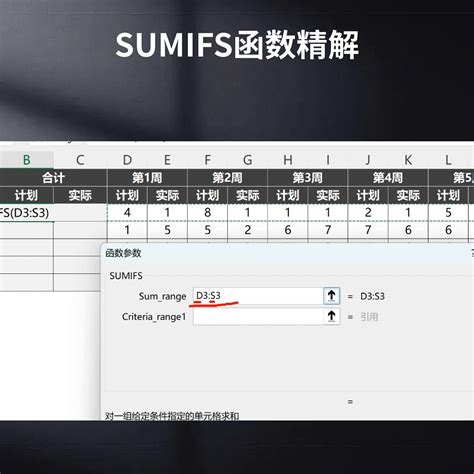
The SUMIFS formula allows you to sum data based on multiple criteria. For example, if you have a table with sales data and you want to sum the sales for a specific region and product, you can use the following formula in cell D92:
=SUMIFS(C:C, A:A, "North", B:B, "Product A")
This formula sums the values in column C (sales data) where the values in column A (region) are "North" and the values in column B (product) are "Product A".
Formula 2: INDEX/MATCH
Looking Up Data in a Table

The INDEX/MATCH formula combination is a powerful tool for looking up data in a table. For example, if you have a table with employee data and you want to find the salary of a specific employee, you can use the following formula in cell D92:
=INDEX(C:C, MATCH(D91, A:A, 0))
This formula looks up the value in cell D91 (employee ID) in column A (employee IDs) and returns the corresponding value in column C (salaries).
Formula 3: AVERAGEIF
Averaging Data Based on a Condition
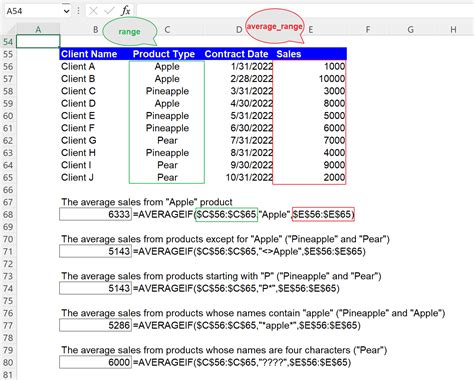
The AVERAGEIF formula allows you to average data based on a condition. For example, if you have a table with exam scores and you want to average the scores for a specific subject, you can use the following formula in cell D92:
=AVERAGEIF(B:B, "Math", C:C)
This formula averages the values in column C (exam scores) where the values in column B (subject) are "Math".
Formula 4: COUNTIFS
Counting Data Based on Multiple Criteria
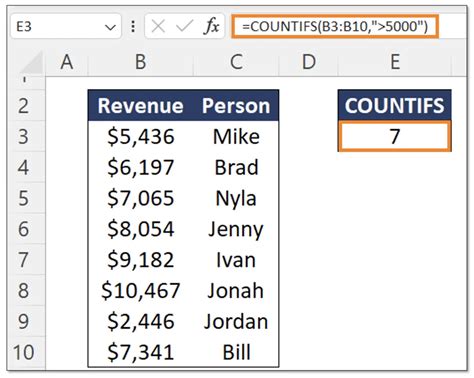
The COUNTIFS formula allows you to count data based on multiple criteria. For example, if you have a table with sales data and you want to count the number of sales for a specific region and product, you can use the following formula in cell D92:
=COUNTIFS(A:A, "North", B:B, "Product A")
This formula counts the number of rows where the values in column A (region) are "North" and the values in column B (product) are "Product A".
Formula 5: XLOOKUP
Looking Up Data in a Table with a Single Formula
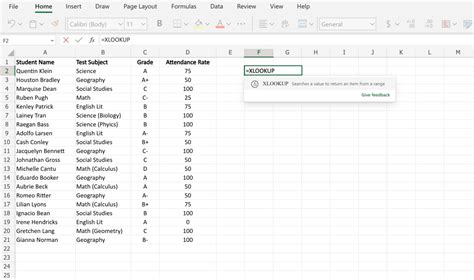
The XLOOKUP formula is a powerful tool for looking up data in a table. For example, if you have a table with employee data and you want to find the salary of a specific employee, you can use the following formula in cell D92:
=XLOOKUP(D91, A:A, C:C)
This formula looks up the value in cell D91 (employee ID) in column A (employee IDs) and returns the corresponding value in column C (salaries).
Excel Formulas Image Gallery



We hope this article has helped you learn more about the different formulas you can use in Excel. Whether you're a beginner or an advanced user, there's always something new to learn. If you have any questions or need further assistance, please don't hesitate to ask.
