Intro
Discover how food stamps impact your new job income. Learn if your benefits will be affected by your employment status, income level, and other factors. Understand the rules and regulations surrounding SNAP benefits and employment to ensure you make informed decisions about your finances and career.
Receiving food stamps, also known as the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), can be a vital lifeline for individuals and families struggling to make ends meet. However, when you start a new job or experience an increase in income, it's natural to wonder how this might affect your eligibility for food stamps. In this article, we'll delve into the details of how food stamps are affected by new job income and what you need to know to navigate the system.
When you start a new job or see an increase in income, it's essential to report this change to your local SNAP office. This is because the amount of food stamps you receive is based on your household's income and expenses. If your income increases, your eligibility for food stamps may be affected. However, the impact on your food stamps will depend on several factors, including the amount of your income increase, your household size, and the specific SNAP rules in your state.
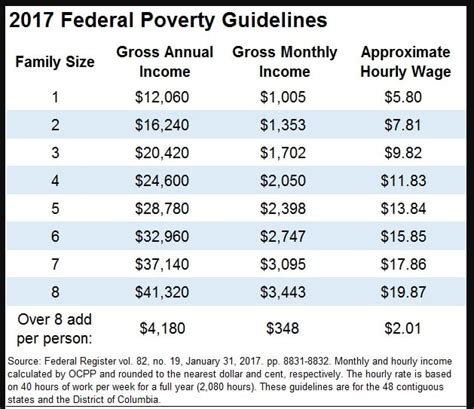
One of the primary concerns for individuals receiving food stamps is that their new job income will disqualify them from receiving benefits. While it's true that an increase in income can affect your eligibility, it's not always the case. In fact, many states have income limits that allow individuals to continue receiving food stamps even if they're working. For example, in some states, individuals can earn up to 165% of the federal poverty level and still be eligible for food stamps.
How Income Affects Food Stamp Eligibility
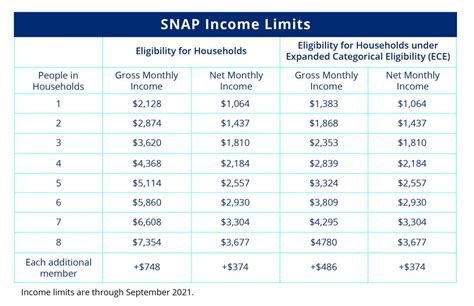
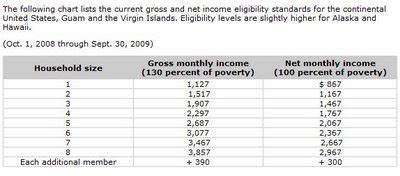
To understand how income affects food stamp eligibility, let's take a closer look at the income limits for SNAP. In general, the income limits for SNAP vary by state and household size. However, most states follow the federal guidelines, which consider two types of income: gross income and net income.
Gross income refers to your total income before deductions, while net income is your income after deductions. When determining eligibility for food stamps, your local SNAP office will consider both your gross and net income.
Here are some general income limits for SNAP:
- Gross income limits:
- 1 person: $1,313/month
- 2 people: $1,755/month
- 3 people: $2,197/month
- 4 people: $2,639/month
- 5 people: $3,081/month
- Net income limits:
- 1 person: $1,012/month
- 2 people: $1,372/month
- 3 people: $1,732/month
- 4 people: $2,092/month
- 5 people: $2,452/month
Keep in mind that these are general income limits, and the specific limits in your state may vary. It's essential to check with your local SNAP office to determine the income limits in your area.
What Counts as Income for SNAP?
When determining your eligibility for food stamps, your local SNAP office will consider various types of income, including:
- Earned income: This includes wages, salaries, and tips from a job.
- Unearned income: This includes benefits like Social Security, Supplemental Security Income (SSI), and unemployment benefits.
- Cash assistance: This includes cash benefits from programs like Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF).
However, some types of income are not considered when determining eligibility for food stamps, including:
- Child support payments
- Foster care payments
- Some types of veterans' benefits
How to Report Changes in Income
If you start a new job or experience an increase in income, it's crucial to report this change to your local SNAP office. You can report changes in income by:
- Calling your local SNAP office
- Visiting your local SNAP office in person
- Submitting a report online or by mail
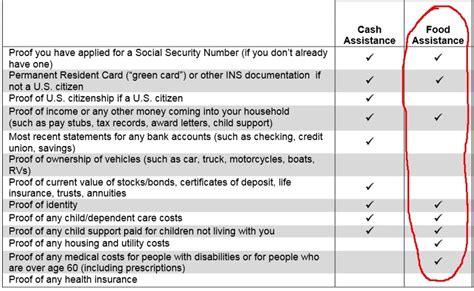
When reporting changes in income, be prepared to provide documentation, such as:
- Pay stubs
- W-2 forms
- Tax returns

What Happens if I Don't Report Changes in Income?
Failing to report changes in income can result in serious consequences, including:
- Overpayment of food stamps: If you're receiving too many food stamps due to unreported income, you may be required to repay the excess amount.
- Loss of eligibility: If you're found to be ineligible for food stamps due to unreported income, you may lose your benefits.
- Penalties and fines: In some cases, you may face penalties and fines for failing to report changes in income.
Conclusion
Starting a new job or experiencing an increase in income can be a significant change, but it doesn't necessarily mean you'll lose your eligibility for food stamps. By understanding how income affects food stamp eligibility and reporting changes in income, you can ensure you're receiving the benefits you're eligible for.
If you have questions about how your new job income will affect your food stamps, don't hesitate to reach out to your local SNAP office. They can provide guidance and help you navigate the system.
Gallery of Food Stamps and Income