Intro
Discover the pivotal moments and strategies that led to the Allied victory in World War I. Explore the historical context, key battles, and leadership decisions that shaped the outcome of the Great War. Learn how diplomacy, trench warfare, and technological advancements influenced the winning of World War I, a turning point in modern history.
The outbreak of World War I in 1914 marked the beginning of a global conflict that would claim millions of lives and reshape the world order. The war, fought between the Allied Powers and the Central Powers, was a complex and multifaceted conflict that involved many countries and empires. In this article, we will explore the historical context of World War I, the major events and battles, and the ultimate victory of the Allied Powers.

The war was sparked by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the heir to the throne of Austria-Hungary, by a Serbian nationalist in June 1914. This event triggered a chain reaction of diplomatic crises and military mobilizations that eventually led to the outbreak of war. The Central Powers, consisting of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire, faced off against the Allied Powers, which included France, Britain, Russia, and the United States.
The War in Europe
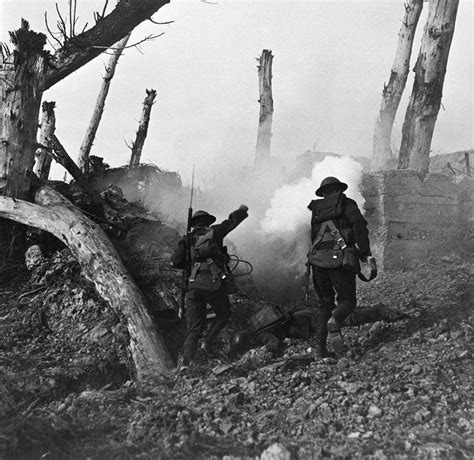
The war in Europe was characterized by a series of bloody battles and stalemates, as both sides dug in and fought for control of the continent. The Western Front, which stretched from the North Sea to the Swiss border, was the main theater of conflict. The war saw the introduction of new technologies, such as tanks, airplanes, and poison gas, which were used to devastating effect.

The war also saw the rise of trench warfare, as both sides dug in and fought from fortified positions. The trenches, which stretched for hundreds of miles, were a testament to the stalemate that had developed on the battlefield. The most famous battles of the war, such as the Battle of the Somme and the Battle of Verdun, were fought on the Western Front.
The Eastern Front
The Eastern Front, which stretched from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea, was another major theater of conflict. The war saw the clash of the Russian Empire and the Austro-Hungarian Empire, as well as the Ottoman Empire. The war on the Eastern Front was marked by a series of bloody battles and massacres, as both sides fought for control of the region.

The war also saw the rise of the Russian Revolution, which would eventually lead to the downfall of the Russian monarchy and the rise of the Soviet Union.
The War at Sea
The war at sea was another important aspect of World War I. The war saw the rise of the German U-boat, which was used to devastating effect against Allied shipping. The U-boats, which were submarines, were able to sink many Allied ships, including the passenger liner Lusitania.

The war also saw the introduction of the convoy system, which was used to protect Allied shipping from U-boat attacks. The convoy system, which involved sailing ships in groups escorted by warships, was a major factor in the Allied victory.
The United States Enters the War
The United States entered the war in April 1917, after Germany resumed unrestricted submarine warfare and sank several American ships. The United States declared war on Germany and began to mobilize its military.

The United States played a major role in the Allied victory, providing significant military and economic support to the other Allied Powers.
The Turning Point of the War
The turning point of the war came in 1918, when the Allies launched a series of successful offensives on the Western Front. The offensives, which were led by the British, French, and American armies, pushed the Germans back and eventually led to the collapse of the German army.

The most famous battle of the war, the Battle of Amiens, was fought in August 1918 and marked the beginning of the end of the war. The battle, which was led by the Canadian Corps, saw the Allies break through the German lines and push the Germans back.
The Armistice and the Treaty of Versailles
The war finally came to an end on November 11, 1918, when the Allies and the Central Powers signed the Armistice of Compiègne. The armistice marked the end of hostilities and paved the way for the Treaty of Versailles, which was signed in June 1919.

The Treaty of Versailles imposed harsh penalties on Germany, including significant territorial losses and reparations. The treaty also established the League of Nations, which was intended to prevent future wars.
Conclusion
In conclusion, World War I was a global conflict that had a profound impact on the world. The war saw the rise of new technologies and the introduction of new tactics, as well as the downfall of several empires. The war also saw the rise of the United States as a major world power and the establishment of the League of Nations.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of World War I and its significance. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
World War I Image Gallery