Intro
Uncover the mysteries of the X-20 Dyna Soar, a top-secret space plane project from the 1950s. Learn about its revolutionary design, propulsion systems, and mission objectives. Discover the history and development of this pioneering spacecraft, and how it paved the way for modern spaceplanes and hypersonic flight.
The concept of a space plane has long fascinated the imagination of scientists, engineers, and the general public alike. The idea of a vehicle that can seamlessly transition from atmospheric flight to space and back again has been a staple of science fiction for decades. However, in the 1950s and 1960s, the United States military began exploring the possibility of creating a real-life space plane. The result was the X-20 Dyna Soar, a top-secret project that aimed to create a reusable spacecraft capable of carrying a single pilot into space.
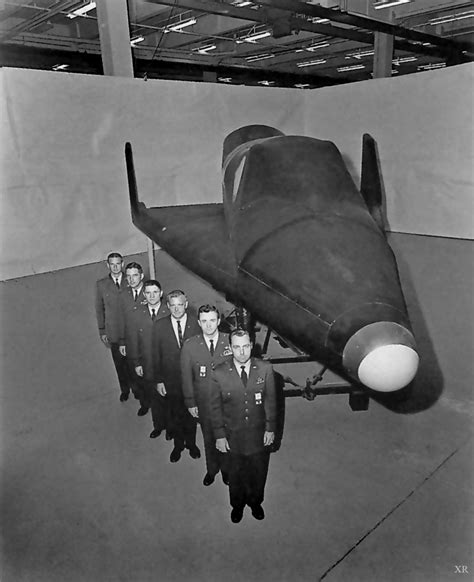

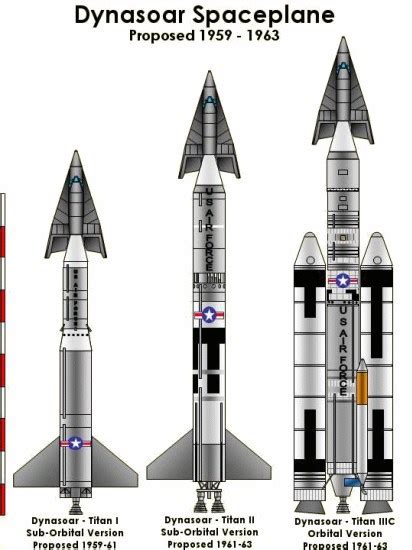
The X-20 Dyna Soar was a unique vehicle that combined the characteristics of a conventional aircraft with those of a spacecraft. It was designed to take off from a conventional runway, accelerate to high speeds using a rocket engine, and then transition into space, where it could orbit the Earth or conduct other space-related missions. The X-20 was also designed to be reusable, with the ability to return to Earth and land like a conventional aircraft.
Development and Design
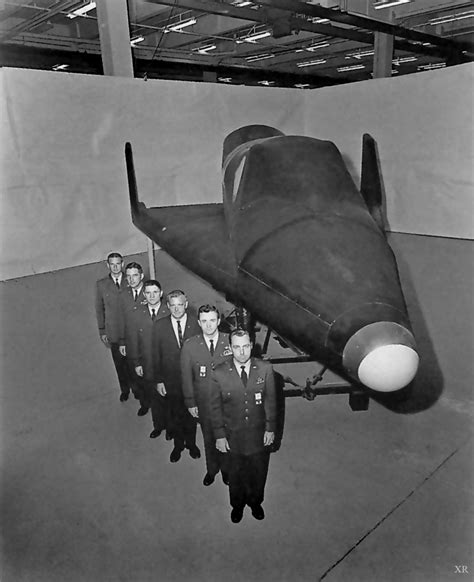
The X-20 Dyna Soar was developed by Boeing in the late 1950s and early 1960s. The project was shrouded in secrecy, and the exact details of the design and development process remain classified to this day. However, it is known that the X-20 was designed to be a single-pilot vehicle, with a length of approximately 35 feet and a wingspan of around 20 feet.
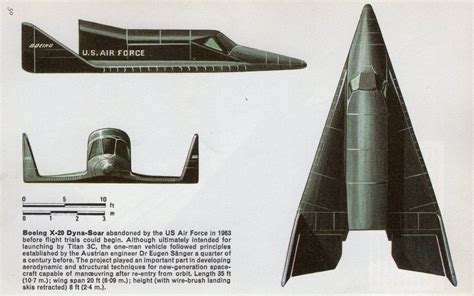
The X-20 was powered by a single rocket engine, which was capable of producing 60,000 pounds of thrust. The vehicle was also equipped with a pair of small jet engines, which were used for atmospheric flight. The X-20's airframe was made of a combination of metal and ceramic materials, which were designed to withstand the extreme temperatures generated during re-entry.
Flight Profile
The X-20 Dyna Soar's flight profile was designed to be highly versatile. The vehicle was capable of taking off from a conventional runway and accelerating to high speeds using its rocket engine. Once in space, the X-20 could orbit the Earth or conduct other space-related missions. The vehicle was also designed to be capable of re-entering the Earth's atmosphere, where it could use its jet engines to slow down and land like a conventional aircraft.

The X-20's flight profile was highly dependent on the mission requirements. For example, if the vehicle was designed to conduct a reconnaissance mission, it would need to enter space, gather data, and then return to Earth without being detected. In this scenario, the X-20 would use its rocket engine to accelerate to high speeds and then transition into space, where it would use its small jet engines to maneuver and gather data.
Cancelation and Legacy
Despite the X-20 Dyna Soar's promising design and capabilities, the project was ultimately canceled in 1963 due to a combination of technical and financial issues. The project's cancellation was also influenced by the development of the Gemini and Apollo programs, which were seen as more feasible and cost-effective.

Despite its cancelation, the X-20 Dyna Soar's legacy lives on. The project's innovative design and capabilities paved the way for future space plane projects, including the Space Shuttle program. The X-20's design also influenced the development of modern-day space planes, such as the X-37B.
Comparison to Modern Space Planes
The X-20 Dyna Soar's design and capabilities can be compared to those of modern space planes, such as the X-37B. The X-37B is a reusable space plane developed by Boeing, which has been used for a variety of space-related missions.

Like the X-20, the X-37B is designed to be reusable and can carry out a variety of space-related missions. However, the X-37B is significantly larger than the X-20, with a length of over 29 feet and a wingspan of around 15 feet. The X-37B is also powered by a more advanced rocket engine, which is capable of producing over 100,000 pounds of thrust.
Gallery of X-20 Dyna Soar Images
X-20 Dyna Soar Image Gallery








The X-20 Dyna Soar was a pioneering project that pushed the boundaries of space exploration. Despite its cancelation, the project's legacy lives on, influencing the development of modern space planes and inspiring new generations of engineers and scientists. As we continue to explore the vast expanse of space, the X-20 Dyna Soar serves as a reminder of the innovative spirit and determination that have driven human progress.
We hope you enjoyed this article and learned more about the X-20 Dyna Soar. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
