Uncover the 5 key differences between the YF-22 and YF-23, two of the most advanced fifth-generation fighter jets in the world. From design and performance to stealth capabilities and engine technology, learn what set these two prototypes apart in the competition for the US Air Forces next-gen fighter contract.
The YF-22 and YF-23 are two of the most iconic and advanced fighter jets in the history of military aviation. Both aircraft were designed to meet the requirements of the United States Air Force's Advanced Tactical Fighter (ATF) program, which aimed to create a next-generation air superiority fighter. Although both aircraft were highly advanced and impressive in their own right, there were significant differences between them. In this article, we will explore the 5 key differences between the YF-22 and YF-23.

1. Design and Aerodynamics
One of the most notable differences between the YF-22 and YF-23 is their design and aerodynamics. The YF-22, built by Lockheed Martin, had a more conventional design with a curved fuselage and a distinctive "sawtooth" shape on its wings. In contrast, the YF-23, built by Northrop Grumman and McDonnell Douglas, had a more radical design with a flattened fuselage and a unique "faceted" shape on its wings.
The YF-23's design was intended to reduce its radar cross-section (RCS) and provide improved stealth capabilities. However, the YF-22's design was also stealthy, although not to the same extent as the YF-23. The YF-22's sawtooth wing design allowed for better maneuverability and stability at high angles of attack.
Stealth Capabilities
Both aircraft were designed to be stealthy, but the YF-23 had a more advanced radar-absorbent material (RAM) coating, which reduced its RCS even further. However, the YF-22's stealth capabilities were still impressive, and its designers made use of a combination of design features, including curved surfaces and serrated edges, to reduce its RCS.

2. Engines and Performance
The YF-22 and YF-23 had different engine configurations, which affected their performance. The YF-22 was powered by two Pratt & Whitney F119 engines, each producing 22,000 pounds of thrust. In contrast, the YF-23 was powered by two Pratt & Whitney F120 engines, each producing 20,000 pounds of thrust.
The YF-22's engines gave it a higher thrust-to-weight ratio, allowing it to accelerate faster and climb more steeply. However, the YF-23's engines were more efficient, providing better range and endurance.
Speed and Maneuverability
The YF-22 was capable of reaching speeds over Mach 2, while the YF-23 had a top speed of around Mach 1.8. However, the YF-23 was more agile and had a tighter turning radius, making it more suitable for close-range combat.
3. Avionics and Radar
The YF-22 and YF-23 had different avionics and radar systems. The YF-22 had an advanced radar system, known as the AN/APG-77, which provided long-range detection and tracking capabilities. In contrast, the YF-23 had a more experimental radar system, known as the AN/APG-76, which was designed to provide improved resolution and accuracy.
The YF-22's radar system was more mature and widely tested, while the YF-23's radar system was still in the experimental phase.
Situational Awareness
The YF-22 had a more advanced situational awareness system, known as the Advanced Tactical Information Distribution System (ATIDS), which provided pilots with real-time information on their surroundings. In contrast, the YF-23 had a more limited situational awareness system, known as the Tactical Information Distribution System (TIDS).

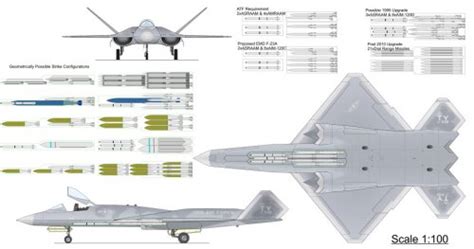
4. Armament and Payload
The YF-22 and YF-23 had different armament and payload configurations. The YF-22 had two internal bays, each capable of carrying up to 1,000 pounds of ordnance. In contrast, the YF-23 had a single internal bay, capable of carrying up to 2,000 pounds of ordnance.
The YF-22's armament configuration was more flexible, allowing it to carry a wider range of missiles and bombs. However, the YF-23's larger internal bay allowed it to carry more fuel, increasing its range and endurance.
Weapondelivery
The YF-22 had a more advanced weapondelivery system, known as the Advanced Tactical Airborne Reconnaissance System (ATARS), which provided pilots with real-time information on their targets. In contrast, the YF-23 had a more limited weapondelivery system, known as the Tactical Airborne Reconnaissance System (TARS).
5. Cost and Development
The YF-22 and YF-23 had different development costs and timelines. The YF-22 was developed at a cost of around $20 billion, while the YF-23 was developed at a cost of around $15 billion.
The YF-22's development timeline was longer, spanning over 10 years, while the YF-23's development timeline was shorter, spanning around 7 years.
Production and Deployment
The YF-22 was produced in larger numbers, with over 180 aircraft delivered to the US Air Force. In contrast, the YF-23 was not produced in large numbers, with only two prototype aircraft built.

Gallery of YF-22 and YF-23 Images
YF-22 and YF-23 Image Gallery










We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the differences between the YF-22 and YF-23. Both aircraft were highly advanced and played a significant role in the development of modern fighter jets. We encourage you to share your thoughts and opinions on these iconic aircraft in the comments section below.
