Intro
Discover ADHD symptoms explained by Mayo Clinic, including attention deficit, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, to understand diagnosis, treatment, and management of this neurodevelopmental disorder.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. According to the Mayo Clinic, ADHD is one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders of childhood, and it can persist into adulthood. Understanding the symptoms of ADHD is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. In this article, we will delve into the world of ADHD, exploring its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
The Mayo Clinic explains that ADHD symptoms can vary from person to person, and they may change over time. The three main categories of symptoms are inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Inattention refers to the inability to focus, pay attention, or follow instructions. Hyperactivity is characterized by excessive restlessness, fidgeting, or talking. Impulsivity involves acting without thinking, interrupting others, or having trouble waiting for one's turn. These symptoms can be mild, moderate, or severe, and they can impact daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
ADHD symptoms can be divided into two main types: predominantly inattentive type (ADHD-PI) and predominantly hyperactive-impulsive type (ADHD-PH). The predominantly inattentive type is characterized by symptoms of inattention, such as disorganization, forgetfulness, and difficulty with time management. The predominantly hyperactive-impulsive type is marked by symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsivity, such as restlessness, fidgeting, and interrupting others. Some people may exhibit symptoms of both types, which is known as combined type ADHD.
Understanding ADHD Symptoms

The Mayo Clinic emphasizes that ADHD symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions, such as anxiety, depression, or sleep disorders. Therefore, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. A comprehensive evaluation, including a physical exam, medical history, and psychological assessments, can help determine whether symptoms are due to ADHD or another condition. The diagnostic criteria for ADHD, as outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), include a persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with functioning or relationships.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of ADHD are still not fully understood, but research suggests that it is a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. The Mayo Clinic notes that certain factors may increase the risk of developing ADHD, such as family history, brain injuries, or exposure to toxins during pregnancy. Additionally, some studies suggest that ADHD may be associated with imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which play a crucial role in attention and impulse control.Diagnosis and Treatment

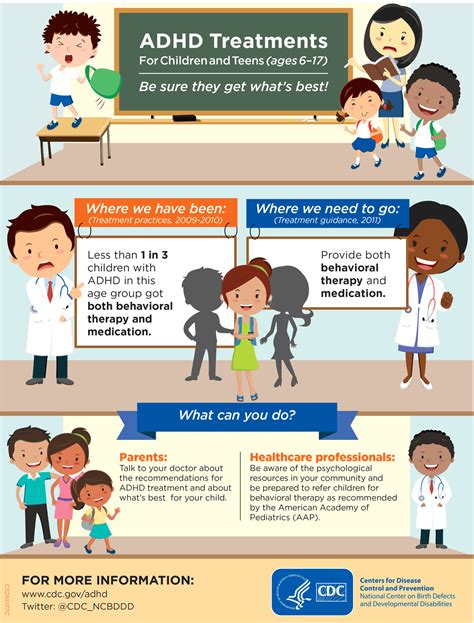
A comprehensive treatment plan for ADHD typically involves a combination of medications, behavioral therapy, and lifestyle changes. The Mayo Clinic recommends that treatment be tailored to the individual's specific needs and circumstances. Medications, such as stimulants and non-stimulants, can help alleviate symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Behavioral therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and behavioral modification, can help individuals develop coping strategies, improve relationships, and enhance overall functioning.
Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy is a crucial component of ADHD treatment, as it can help individuals develop skills to manage symptoms, improve relationships, and enhance overall well-being. The Mayo Clinic suggests that behavioral therapy can be delivered in individual or group settings, and it may involve techniques such as positive reinforcement, token economies, and social skills training. Additionally, behavioral therapy can help individuals develop strategies to improve time management, organization, and self-regulation.Living with ADHD

Living with ADHD can be challenging, but with the right treatment and support, individuals can learn to manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life. The Mayo Clinic emphasizes the importance of self-care, stress management, and social support in managing ADHD. Regular exercise, healthy eating, and adequate sleep can help alleviate symptoms, while stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help reduce anxiety and improve focus.
Coping Strategies
Developing coping strategies is essential for managing ADHD symptoms and improving overall well-being. The Mayo Clinic suggests that individuals with ADHD can benefit from techniques such as breaking tasks into smaller steps, using reminders and calendars, and minimizing distractions. Additionally, individuals can benefit from learning to prioritize tasks, set realistic goals, and seek support from family and friends.ADHD in Children

ADHD can affect children of all ages, from preschool to adolescence. The Mayo Clinic notes that symptoms of ADHD in children can be similar to those in adults, but they may be more pronounced and interfere with academic and social functioning. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for helping children with ADHD develop skills, improve relationships, and enhance overall well-being.
Parenting Strategies
Parenting a child with ADHD can be challenging, but with the right strategies, parents can help their child manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life. The Mayo Clinic suggests that parents can benefit from techniques such as positive reinforcement, consistent discipline, and structured routines. Additionally, parents can help their child develop social skills, improve relationships, and enhance overall functioning by encouraging physical activity, social interaction, and cognitive stimulation.ADHD in Adults

ADHD can affect adults of all ages, from young adulthood to older adulthood. The Mayo Clinic notes that symptoms of ADHD in adults can be similar to those in children, but they may be more subtle and interfere with work, relationships, and overall well-being. Adults with ADHD may experience symptoms such as disorganization, forgetfulness, and difficulty with time management, which can impact daily life and overall quality of life.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for adults with ADHD are similar to those for children, and they typically involve a combination of medications, behavioral therapy, and lifestyle changes. The Mayo Clinic recommends that treatment be tailored to the individual's specific needs and circumstances. Medications, such as stimulants and non-stimulants, can help alleviate symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Behavioral therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and behavioral modification, can help individuals develop coping strategies, improve relationships, and enhance overall functioning.ADHD Image Gallery









In conclusion, ADHD is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. By working with healthcare professionals, individuals with ADHD can develop coping strategies, improve relationships, and enhance overall well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about ADHD in the comments below. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from learning more about ADHD. Together, we can promote awareness, understanding, and support for individuals with ADHD.
