Intro
Discover the ultimate Arachnophile Guide, exploring spider biology, behavior, and conservation, with insights into arachnid habitats, species diversity, and entomology research.
The world of arachnids is a fascinating and often misunderstood realm, full of intriguing creatures that have captivated human imagination for centuries. From the eerie, glowing eyes of spiders to the impressive, leggy strides of scorpions, arachnids have a certain allure that draws in enthusiasts and amateur explorers alike. For those who are just beginning to explore this captivating world, the term "arachnophile" may be unfamiliar, but it refers to individuals who have a deep appreciation and enthusiasm for arachnids. Whether you're a seasoned arachnophile or simply curious about these eight-legged wonders, this guide is designed to provide you with a comprehensive introduction to the world of arachnids, covering their biology, diversity, and the ways in which they interact with their environments and human societies.
Arachnids are a diverse group of arthropods that include spiders, scorpions, ticks, and mites, among others. These creatures have been on Earth for over 400 million years, evolving into a wide range of species that occupy almost every conceivable habitat, from the freezing tundras to the hottest deserts. Their adaptability, resilience, and unique characteristics have allowed them to thrive in environments where other creatures might struggle to survive. For arachnophiles, the study and appreciation of these arachnids offer a window into a world of intricate social behaviors, remarkable engineering feats, and complex ecological relationships.
The appeal of arachnids can be attributed to their enigmatic nature and the crucial roles they play in ecosystems. Spiders, for instance, are master predators that help regulate insect populations, protecting crops and forests from potential pests. Scorpions, on the other hand, are ancient, nocturnal hunters that have evolved sophisticated venom delivery systems, making them both fascinating and formidable. Ticks and mites, though often viewed as pests due to their role in transmitting diseases, are also integral components of ecosystems, serving as both predators and prey in the grand tapestry of life. Understanding and appreciating these roles can foster a deeper respect for arachnids and encourage a more nuanced view of their place in the natural world.
Introduction to Arachnids

Arachnids belong to the phylum Arthropoda, which also includes insects, crustaceans, and others. They are characterized by their jointed legs, hard exoskeletons, and segmented bodies. One of the defining features of arachnids is the presence of eight legs, which distinguishes them from insects, which have six. This basic body plan has been modified over millions of years of evolution to produce the incredible diversity of arachnids we see today, from the diminutive, flower-dwelling spiders to the large, burrowing tarantulas and the elongated, whip-like tails of scorpions.
Biological Characteristics
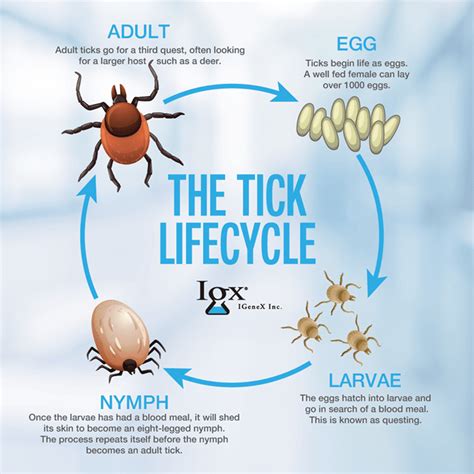
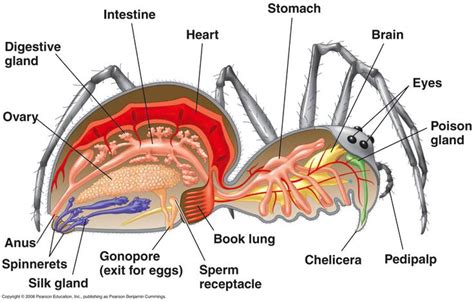
The biology of arachnids is as fascinating as it is complex. They have a unique body structure that includes a cephalothorax (head and thorax combined) and an abdomen. In spiders, the abdomen contains the spinnerets, which are used to produce silk, a material that is not only remarkably strong but also incredibly versatile, used for everything from web construction to egg sacs and protective barriers. Scorpions, on the other hand, have a long, curved tail equipped with a venomous stinger, used for capturing prey and defending against predators.Arachnids also exhibit a range of reproductive strategies, from the complex courtship rituals of some spider species to the simple, yet effective, methods of scorpions, which involve the direct transfer of sperm. The developmental stages of arachnids, including eggs, juveniles, and adults, are marked by molting, a process where the individual sheds its exoskeleton to accommodate growth. This process is crucial for arachnids, as their rigid exoskeletons do not allow for expansion.
Diversity of Arachnids
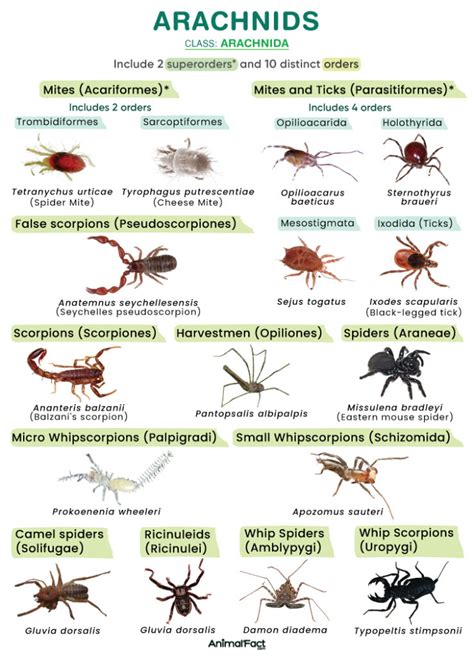
The diversity of arachnids is staggering, with over 48,000 described species, ranging from the tiny, almost microscopic, mites to the large, imposing tarantulas and scorpions. Each of these species has evolved unique adaptations that enable it to thrive in its specific environment. Spiders, for example, have developed an array of web-building techniques, from the orb webs of garden spiders to the sheet webs of sheet web spinners. These webs are not only remarkable feats of engineering but also crucial tools for capturing prey and protecting against predators.
Scorpions, with their nocturnal habits and venomous stingers, have evolved to become apex predators in many ecosystems, feeding on insects, other arachnids, and even small vertebrates. Ticks and mites, often overlooked due to their small size, play critical roles as both predators and prey, and their parasitic lifestyles have significant implications for human and animal health.
Ecological Roles
Arachnids play pivotal ecological roles, serving as both predators and prey in food webs. Spiders are key regulators of insect populations, helping to maintain the balance of ecosystems and preventing any single species from dominating. Scorpions, as top predators, control the populations of other arachnids and insects, ensuring that no single species overexploits resources. Even ticks and mites, despite their reputation as pests, are important food sources for other animals, such as birds, reptiles, and small mammals.The loss of arachnid diversity could have profound effects on ecosystems, potentially leading to the unchecked growth of pest populations and disrupting the delicate balance of nature. Therefore, understanding and conserving arachnid populations is essential for maintaining healthy, resilient ecosystems.
Arachnids and Human Society

Arachnids have been a part of human culture and society for thousands of years, featuring in myths, legends, and folklore from around the world. In some cultures, spiders are revered for their wisdom and industrious nature, while in others, they are feared and avoided. Scorpions, with their potent venom, have been both feared and respected, symbolizing danger and protection in different contexts.
Beyond their cultural significance, arachnids also have practical applications in human society. Spider silk, for example, is one of the strongest natural materials known, with potential uses in textiles, biomedical applications, and even aerospace engineering. The venom of spiders and scorpions is a rich source of bioactive compounds, many of which have been developed into medicines and pesticides.
Conservation Efforts
Despite their importance, many arachnid species are facing threats such as habitat destruction, climate change, and pollution. Conservation efforts are necessary to protect these species and the ecosystems they inhabit. This can involve the establishment of protected areas, research into the ecology and behavior of arachnids, and education programs to raise awareness about the importance of arachnids in ecosystems.Arachnophiles can play a crucial role in these conservation efforts, not only by supporting research and conservation initiatives but also by promoting a greater appreciation and understanding of arachnids among the general public. By sharing knowledge, experiences, and enthusiasm for arachnids, arachnophiles can help challenge common misconceptions and foster a more positive attitude towards these fascinating creatures.
Gallery of Arachnid Images
Arachnid Image Gallery
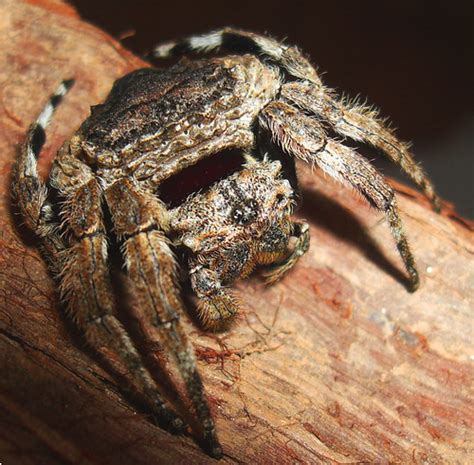





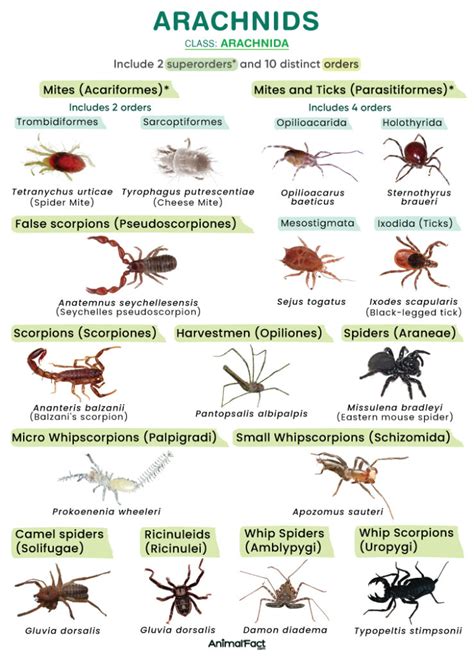

As we delve deeper into the world of arachnids, it becomes clear that these creatures are not just fascinating in their own right but also play a vital role in the health of our ecosystems. Whether you're an arachnophile, a scientist, or simply someone with a curiosity about the natural world, there's much to learn and appreciate about arachnids. By embracing our inner arachnophile and exploring the fascinating realm of arachnids, we can gain a deeper understanding of the intricate web of life that surrounds us and our place within it. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about arachnids in the comments below, and to spread the word about the importance and fascination of these incredible creatures. Together, we can work towards a greater appreciation and conservation of arachnids and the ecosystems they inhabit.
