Discover why mushrooms arent vegetables, exploring fungal biology, plant differences, and nutritional uniqueities, revealing the distinct characteristics of mushrooms.
Mushrooms are often found in the vegetable section of the grocery store, and they're commonly used in dishes alongside other vegetables. However, despite their frequent pairing with vegetables, mushrooms are actually quite distinct from them. In fact, mushrooms belong to their own unique kingdom, separate from both plants and animals. This difference is not just a matter of classification; it reflects fundamental distinctions in the biology, nutrition, and uses of mushrooms. Understanding these differences can help us appreciate the unique value and characteristics of mushrooms.
The classification of mushrooms as non-vegetables is not just a technicality; it has practical implications for how we think about and use them in cooking, health, and environmental contexts. For example, mushrooms have nutritional profiles that are distinct from those of vegetables, offering high levels of certain vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are not commonly found in plant-based foods. Furthermore, the way mushrooms grow and interact with their environments sets them apart from plants, influencing how they can be cultivated and used sustainably.
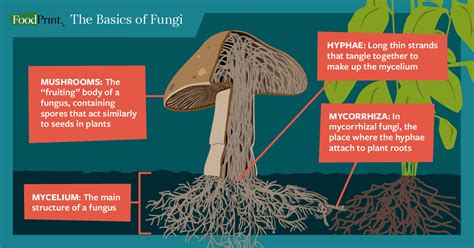
The distinction between mushrooms and vegetables also reflects their evolutionary history and biological characteristics. Mushrooms are the fruiting bodies of fungi, which obtain their nutrients by decomposing organic matter or forming symbiotic relationships with other organisms. This is fundamentally different from how plants grow, using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce their own food through photosynthesis. By recognizing and respecting these differences, we can better appreciate the unique contributions that mushrooms make to ecosystems and to human health and nutrition.
Introduction to Fungal Biology
Unique Nutritional Profile
The nutritional profile of mushrooms is one of the key reasons they are distinct from vegetables. Mushrooms are high in protein, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals, including copper, selenium, and potassium. They are also rich in antioxidants, which can help protect against cell damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Furthermore, mushrooms contain unique compounds such as beta-glucans, which have been shown to have immune-boosting properties.Ecological Role of Mushrooms

Culinary and Cultural Significance
Mushrooms have been a part of human cuisine for thousands of years, with different cultures having their own unique ways of preparing and using them. From the truffles of France to the shiitake of Japan, mushrooms are prized for their flavor, texture, and nutritional value. Beyond their culinary use, mushrooms also have cultural and symbolic significance, often representing fertility, abundance, and spiritual growth.Mushroom Cultivation and Sustainability

Health Benefits and Medicinal Uses
Mushrooms have been used in traditional medicine for centuries, and modern research has confirmed their potential health benefits. Certain species of mushrooms have been shown to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune-boosting properties, making them useful in the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Additionally, mushrooms contain compounds that may have neuroprotective effects, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.Conclusion and Future Perspectives

Final Thoughts
As we move forward, it is essential to approach mushrooms with a deeper understanding and respect for their unique biology and ecological role. This includes adopting sustainable cultivation practices, exploring their full potential in medicine and nutrition, and recognizing their cultural and symbolic significance. By doing so, we can foster a greater appreciation for the natural world and our place within it, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and healthy future for all.Mushroom Image Gallery










We invite you to share your thoughts on the unique characteristics and benefits of mushrooms. Whether you're a seasoned mycologist or just discovering the world of fungi, your insights and experiences can help enrich our understanding and appreciation of these fascinating organisms. Please feel free to comment below, share this article with others, or explore further resources on the topic to deepen your knowledge and connection with the natural world.
