Intro
Discover how to calculate the area under a curve in Excel with ease. Learn various methods, including using formulas, charts, and add-ins, to accurately determine the area under a curve. Master techniques for linear, non-linear, and cumulative distributions, and enhance your data analysis skills with expert tips and tricks.
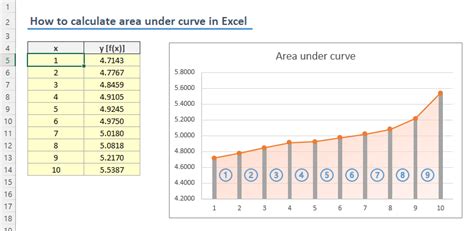
Calculating the area under a curve is a common task in mathematics, physics, and engineering. It can be used to determine the accumulation of a quantity over a defined interval. While it's possible to calculate the area under a curve manually, using Excel can simplify the process and save time. In this article, we'll explore how to calculate the area under a curve in Excel easily.
The Importance of Calculating Area Under Curve
Calculating the area under a curve has numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Physics and Engineering: To calculate the work done by a force, the area under the force-displacement curve is used.
- Economics: To determine the consumer surplus, the area under the demand curve is calculated.
- Biology: To calculate the area under the curve of a population growth model, the area under the curve is used.
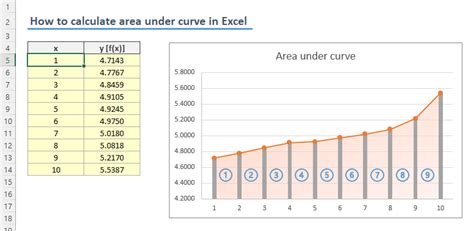
Methods to Calculate Area Under Curve in Excel
There are several methods to calculate the area under a curve in Excel, including:
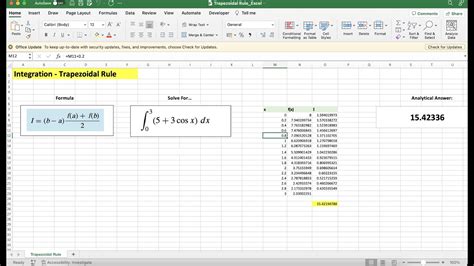
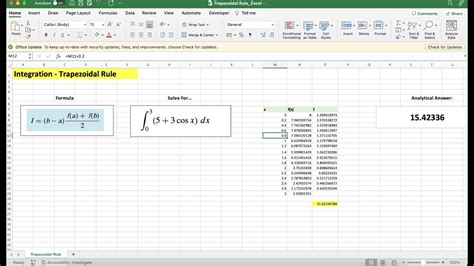
1. Using the Trapezoidal Rule
The trapezoidal rule is a simple method to approximate the area under a curve. It involves dividing the area into small trapezoids and summing up the areas of these trapezoids.
2. Using Simpson's Rule
Simpson's rule is a more accurate method to calculate the area under a curve. It involves dividing the area into small parabolic segments and summing up the areas of these segments.
3. Using the Built-in Function
Excel provides a built-in function, QUAD, to calculate the area under a curve. However, this function is not available in all versions of Excel.
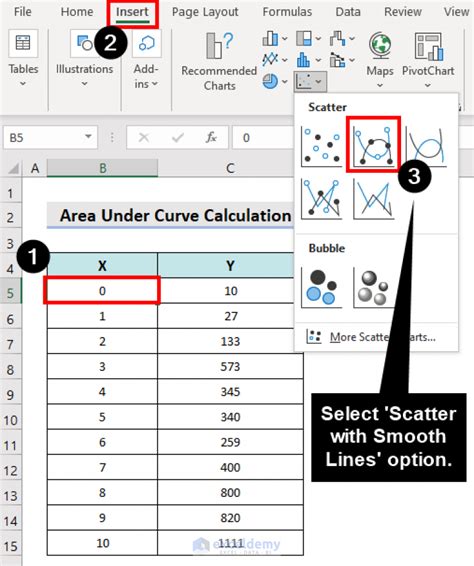
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Area Under Curve in Excel
Here's a step-by-step guide to calculate the area under a curve in Excel using the trapezoidal rule:
Step 1: Prepare the Data
Create a table with the x-values and corresponding y-values.
| X | Y |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 6 |
| 4 | 8 |
| 5 | 10 |
Step 2: Calculate the Width of Each Subinterval
Calculate the width of each subinterval by subtracting the x-values.
| X | Y | Width |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 | 1 |
| 3 | 6 | 1 |
| 4 | 8 | 1 |
| 5 | 10 | 1 |
Step 3: Calculate the Area of Each Trapezoid
Calculate the area of each trapezoid using the formula: (width * (y1 + y2)) / 2.
| X | Y | Width | Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 4 | 1 | 6 |
| 3 | 6 | 1 | 9 |
| 4 | 8 | 1 | 12 |
| 5 | 10 | 1 | 15 |
Step 4: Sum Up the Areas
Sum up the areas of all the trapezoids to get the total area under the curve.
Total Area = 3 + 6 + 9 + 12 + 15 = 45
Gallery of Calculating Area Under Curve in Excel
Calculating Area Under Curve in Excel Image Gallery




Conclusion
Calculating the area under a curve is a common task in mathematics, physics, and engineering. Excel provides several methods to calculate the area under a curve, including the trapezoidal rule, Simpson's rule, and the built-in function. By following the step-by-step guide provided in this article, you can easily calculate the area under a curve in Excel. Remember to choose the method that best suits your needs and to always verify the accuracy of your results.
Share your thoughts and experiences with calculating area under curve in Excel in the comments section below.
