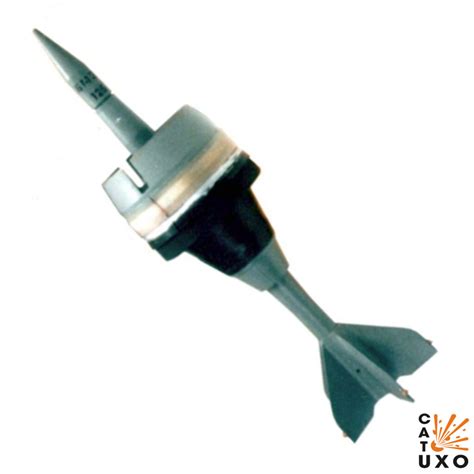
Unlock the secrets of advanced ammunition technology with our in-depth explanation of Armor Piercing Discarding Sabot (APDS) projectiles. Discover how APDS rounds use sabot discarders to enhance penetration, kinetic energy, and range, making them a game-changer in modern warfare and military operations. Learn about their design, functionality, and applications.
The concept of armor-piercing discarding sabot (APDS) is a crucial aspect of modern artillery and armor technology. The APDS is a type of kinetic energy penetrator ammunition that has revolutionized the way armor-piercing projectiles are designed and used in various military applications.
What is Armor Piercing Discarding Sabot (APDS)?

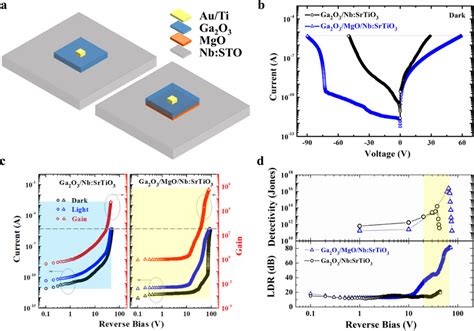
In simple terms, APDS is a type of ammunition that consists of a sub-caliber projectile, a sabot, and a propellant. The sub-caliber projectile is made of a dense, hard material, such as tungsten or depleted uranium, which is designed to penetrate armor. The sabot is a lightweight, aerodynamic casing that surrounds the projectile and helps it maintain its stability and accuracy during flight. The propellant is the explosive material that propels the projectile out of the gun barrel.
How Does APDS Work?
The APDS works by using the sabot to maintain the projectile's stability and accuracy during flight. When the projectile is fired, the sabot helps it maintain its trajectory and ensures that it stays on target. Once the projectile reaches its target, the sabot is discarded, and the sub-caliber projectile penetrates the armor. The sub-caliber projectile is designed to maintain its kinetic energy and penetrate the armor, causing significant damage to the target.
History of APDS

The concept of APDS dates back to World War II, when the Germans developed the first APDS rounds for their anti-tank guns. These early APDS rounds used a simple sabot design and were not very effective against armor. However, they paved the way for the development of modern APDS rounds.
In the post-war period, the development of APDS continued, with the introduction of new materials and designs. The British were among the first to develop a modern APDS round, which they used in their Chieftain tanks. The American M60 tank also used APDS rounds, which were highly effective against armor.
Advantages of APDS
There are several advantages of APDS over traditional armor-piercing ammunition:
- Increased accuracy: APDS rounds are more accurate than traditional armor-piercing rounds, due to the sabot's ability to maintain the projectile's stability during flight.
- Improved penetration: APDS rounds are capable of penetrating thicker armor than traditional armor-piercing rounds, due to the sub-caliber projectile's high kinetic energy.
- Reduced weight: APDS rounds are typically lighter than traditional armor-piercing rounds, making them easier to handle and store.
- Increased range: APDS rounds have a longer range than traditional armor-piercing rounds, due to the sabot's ability to maintain the projectile's velocity during flight.
Types of APDS

There are several types of APDS rounds, including:
- Kinetic energy penetrator (KEP): This type of APDS uses a sub-caliber projectile made of a dense, hard material to penetrate armor.
- Tungsten carbide penetrator: This type of APDS uses a sub-caliber projectile made of tungsten carbide to penetrate armor.
- Depleted uranium penetrator: This type of APDS uses a sub-caliber projectile made of depleted uranium to penetrate armor.
Applications of APDS
APDS rounds are used in various military applications, including:
- Main battle tanks: APDS rounds are used in main battle tanks to penetrate armor and engage enemy tanks.
- Anti-tank guns: APDS rounds are used in anti-tank guns to penetrate armor and engage enemy tanks.
- Infantry fighting vehicles: APDS rounds are used in infantry fighting vehicles to penetrate armor and engage enemy tanks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, armor-piercing discarding sabot (APDS) is a type of kinetic energy penetrator ammunition that has revolutionized the way armor-piercing projectiles are designed and used in various military applications. APDS rounds offer several advantages over traditional armor-piercing ammunition, including increased accuracy, improved penetration, reduced weight, and increased range.
If you're interested in learning more about APDS, we'd love to hear from you! Please leave a comment below or share this article with your friends and colleagues.
Gallery of Armor Piercing Discarding Sabot
APDS Image Gallery