Lorazepam, commonly known by its brand name Ativan, is a benzodiazepine medication used to treat anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. It belongs to a class of medications known as central nervous system (CNS) depressants, which work by slowing down the nervous system to produce a calming effect. In this article, we will explore the uses, benefits, and potential risks of lorazepam, as well as provide a comprehensive guide on its usage.
Understanding Lorazepam and Its Uses
Lorazepam is a prescription medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various conditions. Its primary uses include:
- Anxiety disorders: Lorazepam is effective in reducing anxiety symptoms, such as fear, apprehension, and restlessness.
- Insomnia: Lorazepam can help individuals with insomnia fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer.
- Seizures: Lorazepam is used to treat seizures, including status epilepticus, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
- Muscle relaxation: Lorazepam can help relax muscles, making it useful for treating muscle spasms and tension.
How Lorazepam Works
Lorazepam works by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA is a chemical messenger that helps regulate the activity of nerve cells in the brain. By increasing the activity of GABA, lorazepam produces a calming effect on the nervous system, reducing anxiety, insomnia, and seizures.
Benefits of Lorazepam
Lorazepam has several benefits, including:
- Fast-acting: Lorazepam starts working quickly, usually within 30 minutes of taking the medication.
- Effective: Lorazepam is highly effective in reducing anxiety symptoms, insomnia, and seizures.
- Versatile: Lorazepam can be used to treat a range of conditions, from anxiety disorders to muscle relaxation.
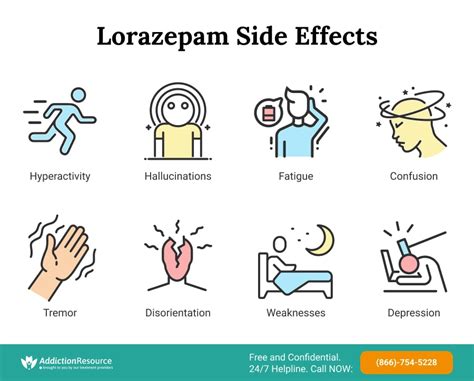
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While lorazepam can be an effective medication, it also carries potential risks and side effects, including:
- Dependence and addiction: Lorazepam can be habit-forming, leading to dependence and addiction.
- Drowsiness and dizziness: Lorazepam can cause drowsiness and dizziness, increasing the risk of falls and accidents.
- Cognitive impairment: Lorazepam can impair cognitive function, including memory and concentration.
- Withdrawal symptoms: Stopping lorazepam abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms, including seizures and anxiety.
Usage Guide
To use lorazepam safely and effectively, follow these guidelines:
- Take the medication as directed by your doctor or pharmacist.
- Start with a low dose and gradually increase as needed and under medical supervision.
- Take lorazepam with food to reduce the risk of stomach upset.
- Avoid taking lorazepam with other CNS depressants, such as alcohol or opioids.
- Monitor your response to the medication and report any side effects to your doctor.
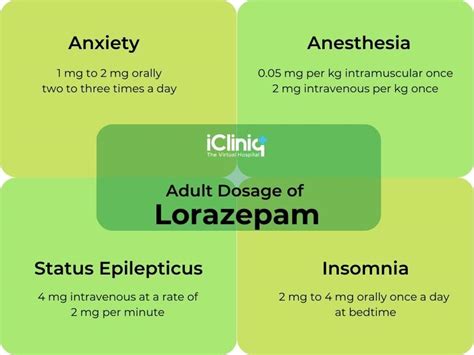
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of lorazepam vary depending on the condition being treated and the individual's response to the medication. Typical dosages include:
- Anxiety disorders: 1-3 mg per day, divided into two or three doses.
- Insomnia: 1-2 mg per day, taken 30 minutes before bedtime.
- Seizures: 1-5 mg per day, divided into two or three doses.
Interactions and Contraindications
Lorazepam can interact with other medications, including:
- CNS depressants: Lorazepam can increase the sedative effects of other CNS depressants, such as alcohol or opioids.
- Antidepressants: Lorazepam can interact with certain antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
- Muscle relaxants: Lorazepam can increase the muscle relaxant effects of other medications.
Contraindications for lorazepam include:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Lorazepam can pass into breast milk and may harm the fetus or baby.
- Respiratory depression: Lorazepam can worsen respiratory depression, a condition that requires immediate medical attention.
- Narrow-angle glaucoma: Lorazepam can worsen narrow-angle glaucoma, a condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Gallery of Lorazepam Images
Lorazepam Image Gallery







Final Thoughts
Lorazepam is a versatile medication that can be effective in treating anxiety disorders, insomnia, and seizures. However, it also carries potential risks and side effects, including dependence and addiction. By following the usage guide and dosage recommendations, individuals can minimize the risks and maximize the benefits of lorazepam. If you have any questions or concerns about lorazepam, consult with your doctor or pharmacist. Share your thoughts and experiences with lorazepam in the comments section below.
