Intro
Discover the risks and benefits of mixing Gabapentin with Tylenol, exploring interactions, side effects, and dosage guidelines for safe pain management and neuropathic relief.
The combination of gabapentin and Tylenol has been a topic of interest for individuals seeking relief from various health conditions, including pain management and neurological disorders. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, is often prescribed to treat epilepsy, nerve pain, and other conditions, while Tylenol (acetaminophen) is a widely used over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer. Understanding the potential interactions and effects of mixing gabapentin and Tylenol is crucial for safe and effective treatment. Here, we delve into the considerations and implications of combining these two medications.
Gabapentin and Tylenol can be used together under medical supervision for managing certain types of pain, especially when the pain is not adequately controlled by a single medication. The rationale behind this combination is to target pain through different mechanisms. Gabapentin works by affecting the way that nerves send messages to your brain, while Tylenol provides relief by blocking the production of prostaglandins in the brain, which are associated with pain and fever. However, it's essential to follow a healthcare provider's guidance to avoid potential side effects and interactions.
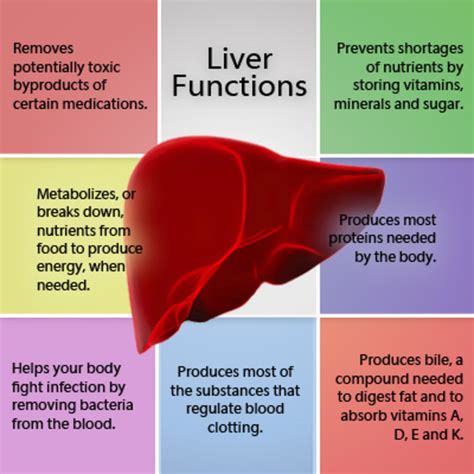
When considering the mix of gabapentin and Tylenol, several factors come into play. The dosage of each medication, the frequency of administration, and the individual's health status are critical. For example, individuals with liver disease should be cautious with Tylenol due to its potential for liver toxicity, especially when taken in high doses or for prolonged periods. Similarly, gabapentin can cause dizziness, drowsiness, and impaired coordination, which may be exacerbated by other medications or conditions.
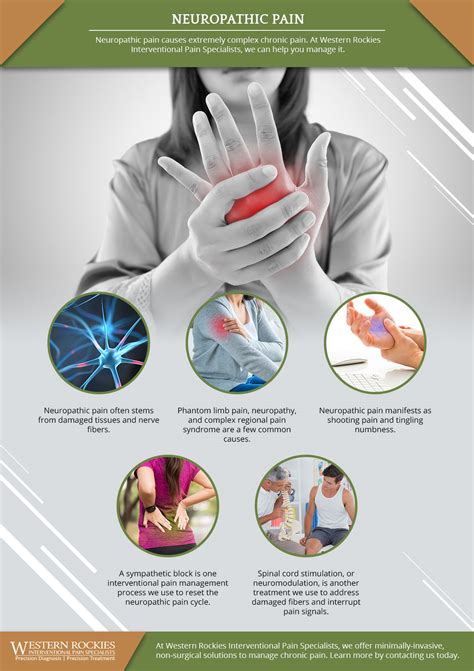
The benefits of combining gabapentin and Tylenol include enhanced pain relief for certain conditions, such as neuropathic pain, which can be challenging to treat. Neuropathic pain results from damage to the nervous system and can manifest as shooting, burning, or stabbing pain, or sometimes as tingling or numbness. This combination may offer a more comprehensive approach to managing such pain by addressing it through multiple pathways.
However, potential risks and side effects must be considered. The combination can increase the risk of adverse effects such as drowsiness, confusion, and impaired cognitive function. Additionally, monitoring liver function is crucial when taking Tylenol, especially in higher doses or with prolonged use, due to its potential for hepatotoxicity. It's also important to be aware of the potential for gabapentin to cause mood changes, including depression and anxiety, and to report any such changes to a healthcare provider.
In terms of the mechanism of action, gabapentin is believed to increase the synthesis of GABA (a neurotransmitter that inhibits nerve excitability) and may also affect the excitability of nerve cells. Tylenol, on the other hand, acts centrally in the brain to reduce pain and fever. The combination of these mechanisms can provide a synergistic effect in pain management, potentially allowing for the use of lower doses of each medication, which can help minimize side effects.
To safely mix gabapentin and Tylenol, it's crucial to follow these guidelines:
- Consult with a healthcare provider before starting or changing any medication regimen.
- Adhere strictly to the prescribed dosages and administration schedules.
- Monitor for potential side effects and report them promptly to a healthcare provider.
- Regularly review and adjust the treatment plan as needed to ensure efficacy and safety.
Given the complexities and potential risks associated with combining gabapentin and Tylenol, it's essential to approach this treatment option under the guidance of a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice based on an individual's specific health conditions, other medications, and lifestyle factors.
Introduction to Gabapentin and Tylenol

When exploring the use of gabapentin and Tylenol together, understanding the pharmacological profiles of both drugs is essential. Gabapentin, with its anticonvulsant and analgesic properties, and Tylenol, with its analgesic and antipyretic effects, can complement each other in treating various pain syndromes. However, their interaction can also lead to increased sedation, cognitive impairment, and other adverse effects, necessitating careful patient selection and monitoring.
Benefits of Gabapentin and Tylenol Combination

The combination of gabapentin and Tylenol can offer several benefits for patients suffering from chronic pain or neuropathic pain conditions. These benefits include:
- Enhanced pain relief: By targeting pain through different mechanisms, the combination can provide more effective relief than either medication alone.
- Reduced medication usage: In some cases, the combination may allow for lower doses of each medication, potentially reducing the risk of side effects.
- Improved quality of life: Effective pain management can significantly improve a patient's quality of life, enabling them to engage more fully in daily activities.
Potential Risks and Side Effects

While the combination of gabapentin and Tylenol can be beneficial, it's crucial to be aware of the potential risks and side effects. These may include:
- Increased sedation and drowsiness
- Cognitive impairment
- Mood changes, such as depression or anxiety
- Liver toxicity associated with Tylenol
- Potential for abuse or dependence, particularly with gabapentin
Guidelines for Safe Use
To ensure the safe use of gabapentin and Tylenol in combination, patients should:
- Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting, stopping, or changing the dosage of either medication.
- Follow the prescribed dosage and administration schedule closely.
- Monitor for signs of liver damage, such as yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, or abdominal pain, especially when taking Tylenol.
- Report any side effects or concerns to a healthcare provider promptly.
Monitoring and Adjustments
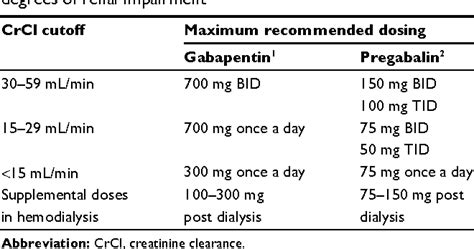
Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan are essential when using gabapentin and Tylenol together. This includes:
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and potential side effects.
- Adjusting the dosages of gabapentin and Tylenol as needed to achieve optimal pain relief while minimizing side effects.
- Considering alternative treatments if the combination is not effective or if significant side effects occur.
Gallery of Gabapentin and Tylenol Images
Gabapentin and Tylenol Image Gallery



In conclusion, the combination of gabapentin and Tylenol can be a valuable treatment option for managing certain types of pain, especially neuropathic pain conditions. However, it's critical to approach this treatment under the guidance of a healthcare provider, carefully monitoring for potential side effects and adjusting the treatment plan as needed. By understanding the benefits and risks associated with this combination and adhering to safe use guidelines, patients can effectively manage their pain and improve their quality of life.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about the use of gabapentin and Tylenol in the comments section below. Additionally, please consider sharing this article with others who may benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in creating a supportive community focused on health and wellness.
