Intro
Understand the crucial distinction between the coding strand and template strand in DNA replication. Learn how the coding strand vs template strand differs in terms of transcription, RNA synthesis, and genetic information transmission. Discover the significance of these strands in molecular biology and genetics, and how they impact gene expression and protein synthesis.
The world of DNA and genetics can be fascinating, yet complex. One of the fundamental concepts in molecular biology is the difference between the coding strand and the template strand of DNA. Understanding this distinction is crucial for grasping how genetic information is stored, replicated, and expressed.
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
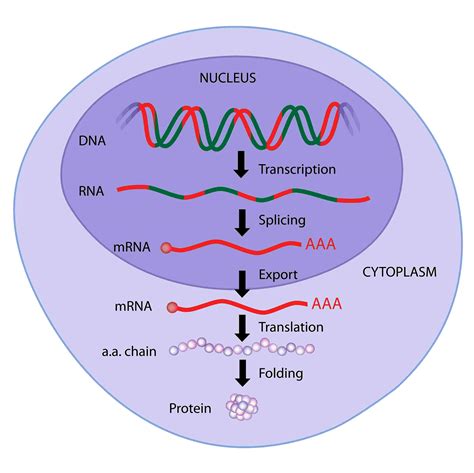
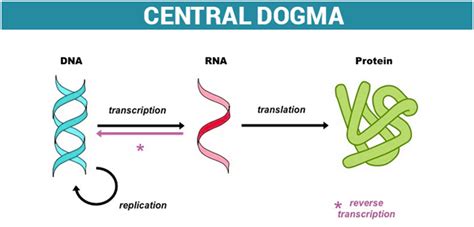
To comprehend the difference between the coding strand and the template strand, it's essential to revisit the central dogma of molecular biology. This fundamental concept describes the flow of genetic information within a biological system. The central dogma states that genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to proteins. In other words, DNA serves as the primary repository of genetic information, which is then transcribed into RNA and eventually translated into proteins.
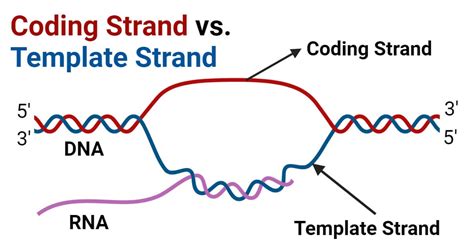
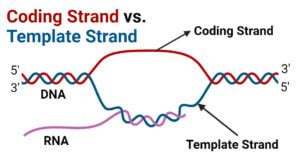
Coding Strand vs Template Strand: The Basics
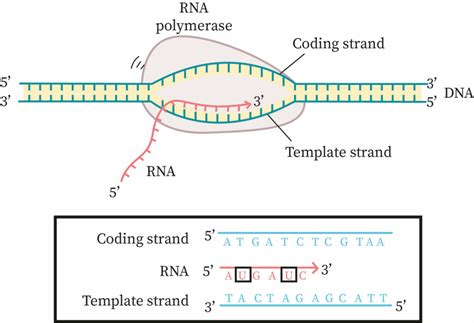
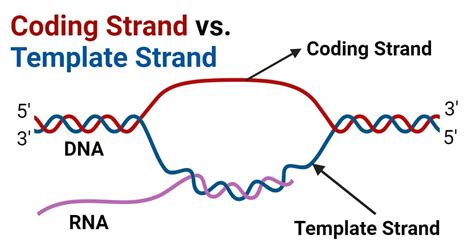
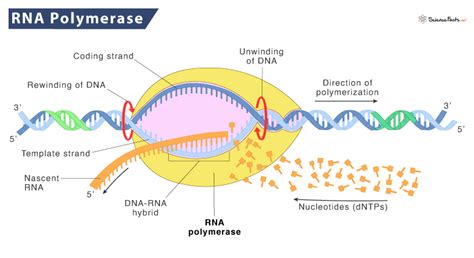
When it comes to DNA replication and transcription, two distinct strands play critical roles: the coding strand and the template strand. These strands are complementary and antiparallel, meaning they run in opposite directions.
Coding Strand
The coding strand, also known as the sense strand, is the strand of DNA that contains the sequence of nucleotides that directly codes for a protein. This strand is complementary to the template strand and has the same sequence as the RNA transcript, except for the replacement of thymine (T) with uracil (U) in RNA. The coding strand is "sense" because it can be directly translated into a protein sequence.
Template Strand
The template strand, also known as the antisense strand, is the strand of DNA that serves as a template for transcription. This strand is complementary to the coding strand and is used as a template for the synthesis of a complementary RNA molecule. The template strand is "antisense" because it is the reverse complement of the coding strand.
Key Differences
The primary differences between the coding strand and the template strand are:
- Sequence: The coding strand has the same sequence as the RNA transcript, while the template strand has the reverse complement sequence.
- Function: The coding strand directly codes for a protein, while the template strand serves as a template for transcription.
- Orientation: The coding strand and template strand are antiparallel, meaning they run in opposite directions.
Transcription and Translation
To further illustrate the difference between the coding strand and the template strand, let's examine the processes of transcription and translation.
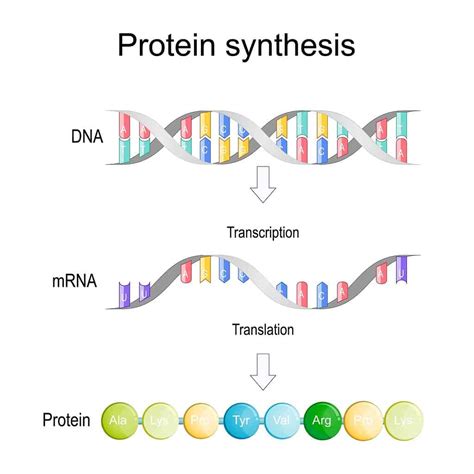
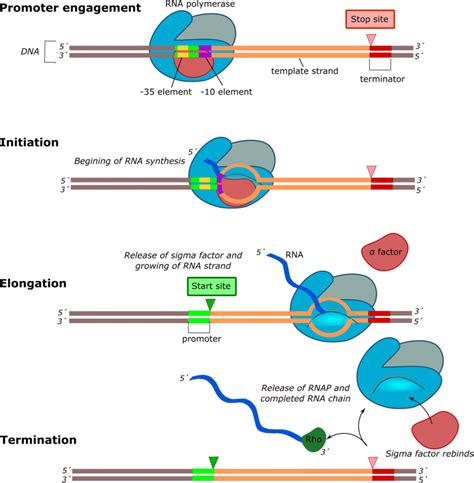
Transcription
During transcription, the template strand of DNA is used as a template for the synthesis of a complementary RNA molecule. The RNA molecule is synthesized by an enzyme called RNA polymerase, which reads the template strand and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules. The resulting RNA molecule is complementary to the template strand and has the same sequence as the coding strand, except for the replacement of thymine (T) with uracil (U).
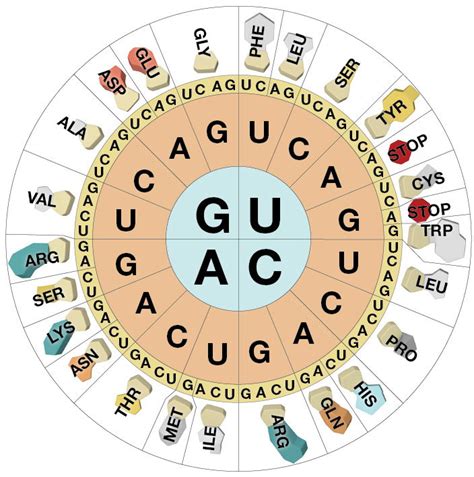
Translation
During translation, the RNA molecule is translated into a protein sequence. The RNA molecule is read in triplets of nucleotides, known as codons, which specify particular amino acids. The sequence of amino acids is then assembled into a protein.
Importance of the Coding Strand and Template Strand
The coding strand and template strand play crucial roles in the central dogma of molecular biology. The coding strand directly codes for a protein, while the template strand serves as a template for transcription. Understanding the difference between these two strands is essential for grasping how genetic information is stored, replicated, and expressed.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the coding strand and template strand are two distinct strands of DNA that play critical roles in the central dogma of molecular biology. Understanding the difference between these two strands is essential for grasping how genetic information is stored, replicated, and expressed. As our understanding of genetics and genomics continues to evolve, the importance of the coding strand and template strand will only continue to grow.
Coding Strand vs Template Strand Image Gallery


Feel free to share your thoughts on the coding strand vs template strand in the comments section below.
