Intro
Discover the complexities of Crohns Disease, a chronic inflammatory bowel disorder affecting the digestive system. Learn about its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, as well as the impact on gut health, immune system, and overall well-being. Understand the role of genetics, nutrition, and lifestyle in managing this complex system disorder.
Living with a chronic illness can be overwhelming, and Crohn's disease is no exception. It is a complex system disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, causing a significant impact on their quality of life. Despite its prevalence, Crohn's disease remains poorly understood, and its symptoms can be difficult to manage. In this article, we will delve into the world of Crohn's disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is Crohn's Disease?
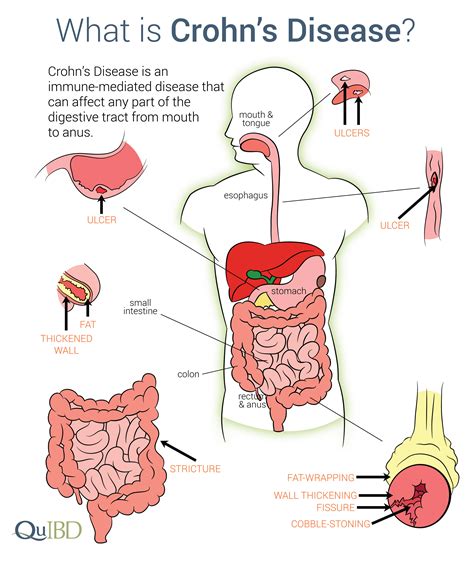
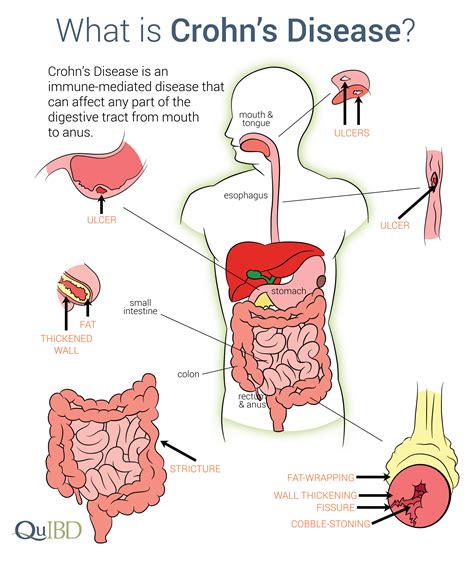
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation and damage to the digestive tract. It can affect any part of the gastrointestinal system, from the mouth to the anus, but it most commonly affects the lower part of the small intestine, known as the ileum. The exact cause of Crohn's disease is still unknown, but it is believed to be the result of a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
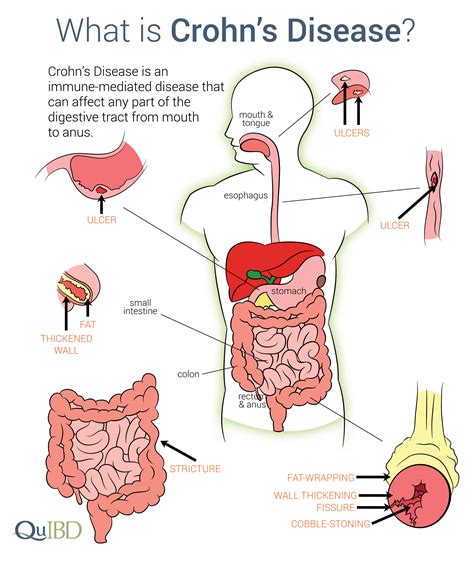
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of Crohn's disease is still unknown, research has identified several factors that may contribute to its development. These include:
- Genetics: Crohn's disease can run in families, and people with a family history of the condition are more likely to develop it.
- Abnormal immune response: The immune system plays a key role in the development of Crohn's disease. In people with the condition, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy bacteria in the gut, leading to chronic inflammation.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as smoking and stress, may trigger the onset of Crohn's disease.
- Diet: A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats may contribute to the development of Crohn's disease.
Symptoms
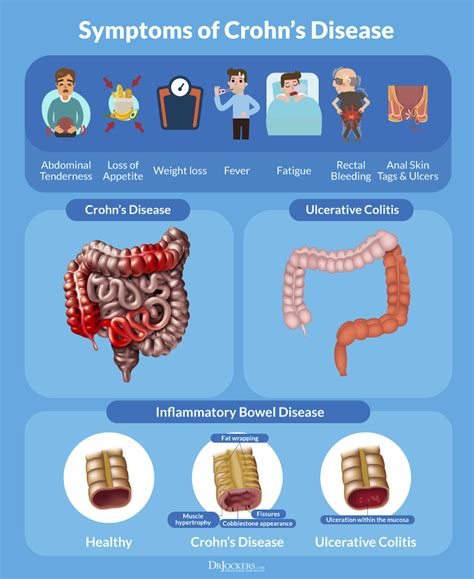
The symptoms of Crohn's disease can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include:
- Diarrhea: Loose, watery stools are a common symptom of Crohn's disease.
- Abdominal pain: Pain in the abdomen, often in the lower right side, is a common symptom of Crohn's disease.
- Weight loss: Malabsorption of nutrients can lead to weight loss in people with Crohn's disease.
- Fatigue: Chronic inflammation and malabsorption of nutrients can cause fatigue in people with Crohn's disease.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing Crohn's disease can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). A diagnosis of Crohn's disease is typically made using a combination of the following tests:
- Endoscopy: A flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth or rectum to visualize the inside of the digestive tract.
- Colonoscopy: A flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the rectum to visualize the inside of the colon and rectum.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans may be used to visualize the digestive tract and look for signs of inflammation.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to check for anemia, inflammation, and malabsorption of nutrients.
Types of Crohn's Disease
There are several types of Crohn's disease, including:
- Ileocolitis: This is the most common type of Crohn's disease, affecting the lower part of the small intestine (ileum) and the beginning of the large intestine (colon).
- Ileitis: This type of Crohn's disease affects only the lower part of the small intestine (ileum).
- Gastroduodenal Crohn's disease: This type of Crohn's disease affects the stomach and the beginning of the small intestine (duodenum).
- Jejunoileitis: This type of Crohn's disease affects the middle part of the small intestine (jejunum).
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for Crohn's disease, several treatment options are available to manage its symptoms and prevent complications. These include:
- Aminosalicylates: These medications, such as sulfasalazine and mesalamine, can help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Corticosteroids: These medications, such as prednisone, can help reduce inflammation and swelling in the digestive tract.
- Immunomodulators: These medications, such as azathioprine and mercaptopurine, can help reduce inflammation and prevent the immune system from attacking healthy tissues.
- Biologics: These medications, such as infliximab and adalimumab, can help reduce inflammation and prevent the immune system from attacking healthy tissues.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged portions of the digestive tract.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatment, several lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms of Crohn's disease. These include:
- Dietary changes: Eating a balanced diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce symptoms.
- Stress management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms of Crohn's disease. Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can help manage stress.
- Smoking cessation: Smoking can worsen symptoms of Crohn's disease. Quitting smoking can help reduce symptoms.

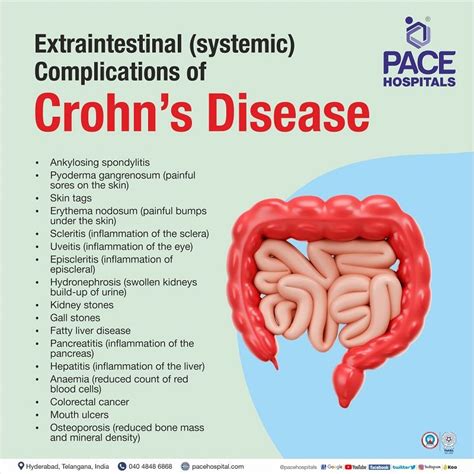
Complications
Untreated or undertreated Crohn's disease can lead to several complications, including:
- Malnutrition: Malabsorption of nutrients can lead to malnutrition and weight loss.
- Osteoporosis: Malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D can lead to osteoporosis.
- Anemia: Malabsorption of iron and vitamin B12 can lead to anemia.
- Increased risk of colon cancer: Untreated or undertreated Crohn's disease can increase the risk of colon cancer.
Living with Crohn's Disease
Living with Crohn's disease can be challenging, but with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage its symptoms and prevent complications. Here are some tips for living with Crohn's disease:
- Keep a food diary: Keeping track of the foods you eat and how they affect your symptoms can help you identify triggers and make informed dietary choices.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help prevent dehydration and reduce symptoms.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help reduce stress and improve overall health.
- Seek support: Connecting with others who have Crohn's disease can provide emotional support and help you feel less isolated.
Crohn's Disease Image Gallery



If you or someone you know is living with Crohn's disease, it's essential to stay informed about the latest research, treatment options, and lifestyle changes that can help manage its symptoms and prevent complications. By taking an active role in your health, you can improve your quality of life and reduce the impact of Crohn's disease. Share your experiences, ask questions, and seek support from others who understand what you're going through.
