Intro
Learn how to manage Diabetes Insipidus with our expert guide. Discover 7 effective ways to regulate fluid balance, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life. From lifestyle changes to medication management, explore treatment options for Central, Nephrogenic, and Gestational DI, and take control of your condition.
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a rare condition that affects the way the body regulates fluids. It is characterized by the excessive production of diluted urine, which can lead to dehydration if left untreated. While there is no cure for DI, there are several ways to manage the condition and prevent its complications.
Understanding Diabetes Insipidus

Diabetes insipidus is caused by the deficiency of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin, which is produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. ADH plays a crucial role in regulating the amount of water in the body by controlling the amount of urine produced by the kidneys.
Types of Diabetes Insipidus
There are four types of diabetes insipidus: central, nephrogenic, dipsogenic, and gestational.
- Central diabetes insipidus is caused by the deficiency of ADH due to a problem with the hypothalamus or pituitary gland.
- Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by the kidneys' inability to respond to ADH.
- Dipsogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by the excessive thirst and consumption of water.
- Gestational diabetes insipidus is a rare condition that occurs during pregnancy.
Managing Diabetes Insipidus

While there is no cure for diabetes insipidus, there are several ways to manage the condition and prevent its complications. Here are seven ways to manage diabetes insipidus:
1. Drinking Enough Water
Drinking enough water is essential to manage diabetes insipidus. People with DI should drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day to replace the lost fluids.
2. Hormone Replacement Therapy
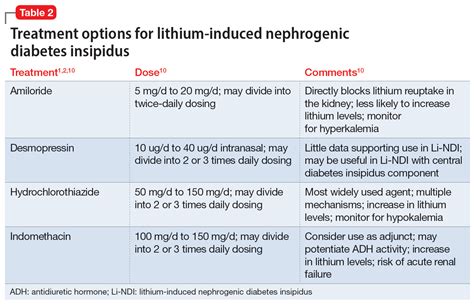
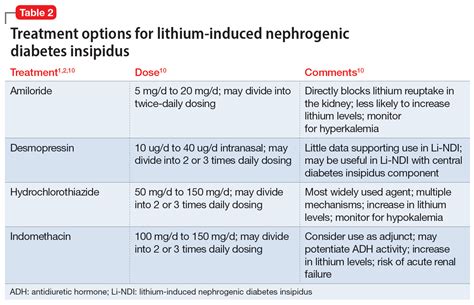
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to replace the deficient ADH in people with central diabetes insipidus. HRT involves taking synthetic ADH injections or nasal sprays to regulate the amount of urine produced by the kidneys.
3. Medications
Medications such as thiazides and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage diabetes insipidus by reducing the amount of urine produced by the kidneys.
4. Low-Sodium Diet
A low-sodium diet can help reduce the amount of urine produced by the kidneys and alleviate symptoms of diabetes insipidus.
5. Avoiding Caffeine and Alcohol
Caffeine and alcohol are diuretics that can exacerbate symptoms of diabetes insipidus. Avoiding these substances can help manage the condition.
6. Monitoring Urine Output
Monitoring urine output is essential to manage diabetes insipidus. People with DI should keep track of their urine output to ensure they are producing enough urine to stay hydrated.
7. Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to manage diabetes insipidus. Regular check-ups can help monitor the condition and prevent its complications.
Complications of Diabetes Insipidus

If left untreated, diabetes insipidus can lead to several complications, including:
- Dehydration
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Kidney damage
- Infections
- Seizures
Gallery of Diabetes Insipidus Images
Diabetes Insipidus Image Gallery







If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with diabetes insipidus, it's essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a management plan that's right for you. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, it's possible to manage the condition and prevent its complications. Share this article with others to raise awareness about diabetes insipidus and its management.
