As the cost of living continues to rise, many individuals and families rely on food stamps to make ends meet. The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), also known as food stamps, provides essential support to low-income households, enabling them to purchase nutritious food. However, the question of taxes on food stamps often raises concerns among recipients. In this article, we will delve into the world of taxes on food stamps, exploring what you need to know about this critical issue.
Food stamps are a vital lifeline for millions of Americans, providing access to healthy food that would otherwise be unaffordable. Despite their importance, food stamps are often subject to various regulations and restrictions. One of the most significant concerns for recipients is the impact of taxes on their benefits. In the following sections, we will examine the tax implications of food stamps, including whether they are taxable, how to report them on tax returns, and the potential consequences of failing to comply with tax regulations.
Are Food Stamps Taxable?
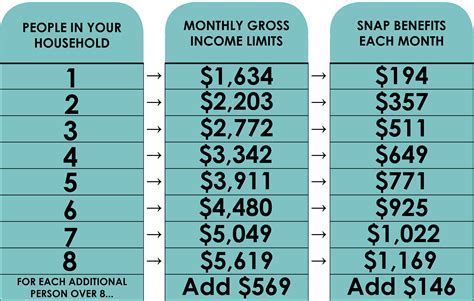
One of the most pressing questions among food stamp recipients is whether they are taxable. The good news is that, in most cases, food stamps are not taxable. According to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), SNAP benefits are not considered taxable income. This means that recipients do not need to report their food stamp benefits on their tax returns.
However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For instance, if a recipient receives cash benefits, such as Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF), these may be taxable. Additionally, if a recipient sells or trades their food stamps for cash or other items, this could be considered taxable income.
Reporting Food Stamps on Tax Returns
While food stamps are generally not taxable, it is essential to understand how to report them on tax returns. As mentioned earlier, recipients do not need to report their food stamp benefits on their tax returns. However, if a recipient receives other forms of assistance, such as TANF or Supplemental Security Income (SSI), these may need to be reported.
To ensure accurate reporting, recipients should keep detailed records of their benefits, including the amount received and the type of assistance. This information can be found on the benefit award letter or by contacting the local social services department.
Tax Implications of Food Stamps
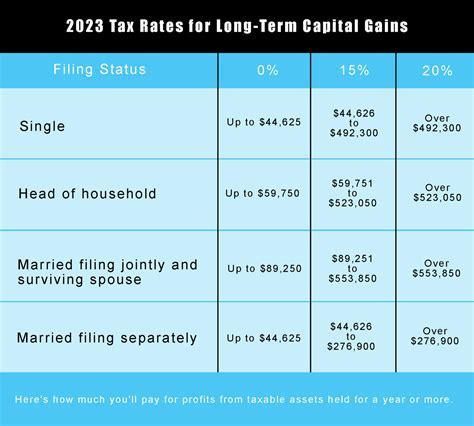
While food stamps are not taxable, there are other tax implications to consider. For instance, recipients may be eligible for the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), which can provide a refundable tax credit. Additionally, recipients may be eligible for other tax credits, such as the Child Tax Credit or the Credit for Other Dependents.
On the other hand, recipients who fail to comply with tax regulations may face consequences, including penalties and fines. For example, if a recipient fails to report taxable income, such as cash benefits, they may be subject to penalties and interest.
Consequences of Failing to Comply with Tax Regulations
Failing to comply with tax regulations can have serious consequences, including:
- Penalties and fines
- Interest on unpaid taxes
- Delayed or denied tax refunds
- Loss of benefits or eligibility for future assistance
To avoid these consequences, recipients should ensure they accurately report their income and benefits on their tax returns. This includes keeping detailed records of benefits received and consulting with a tax professional if necessary.
Food Stamps and Tax Credits

In addition to the tax implications of food stamps, recipients may be eligible for various tax credits. These credits can provide a refundable tax credit, which can help offset the cost of living.
Some of the most common tax credits available to food stamp recipients include:
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Credit for Other Dependents
- Premium Tax Credit (PTC)
To determine eligibility for these credits, recipients should consult with a tax professional or use tax preparation software.
Eligibility for Tax Credits
Eligibility for tax credits varies depending on the specific credit. However, some general requirements include:
- Income limits: Recipients must meet income limits to qualify for tax credits.
- Work requirements: Recipients must meet work requirements, such as having a job or being self-employed.
- Family size: Recipients must meet family size requirements, such as having dependent children.
To determine eligibility, recipients should consult with a tax professional or use tax preparation software.
Gallery of Food Stamps and Taxation
Food Stamps and Taxation Image Gallery





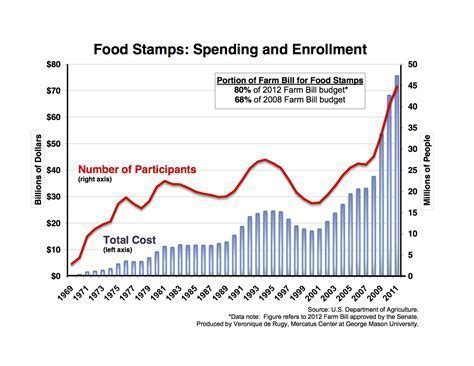

Conclusion
In conclusion, taxes on food stamps can be a complex issue, but understanding the tax implications is essential for recipients. By knowing whether food stamps are taxable, how to report them on tax returns, and the potential consequences of failing to comply with tax regulations, recipients can ensure they receive the benefits they need without facing unexpected tax burdens.
If you have any questions or concerns about taxes on food stamps, we encourage you to share them in the comments below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information.
Remember, taxes on food stamps are just one aspect of the broader issue of food insecurity. By staying informed and advocating for policies that support low-income households, we can work towards a more equitable and just society for all.
