Intro
Improve your electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation skills with these 7 essential EKG practice strips for nurses and students. Enhance your knowledge of arrhythmias, myocardial infarctions, and other cardiac conditions. Master the art of ECG analysis with these real-life practice strips, designed to boost your confidence and competence in cardiovascular care.
EKG practice strips are an essential tool for nurses and students to improve their skills in interpreting electrocardiogram (EKG) readings. EKGs are a crucial diagnostic tool in healthcare, providing valuable information about a patient's heart function and rhythm. Mastering the art of EKG interpretation is a critical skill for nurses and healthcare professionals, as it enables them to quickly identify potential life-threatening conditions and make informed decisions about patient care.
EKG practice strips provide a safe and controlled environment for nurses and students to practice their interpretation skills, without the risk of misdiagnosing a real patient. These practice strips are typically printed or digital recordings of EKG tracings, which can be used to simulate various cardiac rhythms and conditions. By analyzing these practice strips, nurses and students can develop their critical thinking skills, learn to recognize patterns and abnormalities, and become proficient in EKG interpretation.
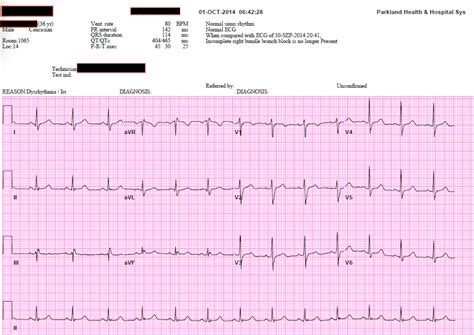
In this article, we will explore seven EKG practice strips for nurses and students, covering a range of common cardiac rhythms and conditions. These practice strips are designed to challenge your skills and help you become more confident in your ability to interpret EKG readings.
Understanding EKG Interpretation
Before we dive into the practice strips, it's essential to review the basics of EKG interpretation. An EKG tracing consists of several key components, including:
- P wave: represents atrial depolarization
- QRS complex: represents ventricular depolarization
- T wave: represents ventricular repolarization
- PR interval: represents the time between atrial and ventricular depolarization
- QT interval: represents the time between ventricular depolarization and repolarization
By analyzing these components, nurses and students can identify various cardiac rhythms and conditions, such as normal sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and more.
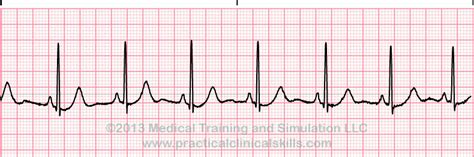
EKG Practice Strip 1: Normal Sinus Rhythm
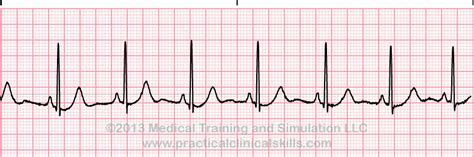
The first practice strip shows a normal sinus rhythm, characterized by a regular P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. The PR interval is within normal limits (0.12-0.20 seconds), and the QT interval is also normal (0.30-0.40 seconds). This rhythm is typically seen in healthy individuals and is an essential baseline for comparison with other rhythms.
Questions to Consider:
- What is the heart rate of this rhythm?
- Is the P wave regular or irregular?
- What is the PR interval, and is it within normal limits?
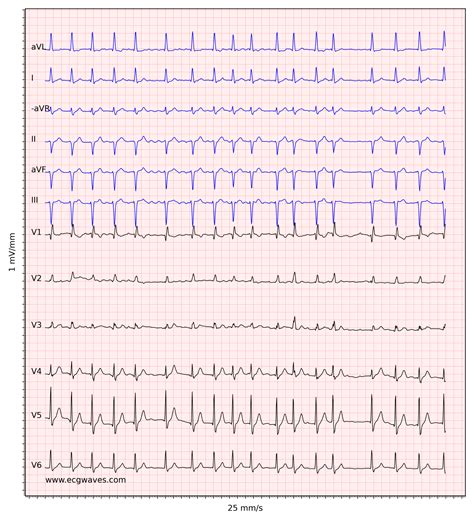
EKG Practice Strip 2: Atrial Fibrillation
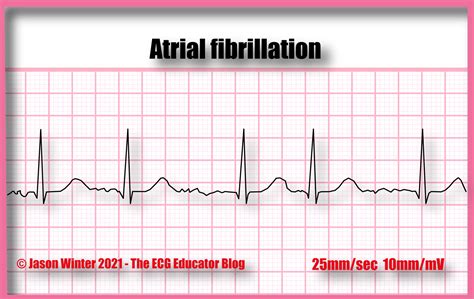
The second practice strip shows atrial fibrillation, characterized by an irregular P wave and an irregularly irregular ventricular response. The QRS complex is normal, but the T wave is often inverted or flat. Atrial fibrillation is a common arrhythmia that can increase the risk of stroke and heart failure.
Questions to Consider:
- What is the characteristic P wave pattern in atrial fibrillation?
- How does the ventricular response vary in atrial fibrillation?
- What is the risk of stroke associated with atrial fibrillation?
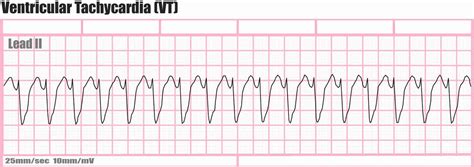
EKG Practice Strip 3: Ventricular Tachycardia
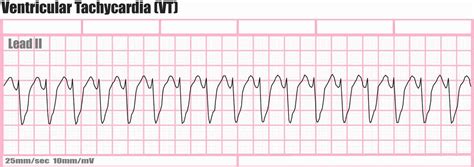
The third practice strip shows ventricular tachycardia, characterized by a wide QRS complex (>0.12 seconds) and a rapid heart rate (>100 beats per minute). Ventricular tachycardia is a life-threatening arrhythmia that requires immediate medical attention.
Questions to Consider:
- What is the defining characteristic of ventricular tachycardia?
- How does ventricular tachycardia affect cardiac output?
- What is the treatment for ventricular tachycardia?
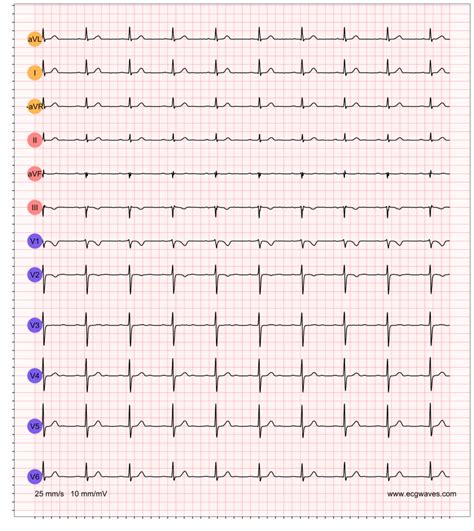
EKG Practice Strip 4: First-Degree AV Block
The fourth practice strip shows a first-degree AV block, characterized by a prolonged PR interval (>0.20 seconds). First-degree AV block is a benign condition that does not typically require treatment.
Questions to Consider:
- What is the definition of first-degree AV block?
- How does first-degree AV block affect cardiac output?
- What is the prognosis for first-degree AV block?
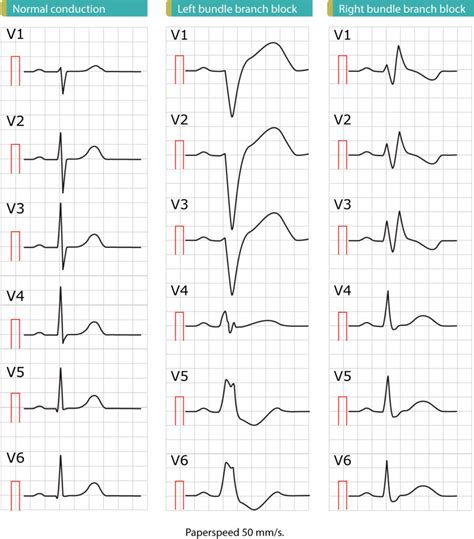
EKG Practice Strip 5: Left Bundle Branch Block
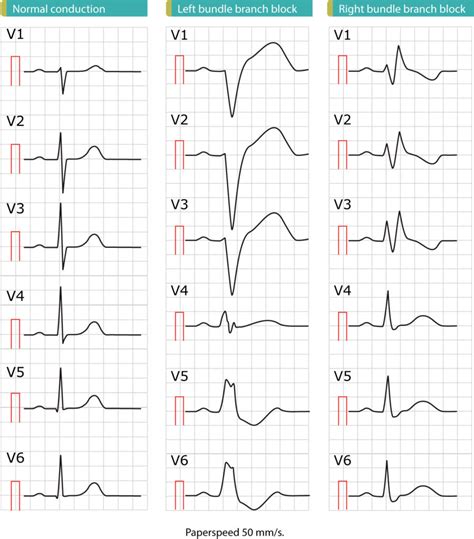
The fifth practice strip shows a left bundle branch block, characterized by a wide QRS complex (>0.12 seconds) and a leftward deviation of the QRS axis. Left bundle branch block is a common finding in patients with coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy.
Questions to Consider:
- What is the definition of left bundle branch block?
- How does left bundle branch block affect cardiac output?
- What is the significance of left bundle branch block in patients with coronary artery disease?
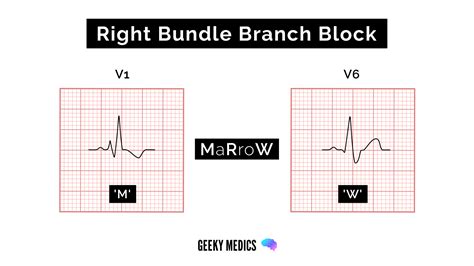
EKG Practice Strip 6: Right Bundle Branch Block
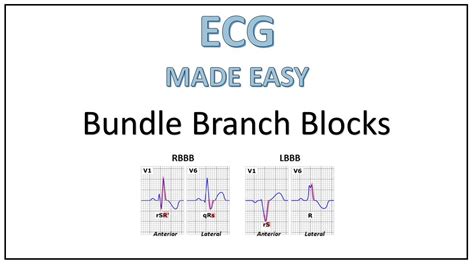
The sixth practice strip shows a right bundle branch block, characterized by a wide QRS complex (>0.12 seconds) and a rightward deviation of the QRS axis. Right bundle branch block is a common finding in patients with pulmonary embolism or other lung diseases.
Questions to Consider:
- What is the definition of right bundle branch block?
- How does right bundle branch block affect cardiac output?
- What is the significance of right bundle branch block in patients with pulmonary embolism?
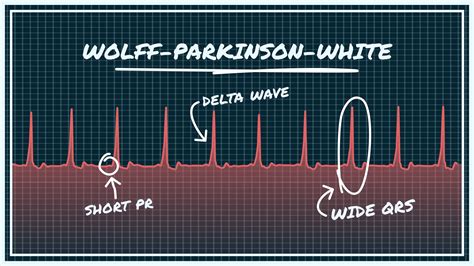
EKG Practice Strip 7: Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
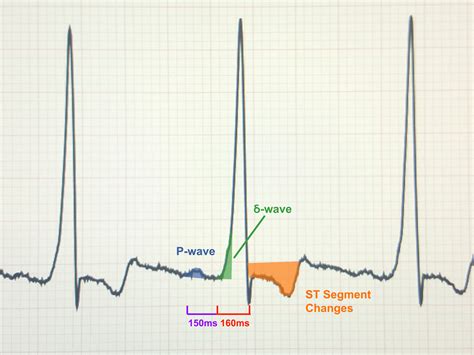
The seventh and final practice strip shows Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, characterized by a short PR interval (<0.12 seconds) and a delta wave (slurred upstroke of the QRS complex). Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a rare congenital condition that can increase the risk of supraventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation.
Questions to Consider:
- What is the definition of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
- How does Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome affect cardiac output?
- What is the treatment for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
EKG Practice Strip Image Gallery
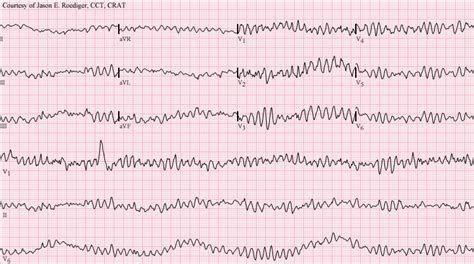
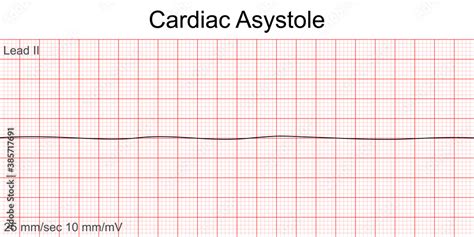
We hope that these EKG practice strips have helped you improve your skills in interpreting EKG readings. Remember to always analyze the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, and consider the clinical context in which the EKG was performed. With practice and experience, you will become more confident in your ability to interpret EKG readings and provide high-quality patient care.
What do you think about these EKG practice strips? Do you have any questions or comments about EKG interpretation? Share your thoughts with us in the comments section below!
