Intro
Master the rate of descent formula with 3 easy methods. Learn how to calculate RoD in aviation, including the standard rate of descent formula, and alternative methods using altitude and airspeed. Improve your flight planning and navigation skills with our step-by-step guide, featuring relevant examples and expert tips.
The rate of descent (ROD) is a critical parameter in various fields, including aviation, physics, and engineering. It is defined as the rate at which an object moves downward, typically measured in feet per minute (fpm) or meters per second (m/s). Calculating the rate of descent is essential to ensure safe and controlled descents, especially in aviation. In this article, we will explore three ways to calculate the rate of descent formula.
Understanding the Rate of Descent Formula
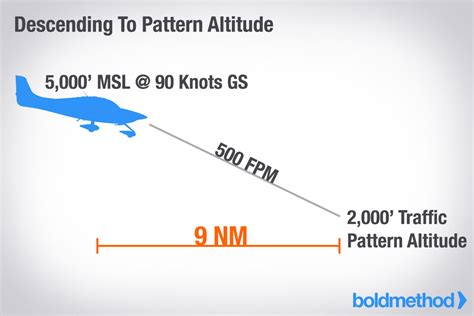
The rate of descent formula is based on the fundamental principle of motion, which relates the distance traveled to the time taken. There are three primary methods to calculate the rate of descent, each with its own advantages and limitations.
Method 1: Using the Distance and Time Formula
The simplest way to calculate the rate of descent is by using the distance and time formula:
ROD = Distance / Time
where ROD is the rate of descent, Distance is the vertical distance traveled, and Time is the time taken to travel that distance.
For example, if an aircraft travels 1,000 feet in 2 minutes, its rate of descent would be:
ROD = 1,000 feet / 2 minutes = 500 fpm
Method 2: Using the Vertical Speed Formula
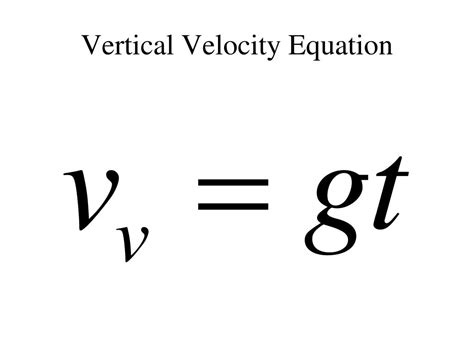
The vertical speed formula is another way to calculate the rate of descent. This method takes into account the object's initial and final velocities, as well as the acceleration due to gravity (g).
ROD = (Vf - Vi) / t + g
where ROD is the rate of descent, Vf is the final velocity, Vi is the initial velocity, t is the time, and g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.81 m/s^2).
For instance, if an object has an initial velocity of 50 m/s and a final velocity of 100 m/s after 5 seconds, its rate of descent would be:
ROD = (100 m/s - 50 m/s) / 5 s + 9.81 m/s^2 = 10.39 m/s
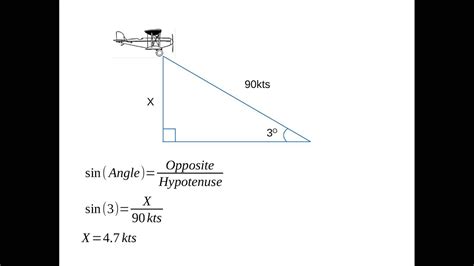
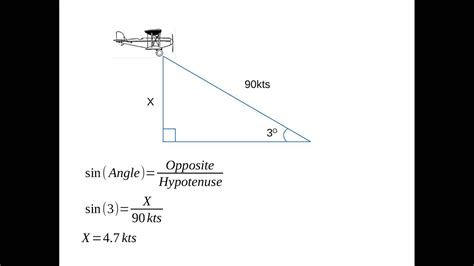
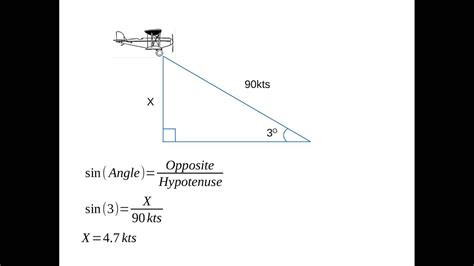
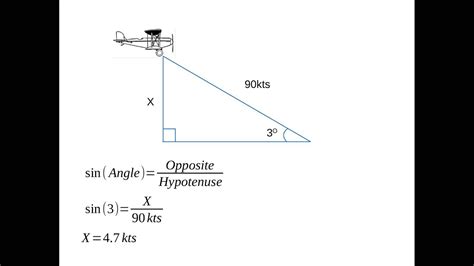
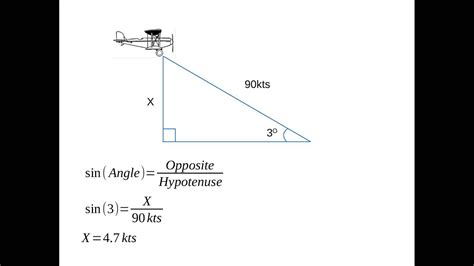
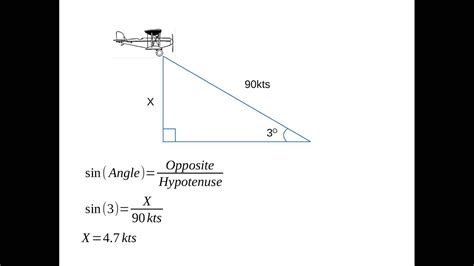
Method 3: Using the Angle of Descent Formula
The angle of descent formula is a more complex method that involves the object's angle of descent, initial velocity, and time.
ROD = Vi * sin(θ) / t
where ROD is the rate of descent, Vi is the initial velocity, θ is the angle of descent, and t is the time.
For example, if an aircraft has an initial velocity of 200 knots and an angle of descent of 30 degrees, its rate of descent would be:
ROD = 200 knots * sin(30°) / 2 minutes = 1,000 fpm
Gallery of Rate of Descent Formulas
Rate of Descent Formula Images
In conclusion, calculating the rate of descent is a crucial aspect of various fields, including aviation and physics. By using one of the three methods outlined in this article, you can accurately determine the rate of descent of an object. Whether you're a pilot, engineer, or simply interested in motion, understanding the rate of descent formula is essential for safe and controlled descents.
We hope this article has been informative and helpful. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
