Intro
Explore 5 pivotal Galileo discoveries, including telescope innovations, Jupiters moons, and astronomical observations, revolutionizing our understanding of the universe, space, and celestial mechanics.
The life and work of Galileo Galilei, a renowned Italian astronomer, physicist, and engineer, have had a profound impact on our understanding of the universe. Born in 1564 in Pisa, Italy, Galileo is widely recognized as one of the most influential scientists in history. His groundbreaking discoveries and innovative approaches to science paved the way for major breakthroughs in various fields, including astronomy, physics, and mathematics. In this article, we will delve into five of Galileo's most significant discoveries, exploring their significance and the impact they had on the scientific community.
Galileo's contributions to science were not limited to a single area of study. He made significant strides in astronomy, physics, and mathematics, often challenging conventional wisdom and pushing the boundaries of human knowledge. His work laid the foundation for many subsequent scientific discoveries, and his legacy continues to inspire scientists and scholars to this day. From the observation of celestial bodies to the study of motion and gravity, Galileo's discoveries have had a lasting impact on our understanding of the world and the universe.
The significance of Galileo's discoveries extends beyond the scientific community. His work has had a profound impact on philosophy, culture, and society as a whole. By challenging traditional views and promoting a more nuanced understanding of the universe, Galileo helped to lay the groundwork for the scientific revolution of the 17th century. This period of rapid scientific progress saw major breakthroughs in fields such as astronomy, physics, and mathematics, and had a profound impact on Western culture and society. As we explore Galileo's discoveries in more detail, we will see how his work contributed to this broader cultural and scientific shift.
Introduction to Galileo's Discoveries

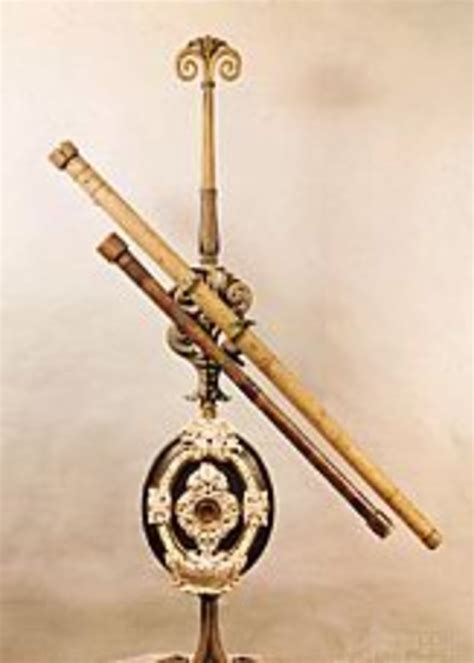
Galileo's discoveries were made possible by his innovative use of the telescope, which allowed him to observe celestial bodies with unprecedented precision. His observations of the night sky challenged traditional views of the universe, revealing new insights into the nature of the cosmos. From the observation of four moons orbiting Jupiter to the discovery of sunspots, Galileo's telescope revealed a universe that was more complex and dynamic than previously thought.
Key Features of Galileo's Telescope
Galileo's telescope was a significant improvement over earlier models, allowing him to observe celestial bodies with greater precision and clarity. The key features of his telescope included: * A larger objective lens, which allowed more light to enter the telescope and produced a brighter image * A more precise eyepiece, which enabled Galileo to observe finer details in the night sky * A sturdy mounting system, which allowed Galileo to track celestial bodies with greater ease and accuracyThe Observation of Four Moons Orbiting Jupiter
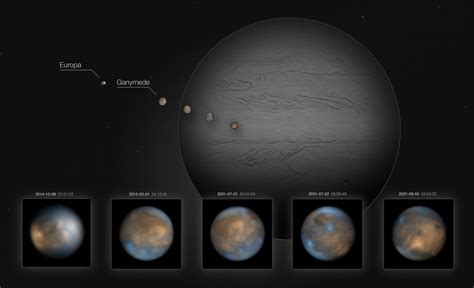
One of Galileo's most significant discoveries was the observation of four moons orbiting Jupiter. This discovery, made in 1610, challenged traditional views of the universe and provided evidence for the Copernican heliocentric model. The four moons, later named Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto, were observed by Galileo using his telescope, and their discovery provided strong evidence for the idea that the planets orbit the Sun, rather than the Earth.
Significance of the Discovery
The discovery of four moons orbiting Jupiter was significant for several reasons: * It provided evidence for the Copernican heliocentric model, which placed the Sun at the center of the solar system * It challenged traditional views of the universe, which held that the Earth was at the center of the cosmos * It demonstrated the power of the telescope as a tool for astronomical observation and discoveryThe Discovery of Sunspots

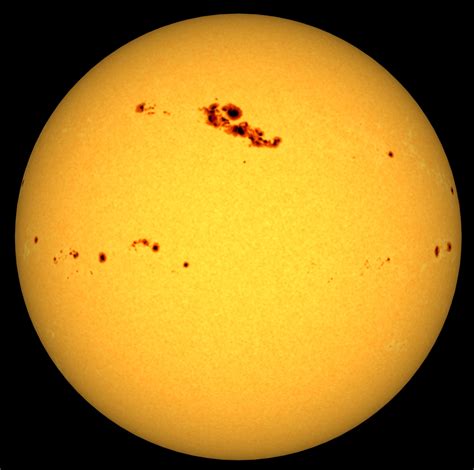
Galileo's discovery of sunspots, made in 1610, was another significant milestone in the history of astronomy. Sunspots are dark regions on the surface of the Sun that are caused by intense magnetic activity. Galileo's observations of sunspots provided evidence for the rotation of the Sun and challenged traditional views of the universe, which held that the Sun was a perfect, unchanging body.
Observations of Sunspots
Galileo's observations of sunspots were made using his telescope, and they provided valuable insights into the nature of the Sun. Some of the key features of sunspots that Galileo observed included: * Their dark color, which was caused by the intense magnetic activity in these regions * Their irregular shape, which was influenced by the complex magnetic fields in the Sun's atmosphere * Their motion, which provided evidence for the rotation of the SunThe Observation of the Phases of Venus

Galileo's observation of the phases of Venus, made in 1610, was another significant discovery that challenged traditional views of the universe. The phases of Venus, which are similar to the phases of the Moon, provided evidence for the Copernican heliocentric model and demonstrated that the planets orbit the Sun, rather than the Earth.
Significance of the Discovery
The discovery of the phases of Venus was significant for several reasons: * It provided evidence for the Copernican heliocentric model, which placed the Sun at the center of the solar system * It challenged traditional views of the universe, which held that the Earth was at the center of the cosmos * It demonstrated the power of the telescope as a tool for astronomical observation and discoveryThe Study of Motion and Gravity
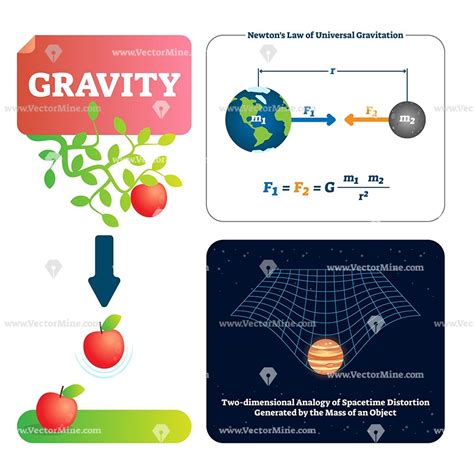
Galileo's study of motion and gravity, which was conducted in the early 17th century, laid the foundation for Sir Isaac Newton's laws of motion and universal gravitation. Galileo's work on motion and gravity challenged traditional views of the universe, which held that objects at rest would remain at rest, and objects in motion would continue to move indefinitely.
Key Principles of Motion and Gravity
Galileo's study of motion and gravity revealed several key principles, including: * The concept of inertia, which holds that objects at rest will remain at rest, and objects in motion will continue to move indefinitely, unless acted upon by an external force * The concept of acceleration, which holds that objects will accelerate, or change their motion, when acted upon by an external force * The concept of gravity, which holds that objects with mass will attract each other, and that the force of gravity will depend on the mass of the objects and the distance between themGallery of Galileo's Discoveries
Galileo Discoveries Image Gallery








As we conclude our exploration of Galileo's discoveries, we are reminded of the significance of his work and its lasting impact on our understanding of the universe. From the observation of celestial bodies to the study of motion and gravity, Galileo's discoveries have had a profound influence on the development of modern science. We invite you to share your thoughts on Galileo's discoveries and their significance, and to explore further the many fascinating topics that his work has touched upon. Whether you are a scientist, a scholar, or simply someone with a curiosity about the universe, Galileo's discoveries are sure to inspire and educate, offering a glimpse into the wonders of the cosmos and the power of human ingenuity.
