Intro
Unlock the power of geospatial intelligence in the Air Force, enhancing national security through advanced mapping, imagery analysis, and spatial data analysis. Discover how the intersection of geography and intelligence informs critical decision-making, supports military operations, and drives innovation in the defense sector, leveraging keywords like GEOINT, spatial analysis, and aerial surveillance.
The United States Air Force is a premier military organization that relies heavily on advanced technologies to maintain national security. One of the critical components of the Air Force's strategic operations is geospatial intelligence (GEOINT). GEOINT is the analysis and interpretation of satellite and aerial imagery, as well as other geospatial data, to support military planning and operations. In this article, we will delve into the world of geospatial intelligence in the Air Force, exploring its significance, applications, and the benefits it provides to national security.
The Importance of Geospatial Intelligence in the Air Force
Geospatial intelligence is a vital component of the Air Force's intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities. GEOINT provides critical information about the location, characteristics, and activities of potential adversaries, allowing the Air Force to make informed decisions about military operations. By analyzing satellite and aerial imagery, as well as other geospatial data, Air Force analysts can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that may indicate enemy activity.

The Applications of Geospatial Intelligence in the Air Force
GEOINT has numerous applications in the Air Force, including:
- Target identification and tracking: Geospatial intelligence is used to identify and track potential targets, such as enemy military installations, command centers, and troop movements.
- Battlefield management: GEOINT provides critical information about the battlefield, including terrain features, obstacles, and enemy positions.
- ISR operations: Geospatial intelligence is used to support ISR operations, including the identification of enemy air defenses, command centers, and communication networks.
- Homeland security: GEOINT is used to support homeland security operations, including the identification of potential terrorist targets and the tracking of suspicious activity.
How Geospatial Intelligence Enhances National Security
Geospatial intelligence plays a critical role in enhancing national security by providing timely and accurate information about potential threats. By analyzing satellite and aerial imagery, as well as other geospatial data, Air Force analysts can identify potential security threats and provide critical information to support military planning and operations.

The Benefits of Geospatial Intelligence in the Air Force
The benefits of geospatial intelligence in the Air Force are numerous, including:
- Enhanced situational awareness: GEOINT provides critical information about the battlefield, allowing Air Force commanders to make informed decisions about military operations.
- Improved target identification and tracking: Geospatial intelligence enables the Air Force to identify and track potential targets, reducing the risk of friendly fire and improving the effectiveness of military operations.
- Increased operational efficiency: GEOINT supports the efficient use of military resources, reducing the need for unnecessary deployments and minimizing the risk of collateral damage.
Geospatial Intelligence Analysts: The Unsung Heroes of the Air Force
Geospatial intelligence analysts are the unsung heroes of the Air Force, working behind the scenes to provide critical information about potential threats. These analysts use advanced technologies, including satellite and aerial imagery, to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that may indicate enemy activity.
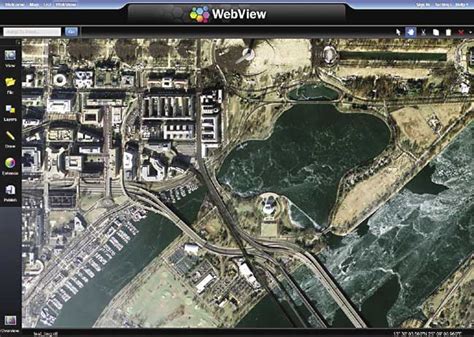
The Future of Geospatial Intelligence in the Air Force
The future of geospatial intelligence in the Air Force is bright, with advancements in technology and analytics enabling the development of more sophisticated GEOINT capabilities. The Air Force is investing in new technologies, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of geospatial intelligence operations.
Challenges and Limitations of Geospatial Intelligence
While geospatial intelligence is a critical component of the Air Force's ISR capabilities, there are challenges and limitations associated with its use. These challenges include:
- Data overload: The vast amounts of geospatial data available can be overwhelming, making it difficult for analysts to identify critical information.
- Analytical complexity: Geospatial intelligence analysis requires specialized training and expertise, making it challenging for analysts to interpret complex data.
- Technological limitations: The accuracy and resolution of satellite and aerial imagery can be limited by technological constraints, such as weather conditions and sensor capabilities.

Conclusion: Geospatial Intelligence in the Air Force
Geospatial intelligence is a critical component of the Air Force's ISR capabilities, providing timely and accurate information about potential threats. By analyzing satellite and aerial imagery, as well as other geospatial data, Air Force analysts can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that may indicate enemy activity. While there are challenges and limitations associated with the use of geospatial intelligence, the benefits of GEOINT to national security are clear.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the importance of geospatial intelligence in the Air Force. How do you think GEOINT will evolve in the future? What challenges and limitations do you think the Air Force will face in its use of geospatial intelligence?
Geospatial Intelligence Image Gallery