Intro
Discover 5 ways to identify beetles, including insect inspection, habitat analysis, and species recognition, to effectively distinguish between different beetle types and species.
Beetles are one of the most diverse and widespread groups of insects, with over 400,000 known species worldwide. They can be found in almost every environment, from deserts to rainforests, and play a vital role in many ecosystems. However, identifying beetles can be a challenging task, even for experienced entomologists. In this article, we will explore five ways to identify beetles, including their physical characteristics, habits, and habitats.
Beetles have been around for millions of years, and their evolution has led to an incredible range of shapes, sizes, and colors. From the tiny feather-winged beetles to the giant Goliath beetles, each species has unique characteristics that set it apart from others. By studying these characteristics, we can gain a better understanding of the different types of beetles and how to identify them. Whether you are a seasoned entomologist or just starting to explore the world of insects, learning about beetles can be a fascinating and rewarding experience.
The importance of identifying beetles cannot be overstated. Many species of beetles are beneficial to the environment, serving as pollinators, decomposers, or predators of other insects. However, some species can be pests, causing damage to crops, trees, or other plants. By being able to identify beetles, we can better understand their roles in the ecosystem and take steps to conserve or manage them. In addition, identifying beetles can also help us to appreciate the incredible diversity of life on Earth and the many fascinating creatures that surround us.
Physical Characteristics of Beetles
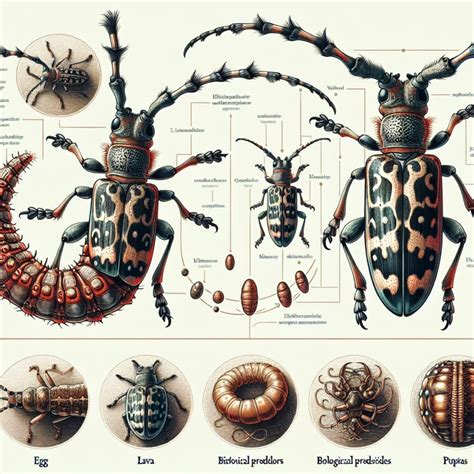
For example, the ground beetles (Carabidae) are characterized by their elongated bodies, long legs, and distinctive antennae. The lady beetles (Coccinellidae), on the other hand, are known for their oval-shaped bodies, short legs, and bright colors. The weevils (Curculionidae) are recognized by their elongated snouts and distinctive body shapes. By studying these physical characteristics, we can begin to identify the different types of beetles and learn more about their habits and habitats.
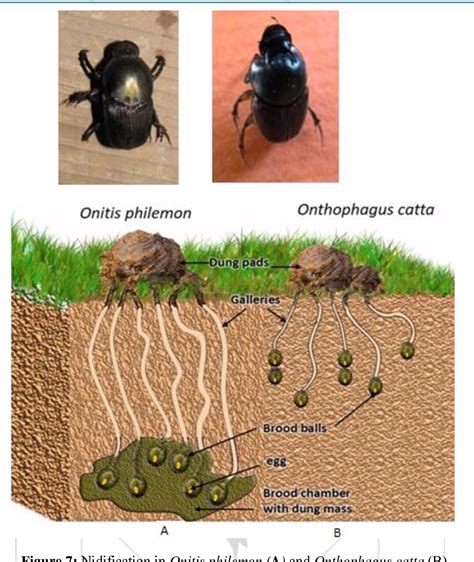
Habitat and Distribution of Beetles
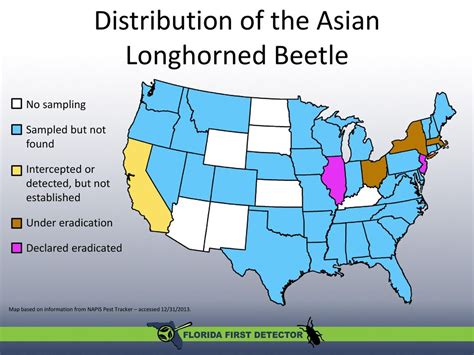
By studying the habitat and distribution of beetles, we can gain a better understanding of their ecology and behavior. For example, some species of beetles are found only in certain types of vegetation, such as trees or flowers. Others are found in specific types of soil or rock. By knowing the habitat and distribution of a beetle, we can often identify the species and learn more about its habits and habitats.
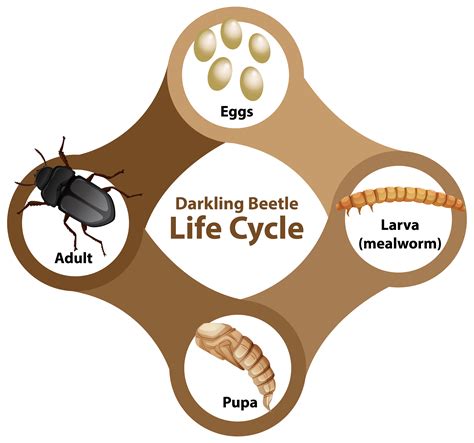
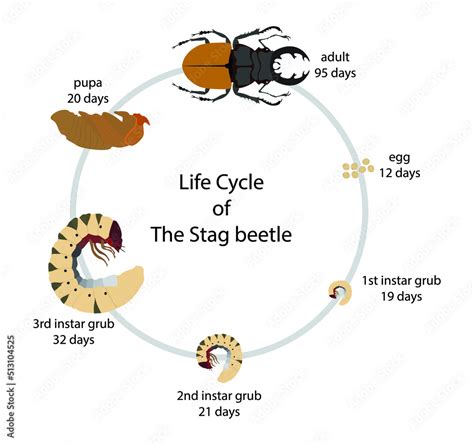
Behavior and Life Cycle of Beetles
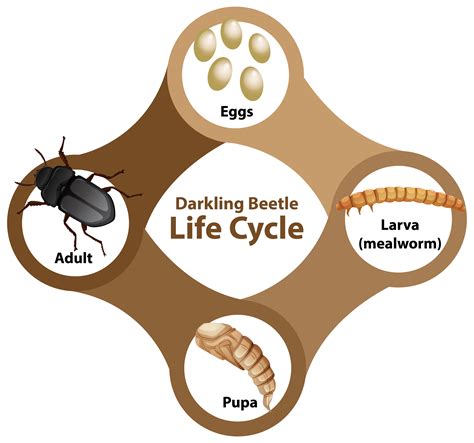
The life cycle of a beetle typically consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The eggs are usually laid in a protected location, such as under bark or in soil. The larvae, also known as grubs, hatch from the eggs and feed on surrounding materials. The pupae are the resting stage, during which the beetle undergoes metamorphosis and develops into an adult. The adult beetles emerge from the pupae and begin the cycle again.
By studying the behavior and life cycle of beetles, we can gain a better understanding of their ecology and behavior. For example, some species of beetles are important pollinators, while others are decomposers or predators. By knowing the behavior and life cycle of a beetle, we can often identify the species and learn more about its habits and habitats.
Diet and Foraging Behavior of Beetles
The diet and foraging behavior of a beetle can often be determined by its mouthparts and other physical characteristics. For example, the ground beetles (Carabidae) have distinctive mouthparts that are adapted for feeding on insects and other small animals. The leaf beetles (Chrysomelidae), on the other hand, have mouthparts that are adapted for feeding on plants.
By studying the diet and foraging behavior of beetles, we can gain a better understanding of their ecology and behavior. For example, some species of beetles are important pollinators, while others are decomposers or predators. By knowing the diet and foraging behavior of a beetle, we can often identify the species and learn more about its habits and habitats.
Conservation Status of Beetles

For example, the Titanus giganteus, a species of longhorn beetle, is listed as endangered due to habitat loss and degradation. The species is found only in the tropical forests of South America, and its population is threatened by deforestation and logging. By knowing the conservation status of a beetle, we can take steps to conserve and protect it, such as protecting its habitat or reducing our impact on the environment.
Gallery of Beetle Images
Beetle Image Gallery







In conclusion, identifying beetles can be a challenging but rewarding task. By studying their physical characteristics, habitat and distribution, behavior and life cycle, diet and foraging behavior, and conservation status, we can gain a better understanding of these fascinating insects. Whether you are a seasoned entomologist or just starting to explore the world of insects, learning about beetles can be a fascinating and rewarding experience. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with beetles in the comments below, and to explore the many resources available for learning more about these incredible creatures. By working together, we can promote a greater appreciation and understanding of beetles and the important roles they play in our ecosystem.
