Intro
Discover Tennessee paycheck tax rates, deductions, and withholding. Learn about state income tax, payroll taxes, and tax brackets to optimize your TN paycheck.
Understanding paycheck tax rates is crucial for individuals to manage their finances effectively. Tax rates can significantly impact the amount of money one takes home, and being aware of these rates can help in making informed decisions about investments, savings, and expenses. In the context of Tennessee (TN), paycheck tax rates are an essential aspect of personal finance that every working individual should comprehend.
The state of Tennessee does not impose a state income tax on wages, which makes it an attractive destination for individuals looking to maximize their take-home pay. However, this does not mean that Tennesseans are exempt from all taxes. Federal income taxes, as well as other forms of taxation, still apply. For those living in Tennessee, understanding how federal tax rates work and how they affect paychecks is vital.
Tennessee's lack of state income tax can be a significant advantage for residents, especially when compared to states with high income tax rates. This advantage can lead to higher take-home pay for individuals, which can then be invested, saved, or spent as they see fit. However, it's also important to consider other taxes and deductions that might affect one's paycheck, such as federal taxes, Social Security taxes, and Medicare taxes.
Understanding Federal Tax Rates
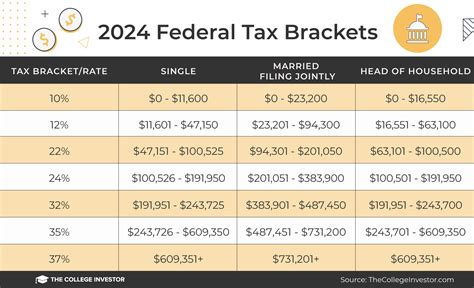
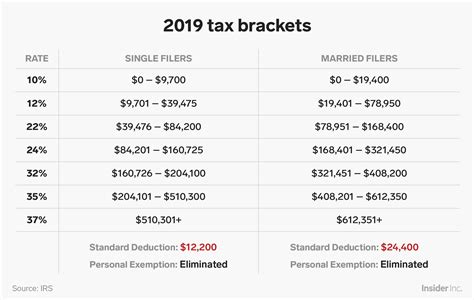
Federal tax rates are progressive, meaning that as income increases, the tax rate applied to the additional income also increases. The federal tax system is divided into several tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. For the 2023 tax year, there are seven tax brackets: 10%, 12%, 22%, 24%, 32%, 35%, and 37%. The tax bracket an individual falls into depends on their filing status and taxable income.
How Tax Brackets Work
To understand how tax brackets work, consider an example. Suppose an individual has a taxable income that falls into the 24% tax bracket. This does not mean that their entire income is taxed at 24%. Instead, they pay the tax rates of the lower brackets on the income within those brackets and then pay 24% on the amount above the threshold for the 22% bracket. This progressive system aims to tax higher-income individuals at a higher rate while providing relief to lower-income individuals.Tax Deductions and Credits

In addition to understanding tax rates, it's essential to be aware of tax deductions and credits. Tax deductions reduce the amount of income that is subject to tax, thereby lowering the amount of taxes owed. Examples of tax deductions include the standard deduction, itemized deductions (such as mortgage interest and charitable contributions), and deductions for certain types of income, like student loan interest.
Tax credits, on the other hand, directly reduce the amount of tax owed. They are often designed to encourage specific behaviors or to support certain groups, such as low-income families or first-time homebuyers. Unlike deductions, credits are applied after calculating the tax liability, providing a dollar-for-dollar reduction in taxes owed.
Common Tax Credits
Some common tax credits include the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), the Child Tax Credit, and education credits like the American Opportunity Tax Credit and the Lifetime Learning Credit. These credits can significantly impact an individual's tax liability and, consequently, their take-home pay.Impact of Tax Rates on Take-Home Pay
The impact of tax rates on take-home pay can be substantial. Higher tax rates can result in a significant reduction in take-home pay, while lower tax rates can lead to more money in one's pocket. For individuals living in Tennessee, the absence of state income tax means that their take-home pay is less affected by state-level taxation compared to individuals in states with high income taxes.
However, federal taxes, Social Security taxes (6.2% for employees, though this is often split with employers), and Medicare taxes (1.45% for employees) still apply. These taxes can reduce take-home pay, and understanding how they work is crucial for managing one's finances effectively.
Calculating Take-Home Pay
Calculating take-home pay involves considering all deductions and taxes. A common approach is to use a paycheck calculator, which can provide an estimate based on income, filing status, and the number of allowances claimed on the W-4 form. The W-4 form is crucial because it determines how much federal income tax is withheld from each paycheck. Claiming more allowances can result in less tax being withheld, leading to higher take-home pay but potentially resulting in a tax bill at the end of the year if too little is withheld.Managing Finances with Variable Tax Rates

Managing finances in an environment with variable tax rates requires a strategic approach. Here are some tips:
- Understand Your Tax Bracket: Knowing which tax bracket you fall into can help you make informed decisions about investments and income.
- Maximize Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Utilizing tax-advantaged accounts such as 401(k), IRA, or Roth IRA for retirement savings, and 529 plans for education expenses, can help reduce taxable income.
- Itemize Deductions: If itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction, it may be beneficial to itemize, especially for homeowners with significant mortgage interest and property taxes.
- Stay Informed: Tax laws and rates can change, so staying informed about updates and adjustments can help in making timely financial decisions.
Strategies for Minimizing Tax Liability
Minimizing tax liability involves a combination of tax planning, investment strategies, and financial management. Some strategies include: - **Tax Loss Harvesting:** Selling securities that have declined in value to realize losses, which can offset gains from other investments. - **Charitable Donations:** Donating to charity can provide a tax deduction, reducing taxable income. - **Retirement Contributions:** Contributing to retirement accounts can reduce taxable income and provide tax-deferred growth.Gallery of Tax-Related Images
Tax-Related Image Gallery






Final Thoughts on Tax Rates and Financial Planning

In conclusion, understanding paycheck tax rates, especially in a state like Tennessee with no state income tax, is vital for effective financial planning. By grasping how federal tax rates work, utilizing tax deductions and credits, and implementing strategies to minimize tax liability, individuals can maximize their take-home pay and achieve their financial goals. Whether it's through optimizing investments, leveraging tax-advantaged accounts, or simply being aware of how tax rates impact income, being informed is the first step towards financial success.
As you consider your own financial situation and how tax rates affect your paycheck, remember the importance of staying informed about tax laws and rates. Share your thoughts on how tax rates impact your financial decisions in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with friends and family who might benefit from understanding more about paycheck tax rates and financial planning.
