Intro
Unlock the power of Excels lookup functions with our comprehensive guide to mastering VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP together. Learn how to use these essential formulas to retrieve data from tables, manage large datasets, and streamline your workflow with precision and speed, using lookup values, table arrays, and range specifications.
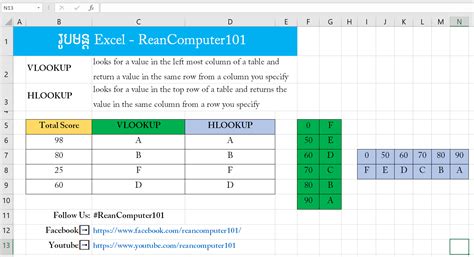
Excel is a powerful tool for data analysis and manipulation. Two of the most commonly used functions in Excel are VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP. These functions allow you to search for specific data within a table and return corresponding values. While they may seem similar, VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP have distinct differences in their syntax and application.
In this article, we will delve into the world of VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP, exploring their benefits, limitations, and practical applications. We will also provide step-by-step examples to help you master these functions and improve your Excel skills.
Understanding VLOOKUP
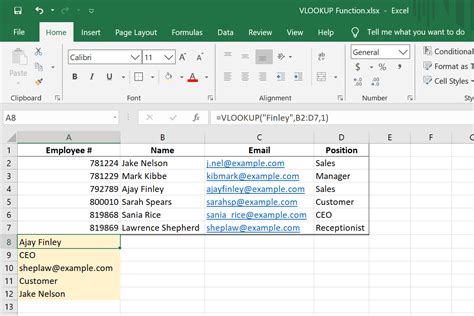
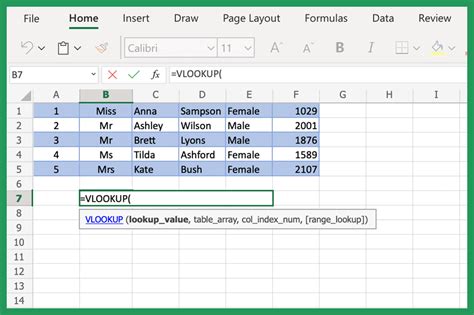
VLOOKUP (Vertical Lookup) is a function that allows you to search for a specific value within a table and return a corresponding value from another column. The syntax for VLOOKUP is as follows:
VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
lookup_value: the value you want to search fortable_array: the range of cells that contains the data you want to searchcol_index_num: the column number that contains the value you want to return[range_lookup]: optional parameter that specifies whether you want an exact match or an approximate match
How VLOOKUP Works
VLOOKUP searches for the lookup_value in the first column of the table_array and returns the value in the corresponding row from the column specified by col_index_num. If the range_lookup parameter is set to FALSE, VLOOKUP will only return an exact match. If it's set to TRUE, VLOOKUP will return an approximate match.
Understanding HLOOKUP
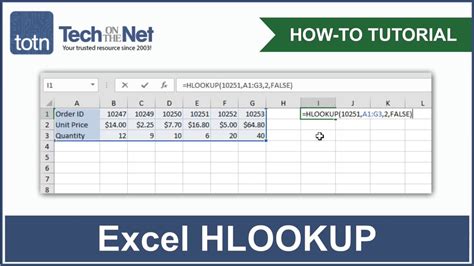
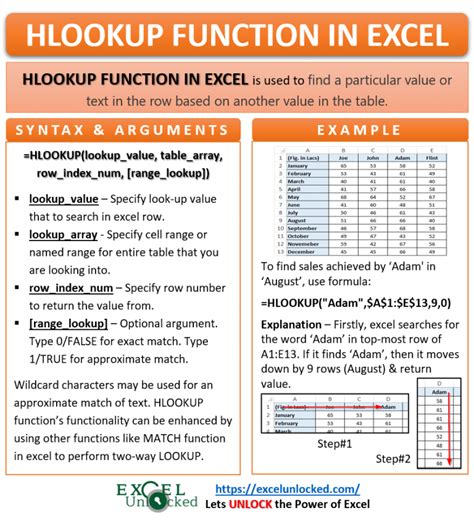
HLOOKUP (Horizontal Lookup) is a function that allows you to search for a specific value within a table and return a corresponding value from another row. The syntax for HLOOKUP is as follows:
HLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, row_index_num, [range_lookup])
lookup_value: the value you want to search fortable_array: the range of cells that contains the data you want to searchrow_index_num: the row number that contains the value you want to return[range_lookup]: optional parameter that specifies whether you want an exact match or an approximate match
How HLOOKUP Works
HLOOKUP searches for the lookup_value in the first row of the table_array and returns the value in the corresponding column from the row specified by row_index_num. If the range_lookup parameter is set to FALSE, HLOOKUP will only return an exact match. If it's set to TRUE, HLOOKUP will return an approximate match.
Mastering VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP
To become proficient in using VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP, you need to understand the syntax and application of each function. Here are some tips to help you master these functions:
- Always specify the
range_lookupparameter to ensure you get the desired results. - Use VLOOKUP when you need to search for a value in a vertical column and return a corresponding value from another column.
- Use HLOOKUP when you need to search for a value in a horizontal row and return a corresponding value from another row.
- Make sure to specify the correct column or row index number to get the desired results.
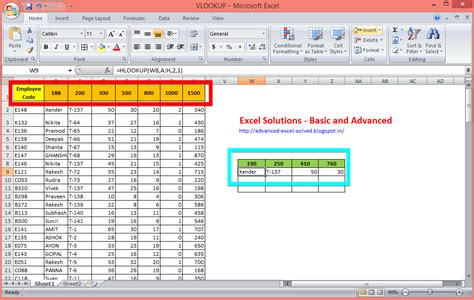
Example 1: Using VLOOKUP to Return a Corresponding Value
Suppose you have a table with employee names, departments, and salaries. You want to find the salary of a specific employee using VLOOKUP.
| Employee Name | Department | Salary |
|---|---|---|
| John Smith | Sales | 50000 |
| Jane Doe | Marketing | 60000 |
| Bob Johnson | IT | 70000 |
Formula: =VLOOKUP("John Smith", A2:C4, 3, FALSE)
Result: 50000
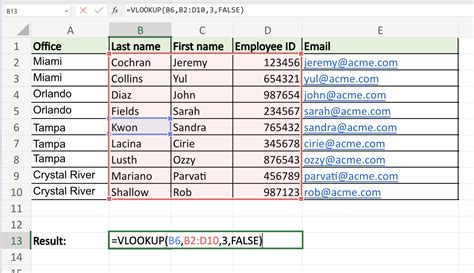
Example 2: Using HLOOKUP to Return a Corresponding Value
Suppose you have a table with exam scores for different subjects. You want to find the score of a specific subject using HLOOKUP.
| Subject | Math | Science | English |
|---|---|---|---|
| Student 1 | 80 | 70 | 90 |
| Student 2 | 90 | 80 | 70 |
| Student 3 | 70 | 90 | 80 |
Formula: =HLOOKUP("Math", A1:D3, 2, FALSE)
Result: 80
Common Errors and Troubleshooting
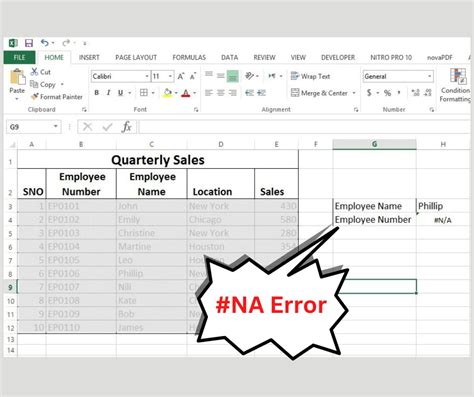
- #N/A Error: This error occurs when the
lookup_valueis not found in thetable_array. Check the spelling and formatting of thelookup_valueand ensure it matches the values in thetable_array. - #REF! Error: This error occurs when the
col_index_numorrow_index_numis incorrect. Check the column or row index number and ensure it corresponds to the correct column or row. - #VALUE! Error: This error occurs when the
lookup_valueis not a number or text value. Check the formatting of thelookup_valueand ensure it matches the values in thetable_array.
Conclusion
VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP are powerful functions in Excel that allow you to search for specific data within a table and return corresponding values. By understanding the syntax and application of each function, you can master these functions and improve your Excel skills. Remember to always specify the range_lookup parameter and ensure you get the desired results. With practice and experience, you can become proficient in using VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP to manipulate and analyze data in Excel.
Gallery of VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP Examples
VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP Image Gallery


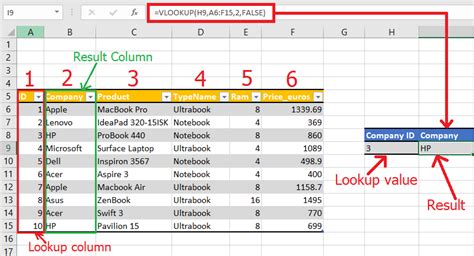
We hope this article has helped you understand the basics of VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP in Excel. With practice and experience, you can master these functions and improve your data analysis skills. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below!
