Intro
Discover the 5 key roles of an industrial engineer, from optimizing manufacturing processes to improving quality control and supply chain management. Learn how industrial engineers apply lean principles, use data analytics, and implement sustainable solutions to drive efficiency and innovation in various industries.
Industrial engineers play a vital role in optimizing the efficiency and productivity of systems, processes, and organizations. They are responsible for designing, implementing, and improving integrated systems that include people, materials, equipment, and energy. As industries continue to evolve and become more complex, the role of industrial engineers has become increasingly important. In this article, we will explore the five key roles of an industrial engineer and how they contribute to the success of organizations.
Role 1: Efficiency Expert

As efficiency experts, industrial engineers are responsible for identifying areas of inefficiency in processes and systems. They use data analysis and modeling techniques to understand the current state of operations and identify opportunities for improvement. By streamlining processes, reducing waste, and optimizing resource allocation, industrial engineers can significantly improve the productivity and efficiency of organizations.
For example, an industrial engineer working in a manufacturing plant might analyze the production line to identify bottlenecks and areas where workflow can be improved. By implementing changes such as reorganizing the layout of the plant, implementing new technologies, or retraining staff, the industrial engineer can help increase productivity and reduce costs.
Key Skills for Efficiency Experts
- Data analysis and modeling
- Process mapping and simulation
- Lean manufacturing principles
- Six Sigma methodologies
Role 2: System Designer
As system designers, industrial engineers are responsible for creating new systems or modifying existing ones to meet the changing needs of organizations. They use a variety of techniques, including simulation modeling and optimization algorithms, to design systems that are efficient, effective, and sustainable.
For example, an industrial engineer working in a healthcare organization might design a new system for managing patient flow. By analyzing data on patient arrival patterns, treatment times, and resource availability, the industrial engineer can design a system that minimizes wait times, reduces congestion, and improves patient outcomes.
Key Skills for System Designers
- System modeling and simulation
- Optimization algorithms and techniques
- Human factors engineering
- Sustainability principles
Role 3: Quality Control Specialist

As quality control specialists, industrial engineers are responsible for ensuring that products meet the required standards of quality. They use statistical process control and other techniques to monitor production processes and identify areas where quality can be improved.
For example, an industrial engineer working in a food processing plant might develop a quality control system to ensure that products meet food safety standards. By monitoring temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors, the industrial engineer can identify potential risks to product quality and implement corrective actions to prevent contamination.
Key Skills for Quality Control Specialists
- Statistical process control
- Quality management systems
- Food safety regulations
- Supply chain management
Role 4: Supply Chain Manager
As supply chain managers, industrial engineers are responsible for coordinating the flow of goods, services, and information from raw materials to end customers. They use a variety of techniques, including network optimization and inventory management, to minimize costs, reduce lead times, and improve customer satisfaction.
For example, an industrial engineer working in a retail organization might develop a supply chain strategy to improve the availability of products during peak demand periods. By analyzing data on customer demand, supplier lead times, and inventory levels, the industrial engineer can identify opportunities to reduce stockouts, improve fill rates, and increase customer satisfaction.
Key Skills for Supply Chain Managers
- Supply chain optimization
- Inventory management
- Logistics and transportation management
- Demand forecasting
Role 5: Ergonomics Specialist
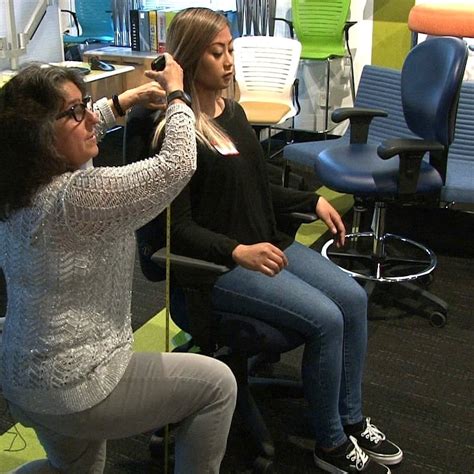

As ergonomics specialists, industrial engineers are responsible for designing workspaces and systems that are safe, comfortable, and efficient for workers. They use a variety of techniques, including human factors engineering and biomechanics, to reduce the risk of injury and improve worker productivity.
For example, an industrial engineer working in a manufacturing plant might design an ergonomic workspace to reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders. By analyzing data on worker movements, postures, and tasks, the industrial engineer can identify opportunities to reduce strain, improve comfort, and increase productivity.
Key Skills for Ergonomics Specialists
- Human factors engineering
- Biomechanics
- Workplace design and layout
- Occupational safety and health regulations
Industrial Engineering Image Gallery







As we have seen, industrial engineers play a vital role in optimizing the efficiency and productivity of systems, processes, and organizations. By performing the five key roles of efficiency expert, system designer, quality control specialist, supply chain manager, and ergonomics specialist, industrial engineers can help organizations achieve their goals and improve their competitiveness. Whether you are an industrial engineer looking to advance your career or an organization looking to improve your operations, understanding the key roles of industrial engineers is essential for success.
