Intro
Infection control is a critical aspect of maintaining a safe and healthy environment, particularly in healthcare settings. The consequences of poor infection control can be severe, resulting in the spread of diseases, increased morbidity and mortality, and significant economic burdens. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to understand the fundamental concepts of infection control. In this article, we will delve into five essential infection control concepts that you need to know.
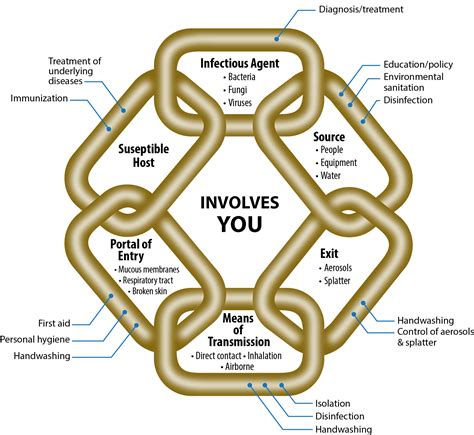
Understanding the Chain of Infection
The chain of infection is a crucial concept in infection control, as it illustrates the sequence of events that must occur for an infection to spread. The chain consists of six links:
1. Infectious Agent
- An infectious agent, such as a bacterium, virus, or fungus, is the primary cause of infection.
- These agents can be found in various environments, including human bodies, contaminated surfaces, and infected animals.
2. Reservoir
- A reservoir is a location where an infectious agent can survive and multiply.
- Common reservoirs include human bodies, contaminated water, and infected animals.
3. Portal of Exit
- A portal of exit is the route by which an infectious agent leaves the reservoir.
- Examples of portals of exit include the nose, mouth, and skin.
4. Mode of Transmission
- A mode of transmission is the mechanism by which an infectious agent is transferred from the reservoir to a new host.
- Common modes of transmission include direct contact, airborne transmission, and vector-borne transmission.
5. Portal of Entry
- A portal of entry is the route by which an infectious agent enters a new host.
- Examples of portals of entry include the eyes, nose, mouth, and skin.
6. Susceptible Host
- A susceptible host is an individual who is vulnerable to infection due to factors such as age, underlying health conditions, or compromised immune system.
Breaking the chain of infection is critical to preventing the spread of diseases. By understanding each link in the chain, healthcare professionals can develop effective strategies to interrupt the transmission of infectious agents.
The Importance of Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene is a fundamental aspect of infection control, as it prevents the spread of infectious agents through direct contact. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the following hand hygiene protocol:
1. Use Soap and Water
- Wash hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, paying particular attention to the backs of hands, wrists, and between fingers.
2. Use Hand Sanitizer
- Use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer when soap and water are not available.
- Apply hand sanitizer to the entire surface of the hands, including the backs of hands, wrists, and between fingers.
3. Avoid Touching Face
- Avoid touching the face, particularly the eyes, nose, and mouth, as these areas are vulnerable to infection.

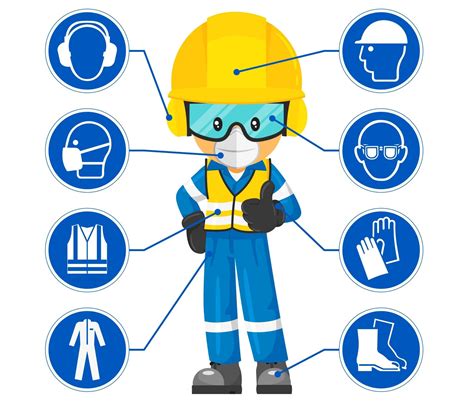
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a critical component of infection control, as it provides a barrier between the wearer and infectious agents. Common types of PPE include:
1. Gloves
- Wear gloves when interacting with patients, handling bodily fluids, or touching contaminated surfaces.
2. Masks
- Wear masks when interacting with patients who have airborne infections, such as tuberculosis.
3. Gowns
- Wear gowns when interacting with patients who have bodily fluid-borne infections, such as Ebola.
4. Eye Protection
- Wear eye protection, such as goggles or face shields, when interacting with patients who have bodily fluid-borne infections.

Sterilization and Disinfection
Sterilization and disinfection are critical components of infection control, as they reduce the number of infectious agents on surfaces and equipment. Sterilization involves the complete elimination of infectious agents, while disinfection involves the reduction of infectious agents to a safe level.
1. Autoclaving
- Autoclaving is a sterilization method that uses high-pressure steam to kill infectious agents.
2. Dry Heat Sterilization
- Dry heat sterilization is a method that uses hot air to kill infectious agents.
3. Chemical Disinfection
- Chemical disinfection involves the use of disinfectants, such as bleach or quaternary ammonium compounds, to reduce infectious agents on surfaces.

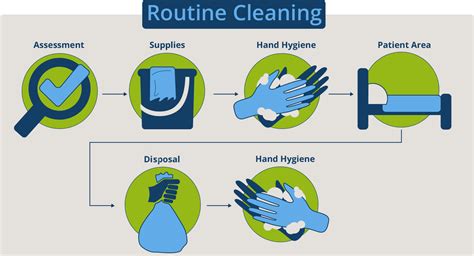
Environmental Cleaning and Disinfection
Environmental cleaning and disinfection are critical components of infection control, as they reduce the number of infectious agents on surfaces and equipment.
1. Clean High-Touch Surfaces
- Clean high-touch surfaces, such as door handles, light switches, and countertops, regularly.
2. Use Disinfectants
- Use disinfectants, such as bleach or quaternary ammonium compounds, to reduce infectious agents on surfaces.
3. Use Microfiber Cloths
- Use microfiber cloths to clean and disinfect surfaces, as they are effective at picking up infectious agents.
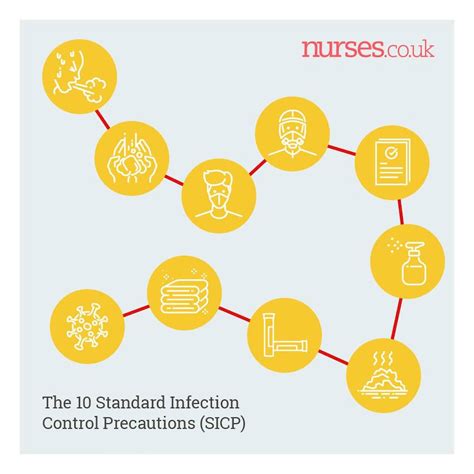
In conclusion, understanding essential infection control concepts is critical to preventing the spread of diseases. By breaking the chain of infection, practicing hand hygiene, using PPE, sterilizing and disinfecting equipment and surfaces, and cleaning and disinfecting the environment, healthcare professionals can reduce the risk of infection transmission.
Gallery of Infection Control Images
Infection Control Image Gallery








We hope you found this article informative and helpful. Share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below.
