Intro
Mammals efficient respiratory system enables optimal oxygen intake, utilizing lungs, airways, and breathing mechanisms for gas exchange, ventilation, and respiration, showcasing adaptability and unique physiological features.
The respiratory system is a vital component of the human body, and it plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of an individual. However, mammals have a unique and highly efficient respiratory system that sets them apart from other animals. The mammalian respiratory system is designed to provide a constant supply of oxygen to the body's cells and to remove carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular metabolism. This system is essential for the survival of mammals, and it has evolved over time to become one of the most efficient and complex systems in the animal kingdom.
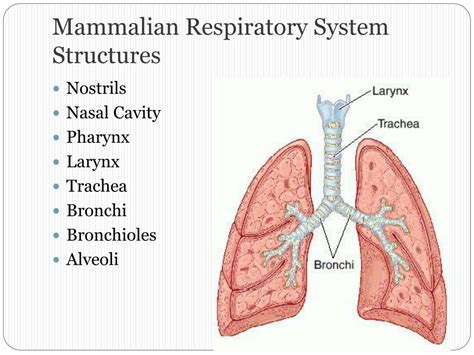
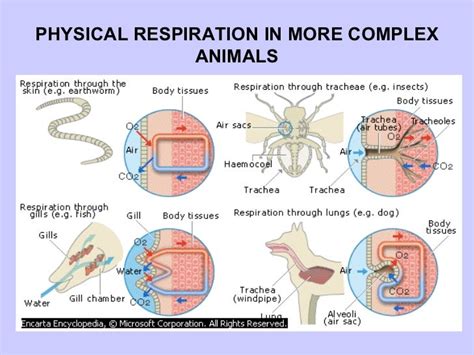
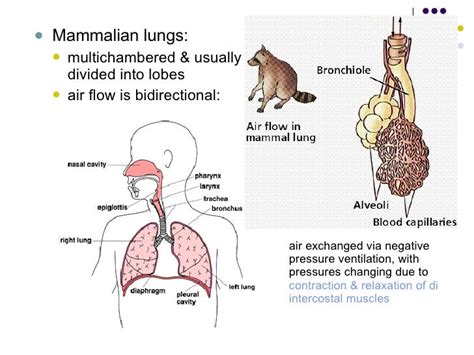
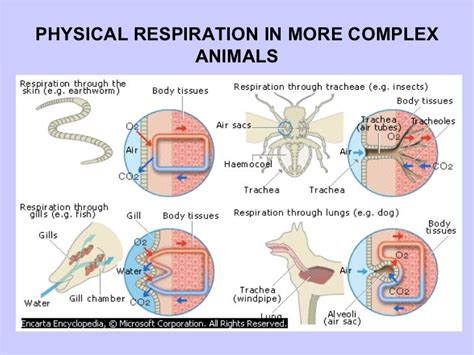
The mammalian respiratory system consists of the nose, mouth, trachea, bronchi, lungs, and diaphragm. The nose and mouth are responsible for inhaling air, which then passes through the trachea and into the bronchi. The bronchi branch off into smaller airways, called bronchioles, which eventually lead to the alveoli, where gas exchange takes place. The diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle, contracts and relaxes to expand and deflate the lungs, allowing for the inhalation and exhalation of air. This complex system works together to provide a constant supply of oxygen to the body's cells and to remove carbon dioxide.
Mammals have evolved a number of adaptations that make their respiratory system highly efficient. For example, the lungs of mammals are highly vascularized, meaning that they have a rich supply of blood vessels. This allows for efficient gas exchange, as oxygen can be quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide can be removed. Additionally, the lungs of mammals have a large surface area, which allows for more efficient gas exchange. The diaphragm also plays a crucial role in the mammalian respiratory system, as it allows for the expansion and deflation of the lungs, making it possible for mammals to breathe efficiently.
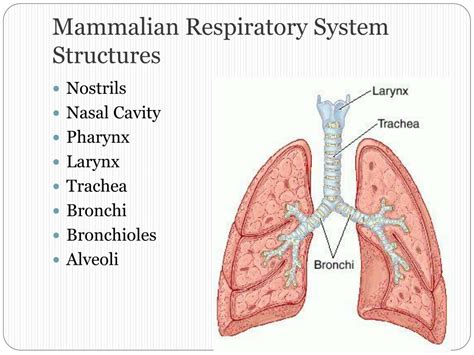
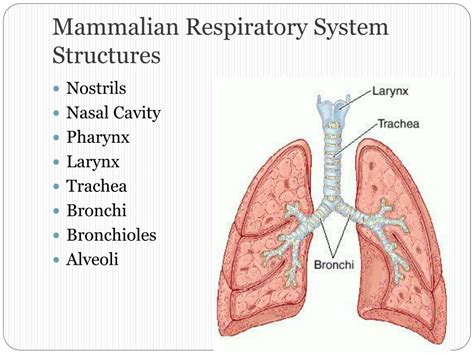
Mammals Respiratory System Structure
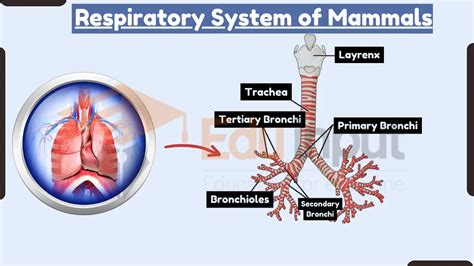
The structure of the mammalian respiratory system is highly specialized and consists of several key components. The nose and mouth are responsible for inhaling air, which then passes through the trachea and into the bronchi. The bronchi branch off into smaller airways, called bronchioles, which eventually lead to the alveoli, where gas exchange takes place. The diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle, contracts and relaxes to expand and deflate the lungs, allowing for the inhalation and exhalation of air. The lungs themselves are highly vascularized, meaning that they have a rich supply of blood vessels, which allows for efficient gas exchange.
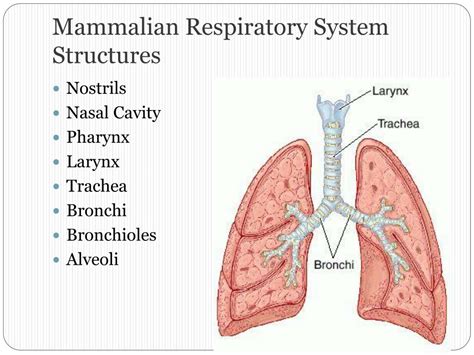
Key Components of Mammals Respiratory System
The key components of the mammalian respiratory system include: * The nose and mouth, which are responsible for inhaling air * The trachea, which carries air from the nose and mouth to the bronchi * The bronchi, which branch off into smaller airways, called bronchioles * The bronchioles, which eventually lead to the alveoli, where gas exchange takes place * The diaphragm, a dome-shaped muscle that contracts and relaxes to expand and deflate the lungs * The lungs, which are highly vascularized and have a large surface area, allowing for efficient gas exchangeMammals Respiratory System Function
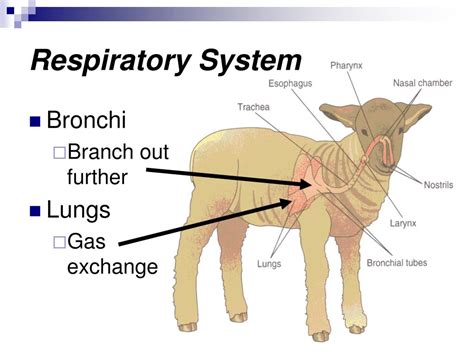
The function of the mammalian respiratory system is to provide a constant supply of oxygen to the body's cells and to remove carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular metabolism. This is achieved through the process of breathing, which involves the inhalation of air, the exchange of gases in the lungs, and the exhalation of air. The diaphragm plays a crucial role in this process, as it contracts and relaxes to expand and deflate the lungs, allowing for the inhalation and exhalation of air.
Process of Breathing in Mammals
The process of breathing in mammals involves the following steps: 1. Inhalation: Air is inhaled through the nose and mouth, and passes through the trachea and into the bronchi. 2. Gas exchange: The air reaches the alveoli, where oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is removed. 3. Exhalation: The diaphragm relaxes, and the lungs deflate, allowing for the exhalation of air. 4. Repeat: The process is repeated, with the diaphragm contracting and relaxing to expand and deflate the lungs, allowing for the inhalation and exhalation of air.Mammals Respiratory System Efficiency
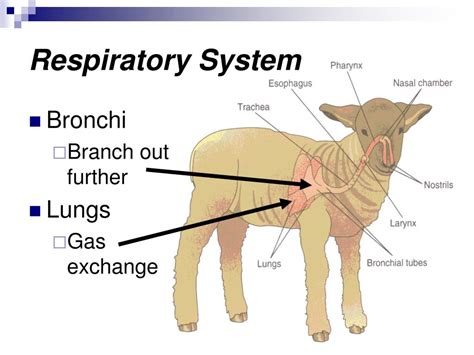
The mammalian respiratory system is highly efficient, with a number of adaptations that allow for efficient gas exchange. The lungs of mammals are highly vascularized, meaning that they have a rich supply of blood vessels, which allows for efficient gas exchange. Additionally, the lungs have a large surface area, which allows for more efficient gas exchange. The diaphragm also plays a crucial role in the mammalian respiratory system, as it allows for the expansion and deflation of the lungs, making it possible for mammals to breathe efficiently.
Adaptations for Efficient Gas Exchange
The mammalian respiratory system has a number of adaptations that allow for efficient gas exchange, including: * Highly vascularized lungs, which allow for efficient gas exchange * A large surface area, which allows for more efficient gas exchange * A diaphragm that contracts and relaxes to expand and deflate the lungs, allowing for the inhalation and exhalation of air * A highly efficient gas exchange system, which allows for the rapid absorption of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxideMammals Respiratory System Evolution
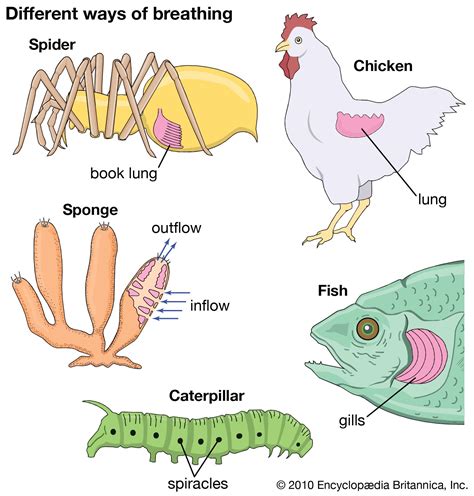
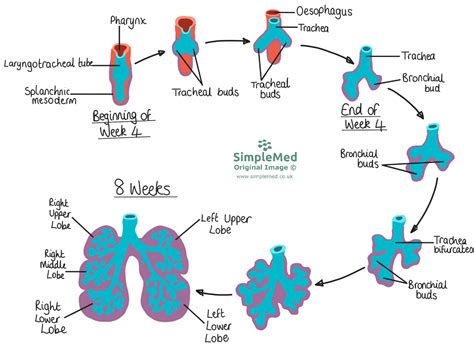
The mammalian respiratory system has evolved over time to become one of the most efficient and complex systems in the animal kingdom. The earliest mammals were small, insectivorous creatures that lived during the time of the dinosaurs. These early mammals had a simple respiratory system that was similar to that of modern reptiles. However, as mammals evolved and became more complex, their respiratory system also evolved to become more efficient.
Key Events in the Evolution of Mammals Respiratory System
The key events in the evolution of the mammalian respiratory system include: * The development of a diaphragm, which allowed for the expansion and deflation of the lungs * The evolution of highly vascularized lungs, which allowed for efficient gas exchange * The development of a large surface area, which allowed for more efficient gas exchange * The evolution of a highly efficient gas exchange system, which allowed for the rapid absorption of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxideMammals Respiratory System Image Gallery


In conclusion, the mammalian respiratory system is a highly efficient and complex system that plays a vital role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of mammals. The system has evolved over time to become one of the most efficient and specialized systems in the animal kingdom, with a number of adaptations that allow for efficient gas exchange. By understanding the structure, function, and evolution of the mammalian respiratory system, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and diversity of life on Earth. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this article, and to explore further the fascinating world of mammalian biology.
