The Mann Whitney U test is a widely used non-parametric statistical test that helps determine if there's a significant difference between two independent groups. While it's a powerful tool, many users find it challenging to perform in Excel. But don't worry, we've got you covered! In this article, we'll break down the Mann Whitney U test in Excel, making it easy to understand and apply.
Why Use the Mann Whitney U Test?
The Mann Whitney U test is an excellent alternative to the independent samples t-test when your data doesn't meet the assumptions of normality or equal variances. It's particularly useful when dealing with ordinal data or non-normal distributions. The test is also robust and can handle outliers, making it a popular choice among researchers and data analysts.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing the Mann Whitney U Test in Excel
To perform the Mann Whitney U test in Excel, you'll need to follow these steps:
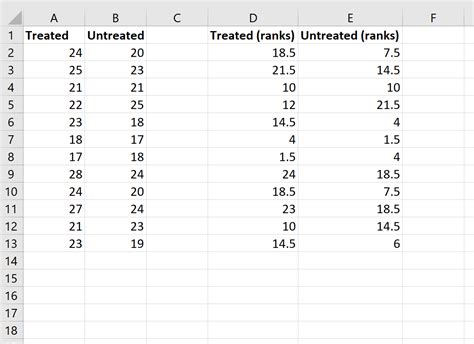
- Prepare your data: Ensure your data is organized in two separate columns, each representing one of the groups you want to compare.
- Choose the right tool: Since Excel doesn't have a built-in Mann Whitney U test function, you'll need to use the "Real Statistics" add-in or the "XLSTAT" software. For this example, we'll use the Real Statistics add-in.
- Install the Real Statistics add-in: If you haven't already, download and install the Real Statistics add-in from the official website.
- Select the data range: Highlight the data range that includes the two groups you want to compare.
- Go to the Real Statistics tab: Click on the "Real Statistics" tab in the Excel ribbon.
- Select the Mann Whitney U test: Click on the "Non-parametric Tests" dropdown menu and select "Mann Whitney U Test."
- Specify the input range: Enter the input range that includes the two groups you want to compare.
- Specify the group labels: Enter the labels for the two groups.
- Choose the alternative hypothesis: Select the alternative hypothesis (two-tailed or one-tailed).
- Click "OK": Click the "OK" button to run the test.
Interpreting the Results
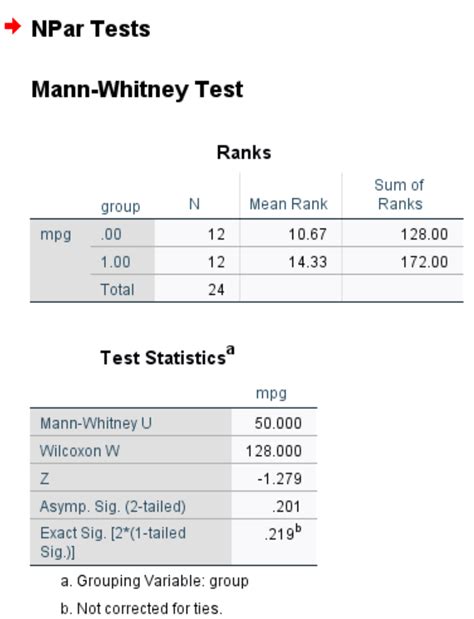
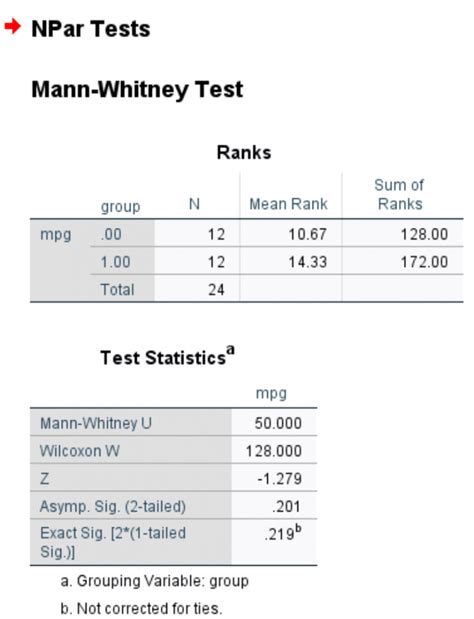
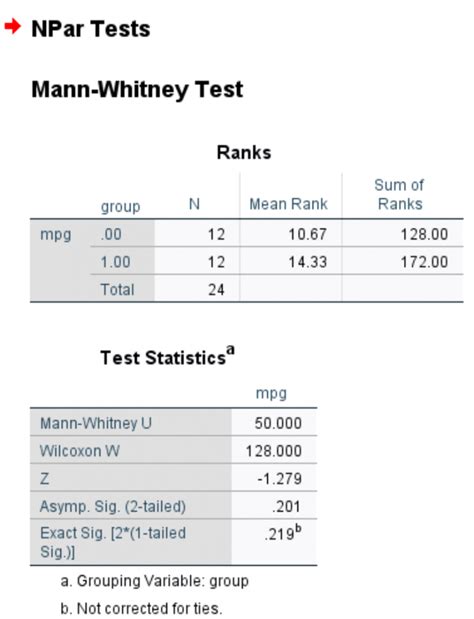
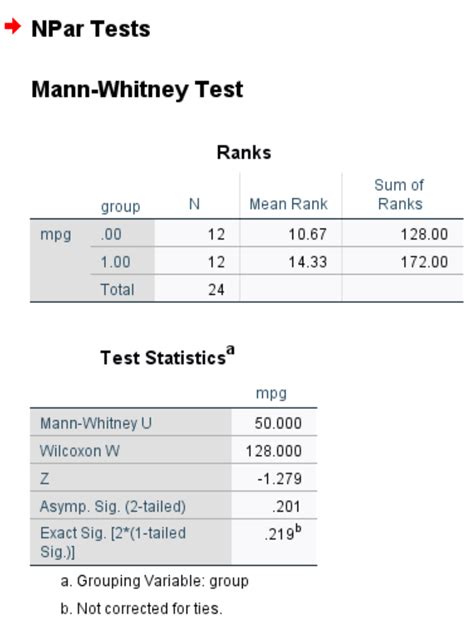
Once you've run the Mann Whitney U test, you'll get a output that includes the following:
- U-statistic: The calculated U-statistic value.
- p-value: The p-value associated with the U-statistic.
- Decision: The decision based on the p-value (reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When performing the Mann Whitney U test in Excel, keep in mind the following common mistakes to avoid:
- Incorrect data formatting: Ensure your data is organized correctly, with each group in a separate column.
- Incorrect choice of alternative hypothesis: Choose the correct alternative hypothesis (two-tailed or one-tailed) based on your research question.
- Ignoring assumptions: While the Mann Whitney U test is robust, it's still essential to check for assumptions such as independence and random sampling.
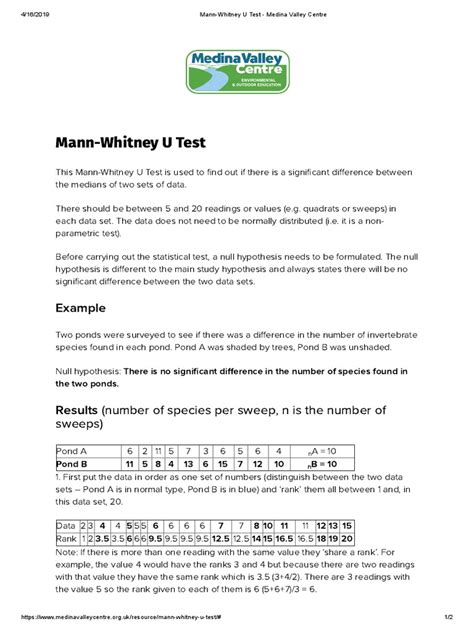
Practical Example: Comparing Exam Scores
Suppose we want to compare the exam scores of two groups of students: those who received additional tutoring and those who didn't. We'll use the Mann Whitney U test to determine if there's a significant difference between the two groups.
Step-by-Step Solution
- Prepare the data: Organize the exam scores in two separate columns, one for each group.
- Choose the right tool: Use the Real Statistics add-in.
- Select the data range: Highlight the data range that includes the two groups.
- Go to the Real Statistics tab: Click on the "Real Statistics" tab in the Excel ribbon.
- Select the Mann Whitney U test: Click on the "Non-parametric Tests" dropdown menu and select "Mann Whitney U Test."
- Specify the input range: Enter the input range that includes the two groups.
- Specify the group labels: Enter the labels for the two groups.
- Choose the alternative hypothesis: Select the two-tailed alternative hypothesis.
- Click "OK": Click the "OK" button to run the test.
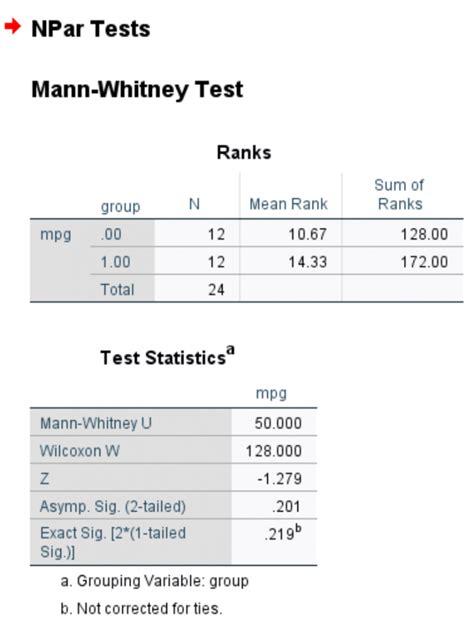
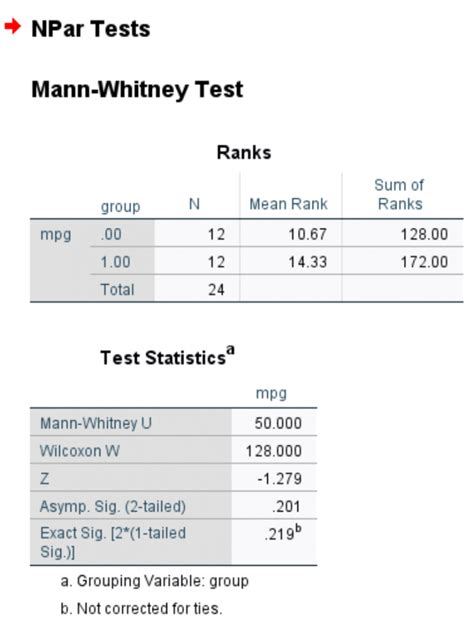
Results
The output shows a U-statistic value of 23.5 and a p-value of 0.012. Since the p-value is less than the significance level (0.05), we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there's a significant difference between the exam scores of the two groups.
Gallery of Mann Whitney U Test Images
Mann Whitney U Test Images

We hope this article has made the Mann Whitney U test in Excel easy to understand and apply. Remember to follow the step-by-step guide and avoid common mistakes. If you have any questions or need further clarification, feel free to ask in the comments below. Happy testing!
