Intro
Discover the exact latitude of North Carolina, a crucial geographic coordinate shaping the states climate, geography, and lifestyle. Learn about North Carolinas latitude range, from its northernmost point to the southernmost tip, and explore how it influences the states regional characteristics, weather patterns, and seasonal variations.
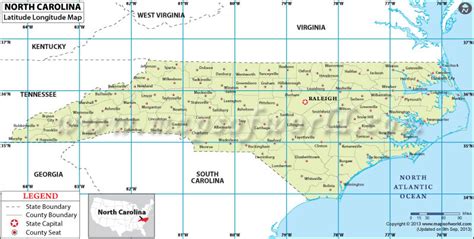
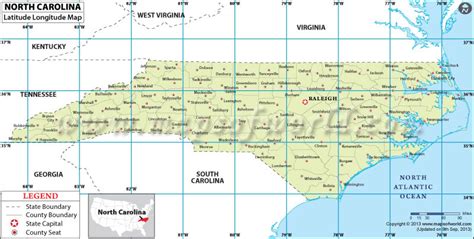
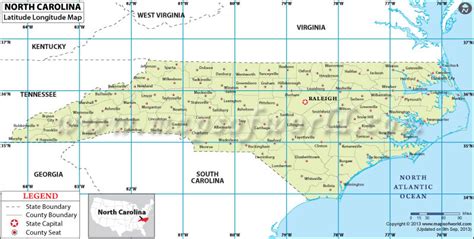
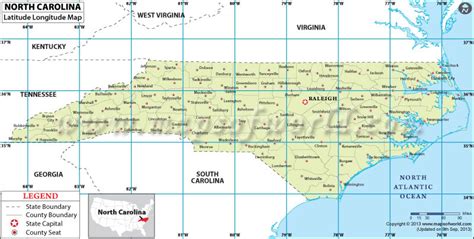
North Carolina, a state located in the southeastern region of the United States, has a unique geography that spans across various latitudes. The state's latitude ranges from approximately 33.8°N to 36.6°N.
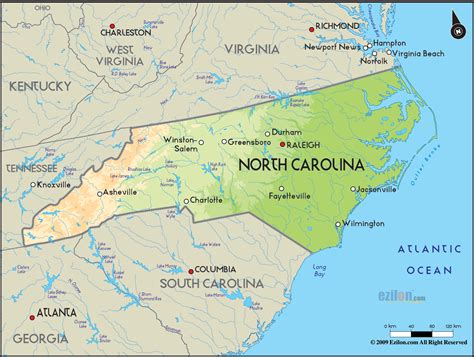
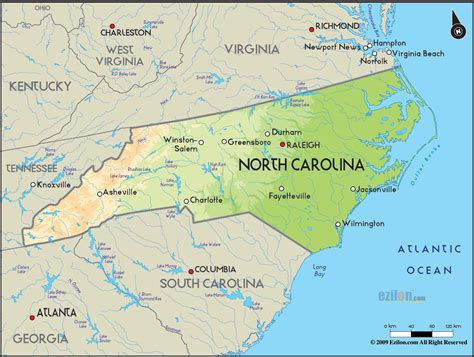
North Carolina's geography is diverse, with the state bordering the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Tennessee and South Carolina to the west and south, and Virginia to the north. The state's latitude plays a significant role in shaping its climate, with the southeastern coast experiencing a humid subtropical climate and the western mountains having a milder climate.
The state's latitude also affects its agriculture, with the eastern coastal plain being suitable for growing crops such as tobacco, cotton, and soybeans, while the western mountains are better suited for growing fruits, vegetables, and livestock.
Understanding North Carolina's latitude is essential for various purposes, including navigation, climate studies, and agriculture. In this article, we will delve deeper into the state's geography, climate, and how its latitude affects its economy and daily life.
Latitude and Geography of North Carolina
North Carolina's latitude is between 33.8°N and 36.6°N, which places it in the southeastern region of the United States. The state's geography is diverse, with the eastern coastal plain, the piedmont region, and the western mountains.
The eastern coastal plain, which borders the Atlantic Ocean, is a low-lying region with a gentle slope. This region is prone to hurricanes and flooding, especially during the summer and fall months. The piedmont region, which lies between the coastal plain and the mountains, is a plateau region with a mix of rolling hills and flat plains.
The western mountains, which include the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Great Smoky Mountains, are the highest region in the state, with peaks reaching elevations of over 6,000 feet. This region is known for its natural beauty, with scenic vistas, waterfalls, and hiking trails.
Effects of Latitude on Climate
North Carolina's latitude has a significant impact on its climate. The state's southeastern coast experiences a humid subtropical climate, with hot summers and mild winters. The western mountains, on the other hand, have a milder climate, with cooler summers and colder winters.
The state's latitude also affects its precipitation patterns, with the western mountains receiving more rainfall than the eastern coastal plain. The state's climate is also influenced by its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean, which moderates temperatures and provides moisture.
Agriculture in North Carolina
North Carolina's latitude and geography make it suitable for growing a variety of crops and livestock. The eastern coastal plain is ideal for growing crops such as tobacco, cotton, and soybeans, while the western mountains are better suited for growing fruits, vegetables, and livestock.
The state's agriculture industry is a significant contributor to its economy, with the state ranking among the top producers of tobacco, sweet potatoes, and Christmas trees. The state's latitude and climate also make it suitable for growing a variety of nursery crops, including flowers, shrubs, and trees.

Latitude and Navigation
Understanding North Carolina's latitude is essential for navigation, whether it's by land, sea, or air. The state's latitude is used to determine its position relative to the equator and the North Pole, which is critical for navigation and mapping.
The state's latitude is also used in aviation, where it's used to determine flight routes and altitudes. The state's latitude is also used in maritime navigation, where it's used to determine ship routes and cargo handling.
Latitude and Climate Change
North Carolina's latitude makes it vulnerable to climate change. Rising temperatures and sea levels are expected to have a significant impact on the state's coastal communities, with increased flooding and erosion expected.
The state's latitude also makes it susceptible to extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and droughts. Understanding the state's latitude and its effects on climate is essential for mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, North Carolina's latitude plays a significant role in shaping its geography, climate, and economy. Understanding the state's latitude is essential for various purposes, including navigation, climate studies, and agriculture.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of North Carolina's latitude and its effects on the state's geography, climate, and economy. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
North Carolina Latitude Image Gallery