The world's reliance on oil has been a cornerstone of modern society, powering vehicles, heating homes, and fueling industries. Despite its ubiquity, there are many fascinating and lesser-known aspects of oil that are worth exploring. From its formation to its uses, the story of oil is complex and multifaceted. As the world continues to grapple with energy demands and environmental concerns, understanding oil is more crucial than ever. In this article, we will delve into the world of oil, uncovering its secrets and shedding light on its significance.
The importance of oil cannot be overstated. It is a vital component of the global economy, influencing everything from transportation to manufacturing. The extraction, refining, and distribution of oil are massive industries that employ millions of people worldwide. Moreover, oil is a key factor in geopolitical relations, with many countries relying heavily on oil exports or imports to sustain their economies. As the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources, the role of oil will continue to evolve, making it essential to understand its current state and future prospects.
The history of oil dates back thousands of years, with ancient civilizations using it for various purposes, including medicinal and lighting applications. However, it wasn't until the late 19th century that oil began to be extracted and refined on a large scale. The discovery of oil in Pennsylvania in 1859 marked the beginning of the modern oil industry, which rapidly expanded across the globe. Today, oil is extracted from numerous sources, including onshore and offshore fields, and is refined into a wide range of products, from gasoline and diesel to plastics and fertilizers.
Formation of Oil
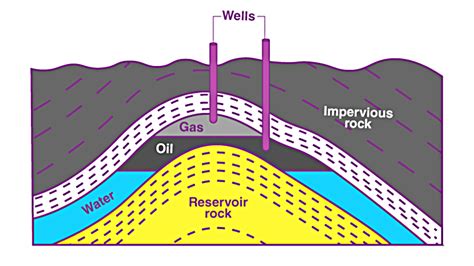
The formation of oil is a complex process that involves the transformation of organic matter over millions of years. It begins with the accumulation of plant and animal remains in marine environments, such as oceans and lakes. As these organisms die and sink to the bottom, they are buried by layers of sediment, protecting them from oxygen and allowing them to undergo a process called diagenesis. During this stage, the organic matter is subjected to increasing heat and pressure, causing it to break down into a waxy substance called kerogen. Over time, the kerogen is further transformed into liquid and gaseous hydrocarbons, which eventually migrate through porous rock formations and accumulate in reservoirs, forming oil fields.
Types of Oil
There are several types of oil, each with its unique characteristics and uses. Crude oil, also known as petroleum, is the raw material extracted from the ground. It is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, which are separated into various fractions during the refining process. These fractions include gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, and heavy fuel oil, among others. In addition to crude oil, there are also synthetic oils, such as lubricants and plastics, which are manufactured from petroleum-based feedstocks. Bio-oils, derived from organic materials like plants and algae, are another type of oil that is gaining attention as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Oil Extraction and Refining
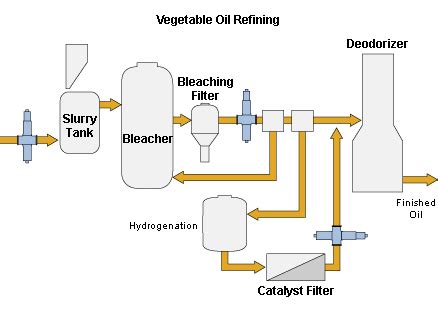
The extraction of oil involves several techniques, including drilling, completion, and production. Drilling is the process of creating a wellbore into the reservoir, while completion involves preparing the well for production. Once the well is producing, the oil is transported to a refinery, where it is processed into various products. Refining involves a series of physical and chemical transformations, including separation, conversion, and purification. The goal of refining is to produce high-quality products that meet specific standards and specifications.
Uses of Oil
Oil is an incredibly versatile substance, with a wide range of applications. The most obvious use of oil is as a fuel source, powering vehicles, airplanes, and industrial processes. However, oil is also used in the production of plastics, fertilizers, and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, oil is used in the manufacturing of cosmetics, detergents, and lubricants. In some parts of the world, oil is even used as a source of electricity, particularly in areas where other forms of energy are scarce.
Environmental Impact of Oil
The extraction, transportation, and use of oil have significant environmental implications. Oil spills, which can occur during drilling, transportation, or storage, can devastate ecosystems and harm wildlife. The refining process also releases pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and particulate matter, into the air. Furthermore, the combustion of oil products releases greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. As the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources, it is essential to mitigate the environmental impact of oil and develop more sustainable practices.
Future of Oil
The future of oil is uncertain, as the world grapples with energy demands, environmental concerns, and geopolitical tensions. As renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, become increasingly cost-competitive, the demand for oil is likely to decline. However, oil will continue to play a significant role in the global energy mix, particularly in the transportation sector. To ensure a sustainable future, it is essential to develop more efficient extraction and refining technologies, reduce waste and emissions, and invest in alternative energy sources.
Gallery of Oil-Related Images
As we conclude our exploration of the world of oil, it is clear that this complex and multifaceted substance will continue to play a significant role in shaping our world. Whether you are an industry expert or simply a curious reader, understanding the intricacies of oil is essential for navigating the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. We invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, and join the conversation about the future of oil and its impact on our planet. Together, we can work towards a more sustainable and energy-secure future for all.