Intro
Discover alternative words for thrust and elevate your writing. Learn 7 synonyms for thrust, including push, drive, propel, boost, urge, jolt, and impel, each with nuanced meanings. Expand your vocabulary and enhance your descriptive language with these LSI keywords, perfect for writers, marketers, and communicators seeking to add depth and precision to their words.
The concept of thrust is a fundamental aspect of physics and engineering, referring to the force that propels an object forward. However, there are various synonyms and related terms that can be used to describe thrust, depending on the context and application. Here, we'll explore 7 other words for thrust, shedding light on their meanings, usage, and examples.
Understanding Thrust and Its Alternatives
Thrust is a term commonly used in physics, aerospace, and engineering to describe the forward force that propels an object, such as a rocket, aircraft, or boat. However, there are other words that can be used to convey the same idea, each with its own nuances and connotations.
1. Propulsion
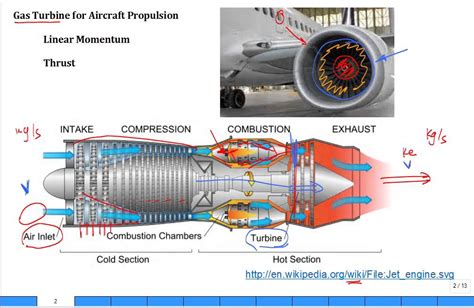
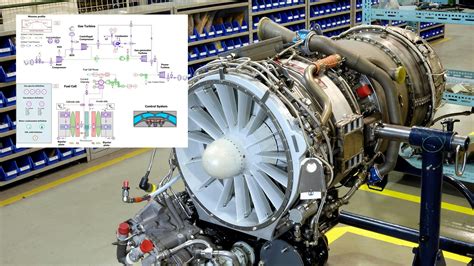
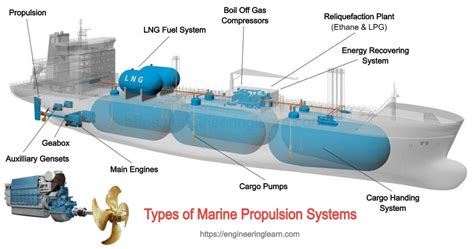
Propulsion refers to the act of propelling or driving an object forward, often using a combination of forces, such as thrust, drag, and lift. In the context of space exploration, propulsion systems are designed to provide the necessary thrust to overcome the forces of gravity and propel a spacecraft forward.
Example: "The new propulsion system used in the spacecraft enabled it to reach unprecedented speeds."
2. Drive
Drive refers to the force or energy that propels an object forward, often used in the context of machinery or engines. In this sense, drive is similar to thrust, but with a greater emphasis on the energy or power behind the motion.
Example: "The engine's drive system enabled it to haul heavy loads up steep inclines."
3. Momentum
Momentum refers to the product of an object's mass and velocity, describing the tendency of an object to maintain its motion. While not exactly synonymous with thrust, momentum is closely related, as an object's momentum is often the result of the thrust applied to it.
Example: "The football player's momentum carried him across the goal line for a touchdown."

4. Impulse
Impulse refers to the sudden, brief application of force that propels an object forward. Impulse is often used in the context of impact or collision, where a sudden force is applied to an object, causing it to change its motion.
Example: "The impulse of the crash propelled the car forward, causing significant damage."
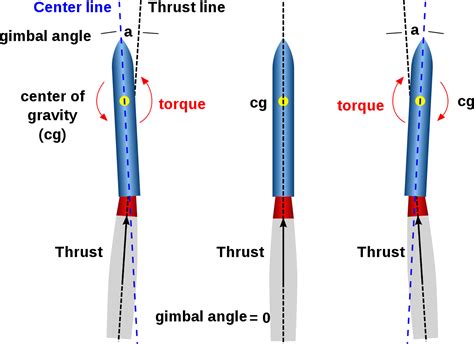
5. Boost
Boost refers to the sudden increase in speed or energy that propels an object forward. Boost is often used in the context of rocketry or aerospace, where a sudden increase in thrust is needed to overcome gravity or achieve orbit.
Example: "The rocket's boost phase enabled it to reach orbit in a matter of minutes."

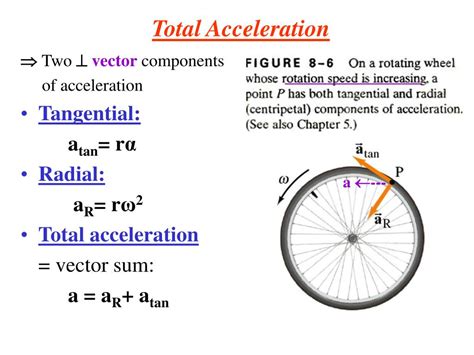
6. Acceleration
Acceleration refers to the rate of change of an object's velocity, describing the force or thrust applied to an object to increase its speed. Acceleration is closely related to thrust, as the force applied to an object determines its acceleration.
Example: "The car's acceleration from 0-60 mph was impressive, thanks to its powerful engine."
7. Force
Force refers to the push or pull that propels an object forward, often used in a broader sense to describe any influence that causes an object to change its motion. While not exclusively synonymous with thrust, force is a fundamental concept in physics that underlies the idea of thrust.
Example: "The force of the wind propelled the sailboat forward, enabling it to reach its destination quickly."
Thrust and Propulsion Systems Image Gallery
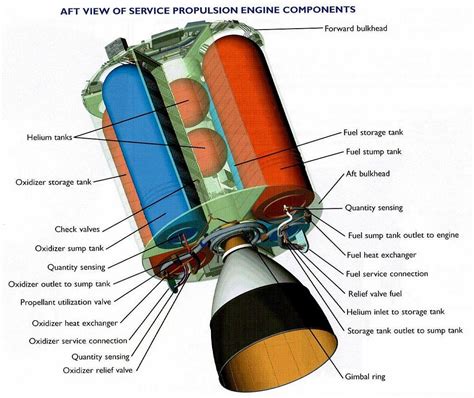
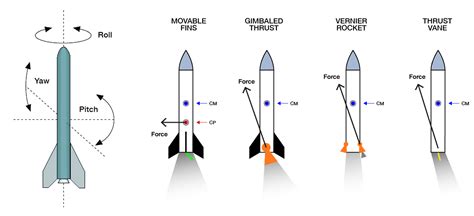



In conclusion, the concept of thrust is a fundamental aspect of physics and engineering, with various synonyms and related terms that can be used to describe the force or energy that propels an object forward. By understanding these alternatives, we can better appreciate the complexities of thrust and its applications in various fields.
