Intro
Discover the population of Canadian provinces in detail, from Alberta to Quebec and beyond. Explore the demographic breakdown, growth rates, and statistics for each province, including Ontario, British Columbia, and the Maritimes. Get insights into Canadas regional population trends, density, and diversity, and learn how they shape the nations economy and society.
The vast and diverse country of Canada is comprised of ten provinces and three territories, each with its unique characteristics, culture, and population dynamics. Understanding the population of Canadian provinces is essential for various reasons, including economic development, resource allocation, and social services planning. In this article, we will delve into a detailed breakdown of the population of Canadian provinces, exploring the trends, demographics, and statistics that shape the country's population landscape.
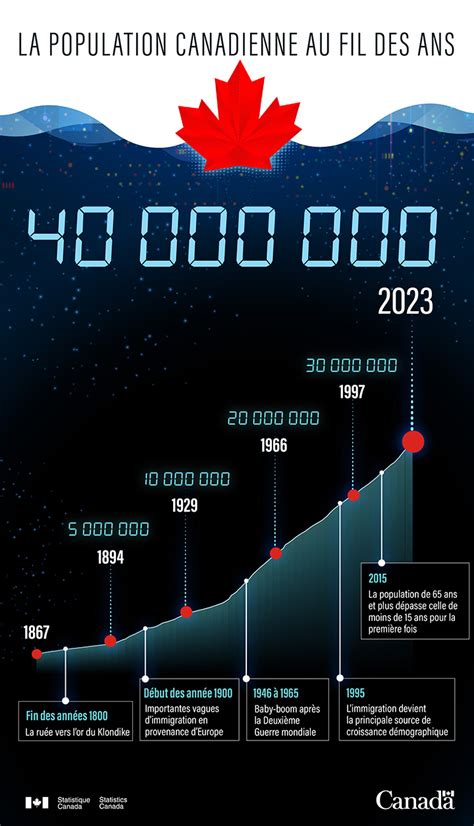
According to the 2020 estimates from Statistics Canada, the country's population stands at approximately 37.7 million people. The population is distributed unevenly across the provinces, with some provinces having a significantly larger population than others. The most populous province, Ontario, accounts for nearly 40% of the country's population, while the least populous province, Prince Edward Island, accounts for less than 1%.
Population Distribution by Province
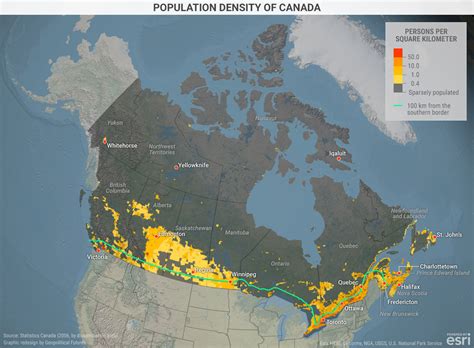
Here is a breakdown of the estimated population of each Canadian province, based on 2020 data from Statistics Canada:
- Ontario: 14,752,995
- Quebec: 8,445,713
- British Columbia: 5,224,115
- Alberta: 4,324,827
- Manitoba: 1,369,331
- Saskatchewan: 1,174,917
- Nova Scotia: 978,790
- New Brunswick: 781,862
- Newfoundland and Labrador: 521,542
- Prince Edward Island: 157,029
Population Growth and Trends
The population of Canadian provinces is influenced by various factors, including natural increase (births minus deaths), migration, and urbanization. Between 2019 and 2020, the population of Canada grew by 1.3%, with the fastest-growing provinces being Ontario, British Columbia, and Alberta.
Urbanization and City Population
Canada is a highly urbanized country, with over 80% of the population living in urban areas. The largest cities in Canada are Toronto, Ontario (2,731,571); Montreal, Quebec (1,704,694); Vancouver, British Columbia (648,477); Calgary, Alberta (632,382); and Ottawa, Ontario (983,833).

Aging Population and Demographics
Canada's population is aging, with the median age increasing from 41.9 years in 2016 to 42.4 years in 2020. The proportion of seniors (65 years and older) in the population is also increasing, with significant implications for healthcare, social services, and pension systems.

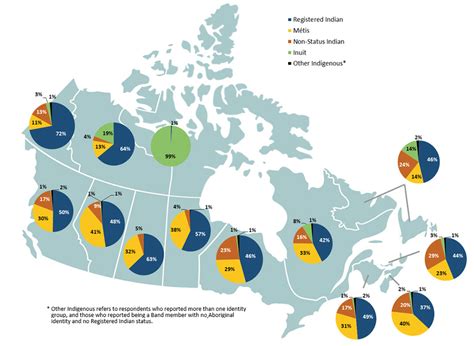
Indigenous Population
Canada's Indigenous population, including First Nations, Métis, and Inuit, accounts for approximately 4.9% of the country's population. The Indigenous population is younger than the non-Indigenous population, with a median age of 26.4 years compared to 42.4 years.
Immigration and Diversity
Canada is a country of immigrants, with over 20% of the population born outside of Canada. The majority of immigrants come from Asia, followed by Europe, Africa, and the Americas. The country's diversity is reflected in the many languages spoken, with over 200 languages spoken across the country.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the population of Canadian provinces is a complex and dynamic phenomenon, influenced by various factors, including natural increase, migration, urbanization, and aging. Understanding the population dynamics of each province is essential for informed decision-making, policy development, and resource allocation. As Canada continues to grow and evolve, it is crucial to monitor and analyze population trends to ensure the country's social, economic, and environmental well-being.
Gallery of Canadian Provinces










We hope you have enjoyed this article on the population of Canadian provinces. Please share your thoughts and comments below, and don't forget to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about Canada's population dynamics.
