Intro
Unlock healthy eating with our printable glycemic index chart! Easily track and manage blood sugar levels with this handy guide. Learn which foods to choose for a balanced diet, and discover low-GI alternatives to your favorite treats. Take control of your nutrition with our comprehensive glycemic index chart and start eating smarter today!
As we navigate the complex world of healthy eating, it's essential to understand the impact of different foods on our blood sugar levels. The Glycemic Index (GI) is a valuable tool that helps us make informed choices about the carbohydrates we consume. In this article, we'll delve into the world of GI, exploring its significance, how it works, and providing a comprehensive Glycemic Index chart printable for your reference.
Understanding the Glycemic Index
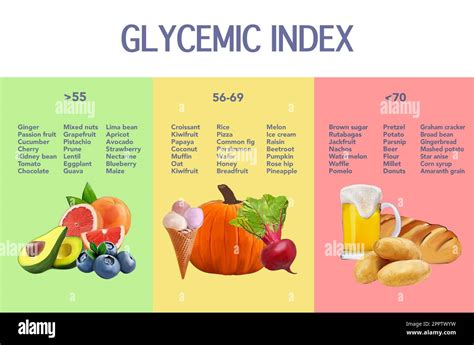
The Glycemic Index is a measure of how quickly the carbohydrates in a particular food raise blood sugar levels. Developed by Dr. David Jenkins in the 1980s, the GI scale ranges from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating a more rapid increase in blood sugar. The GI is calculated by comparing the blood sugar response of a test food to that of pure glucose, which has a GI of 100.
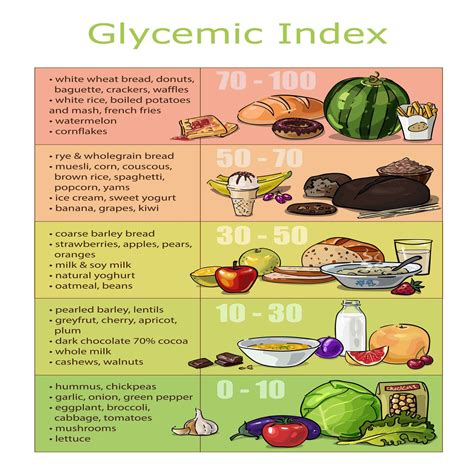
Why is the Glycemic Index Important?
Understanding the GI of different foods can have a significant impact on our overall health and well-being. Here are just a few reasons why:
- Blood Sugar Control: By choosing low-GI foods, individuals with diabetes or prediabetes can better manage their blood sugar levels.
- Weight Management: Low-GI foods tend to be more filling, making them a valuable tool for weight loss and maintenance.
- Heart Health: Consuming low-GI foods has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Energy Levels: Low-GI foods can help regulate energy levels, reducing the likelihood of energy crashes and mood swings.
How to Use the Glycemic Index Chart
Now that we've explored the importance of the GI, let's take a look at how to use the chart. Here are some tips:
- Choose Low-GI Foods: Aim for foods with a GI of 55 or less, which are considered low-GI.
- Be Mindful of Portion Sizes: Even low-GI foods can cause a spike in blood sugar if consumed in excess.
- Combine Foods: Pairing low-GI foods with protein or healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels.
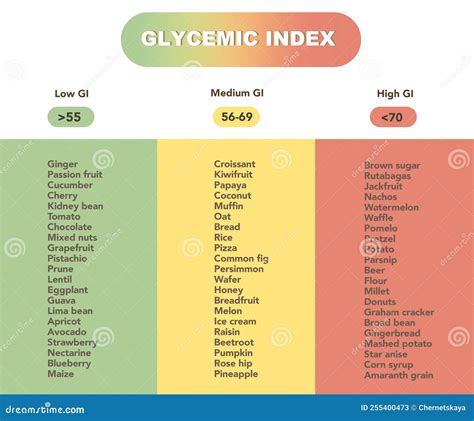
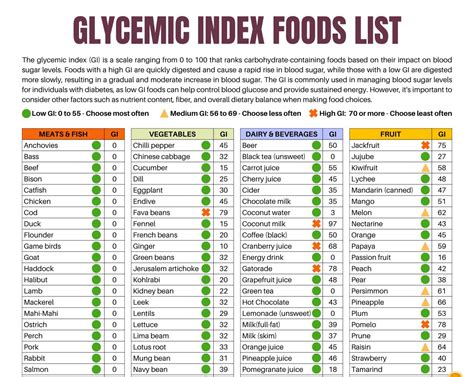
Glycemic Index Chart Printable
Here is a comprehensive Glycemic Index chart printable for your reference:
| Food | Glycemic Index |
|---|---|
| Glucose | 100 |
| White bread | 70 |
| Whole wheat bread | 30 |
| Brown rice | 50 |
| Quinoa | 35 |
| Oats | 40 |
| Sweet potato | 50 |
| Broccoli | 10 |
| Apple | 38 |
| Banana | 42 |
| Carrots | 25 |
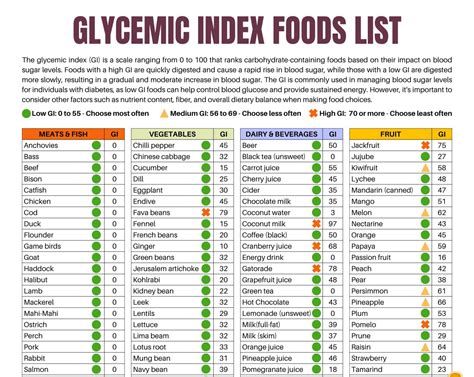
Gallery of Glycemic Index Foods
Glycemic Index Foods Gallery
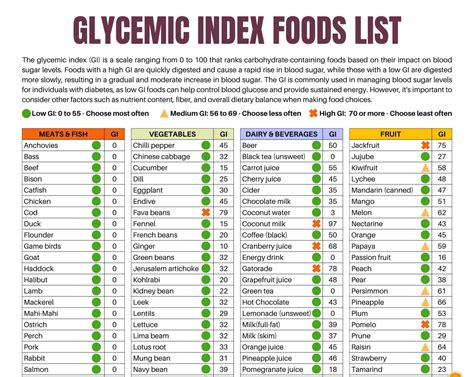






We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the Glycemic Index and its importance in healthy eating. By incorporating the GI chart into your daily meal planning, you'll be well on your way to regulating your blood sugar levels, managing your weight, and maintaining overall health and well-being.
