Intro
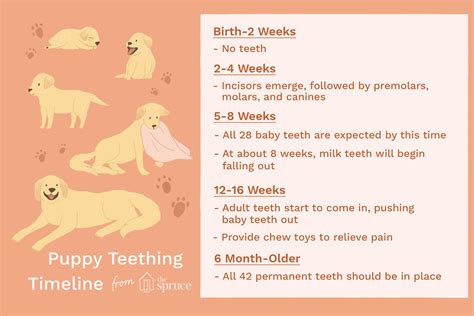
Master the 7 essential stages of puppy teething and track your pups progress. Learn how to identify teething symptoms, soothe pain, and prevent destructive chewing. From baby teeth eruption to teething relief, discover the ultimate guide to a happier, healthier puppy teething experience, ensuring a stronger bond and a lifetime of loving companionship.
Welcoming a new puppy into your family can be a thrilling experience, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. One of the most critical periods in a puppy's life is teething, which can be a trying time for both the puppy and the owner. As a responsible dog owner, it's essential to understand the different stages of teething to provide your puppy with the necessary care and support. In this article, we'll delve into the 7 essential stages of puppy teething, helping you navigate this critical period with confidence.
Teething is a natural process where puppies lose their baby teeth and develop permanent ones. This process usually starts when the puppy is around 3-4 months old and can last until they are about 6-7 months old. During this period, puppies may exhibit unusual behavior, such as chewing, whining, and irritability, due to the discomfort and pain caused by the teething process.
Understanding the Importance of Teething
Teething is a critical stage in a puppy's development, and it's essential to understand the importance of this process. Teething helps puppies develop their jaw muscles, which are crucial for eating and chewing. It also helps to loosen and remove baby teeth, making way for permanent teeth to grow. Moreover, teething helps puppies learn how to regulate their biting and chewing, which is vital for their social and emotional development.
Stage 1: Incisors (3-4 months)
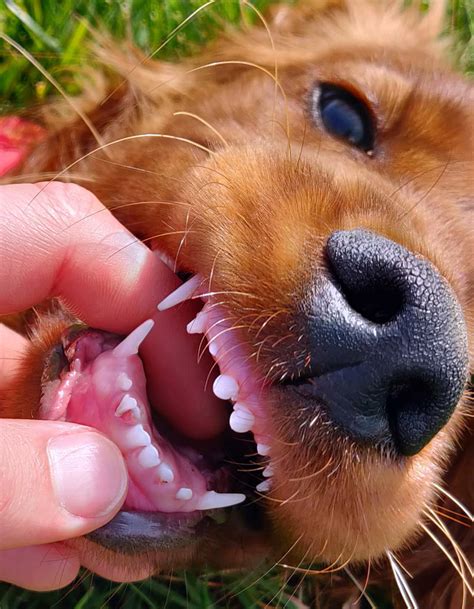

The first stage of teething begins when the puppy is around 3-4 months old. During this stage, the incisors, which are the front teeth, start to erupt. This can be a painful process, and puppies may exhibit unusual behavior, such as chewing on furniture or whining. As the incisors erupt, puppies may start to drool and may have a decreased appetite.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Drooling
- Decreased appetite
- Chewing on furniture or other objects
- Whining and irritability
Stage 2: Canines (4-5 months)

The second stage of teething begins when the puppy is around 4-5 months old. During this stage, the canines, which are the pointed teeth on either side of the incisors, start to erupt. This stage can be more painful than the first stage, and puppies may exhibit more intense behavior, such as chewing on hard objects or biting.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Increased chewing on hard objects
- Biting and nipping
- Whining and irritability
- Swelling of the gums
Stage 3: Premolars (5-6 months)
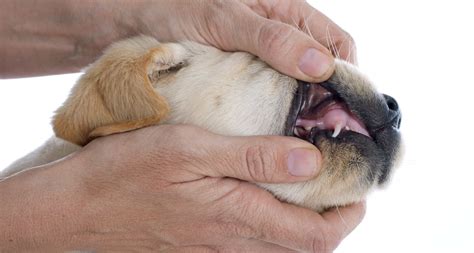
The third stage of teething begins when the puppy is around 5-6 months old. During this stage, the premolars, which are the teeth behind the canines, start to erupt. This stage can be less painful than the previous stages, and puppies may start to exhibit more normal behavior.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Decreased chewing on hard objects
- Less whining and irritability
- Increased appetite
Stage 4: Molars (6-7 months)
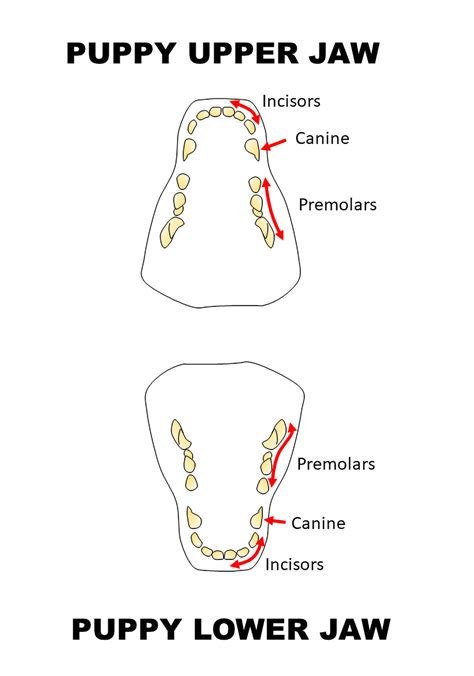
The fourth stage of teething begins when the puppy is around 6-7 months old. During this stage, the molars, which are the back teeth, start to erupt. This stage can be less painful than the previous stages, and puppies may start to exhibit more normal behavior.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Decreased chewing on hard objects
- Less whining and irritability
- Increased appetite
Stage 5: Losing Baby Teeth (6-7 months)

The fifth stage of teething begins when the puppy is around 6-7 months old. During this stage, the baby teeth start to fall out, making way for the permanent teeth to grow. This stage can be less painful than the previous stages, and puppies may start to exhibit more normal behavior.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Baby teeth falling out
- Increased appetite
- Less whining and irritability
Stage 6: Permanent Teeth (7-8 months)

The sixth stage of teething begins when the puppy is around 7-8 months old. During this stage, the permanent teeth start to grow, replacing the baby teeth. This stage can be less painful than the previous stages, and puppies may start to exhibit more normal behavior.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Permanent teeth growing
- Increased appetite
- Less whining and irritability
Stage 7: Complete Teething (8-10 months)

The seventh and final stage of teething begins when the puppy is around 8-10 months old. During this stage, the teething process is complete, and the puppy has a full set of permanent teeth. This stage marks the end of the teething process, and puppies may start to exhibit more normal behavior.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Complete set of permanent teeth
- Increased appetite
- Less whining and irritability
Puppy Teething Gallery
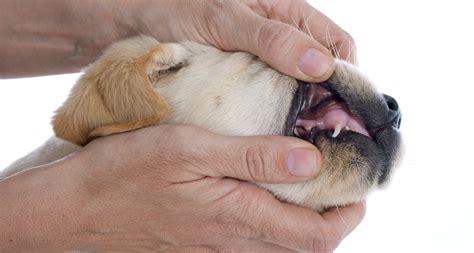





In conclusion, tracking your puppy's teething is essential to provide them with the necessary care and support during this critical period. By understanding the 7 essential stages of puppy teething, you can help your puppy navigate this process with confidence. Remember to be patient, provide plenty of chew toys, and offer lots of love and affection to your puppy during this time.
We hope you found this article informative and helpful. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
