Intro
Discover 5 ways rock weakens, including weathering, erosion, and human impact, affecting geological formations and landscapes through fragmentation, decomposition, and structural damage.
The world of geology is fascinating, with its diverse range of rocks and minerals that make up our planet. Among these, rocks are classified into three main types: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Each type has its unique characteristics, formation processes, and weaknesses. Understanding the weaknesses of rocks is crucial in various fields, including construction, mining, and environmental science. In this article, we will delve into the concept of rock weakness, exploring five ways in which rocks can be weak, and discuss their implications.
Rocks are the building blocks of our planet, and their strength and durability are essential for supporting the structures we build, from houses to skyscrapers. However, rocks are not invincible, and they can be susceptible to various types of weaknesses. These weaknesses can be due to their composition, structure, or the processes they undergo. By understanding these weaknesses, we can better appreciate the complexities of geology and the importance of careful planning and management in construction and other activities that involve rocks.
The study of rock weaknesses is also crucial for environmental scientists, who seek to understand the impact of human activities on the natural world. Rocks play a vital role in shaping our landscape, and their weaknesses can affect the stability of soil, the flow of water, and the formation of natural hazards such as landslides and earthquakes. By recognizing the weaknesses of rocks, we can take steps to mitigate these risks and protect our environment. In the following sections, we will explore five ways in which rocks can be weak, and discuss their implications for construction, mining, and environmental science.
Introduction to Rock Weakness
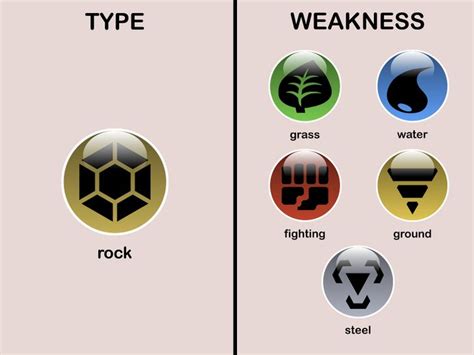
Rock weakness refers to the susceptibility of rocks to deformation, fracture, or failure under stress. This can be due to various factors, including their mineral composition, grain size, and structural defects. Rocks can be weak due to their inherent properties or as a result of external factors such as weathering, erosion, or tectonic activity. Understanding rock weakness is essential for predicting the behavior of rocks in different situations and for developing strategies to mitigate their weaknesses.
Types of Rock Weakness
There are several types of rock weakness, including mechanical weakness, chemical weakness, and thermal weakness. Mechanical weakness refers to the susceptibility of rocks to deformation or fracture under mechanical stress. Chemical weakness refers to the susceptibility of rocks to chemical alteration or reaction, which can lead to changes in their composition or structure. Thermal weakness refers to the susceptibility of rocks to thermal stress, which can cause them to expand, contract, or undergo phase changes.
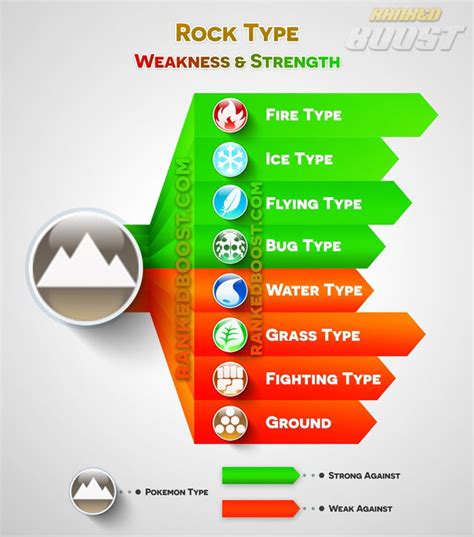
Mechanical Weakness
Mechanical weakness is one of the most common types of rock weakness. It can be due to various factors, including the mineral composition of the rock, its grain size, and the presence of structural defects such as fractures or faults. Rocks with high concentrations of soft minerals such as clay or shale are more susceptible to mechanical weakness than those with high concentrations of hard minerals such as quartz or feldspar.Causes of Rock Weakness
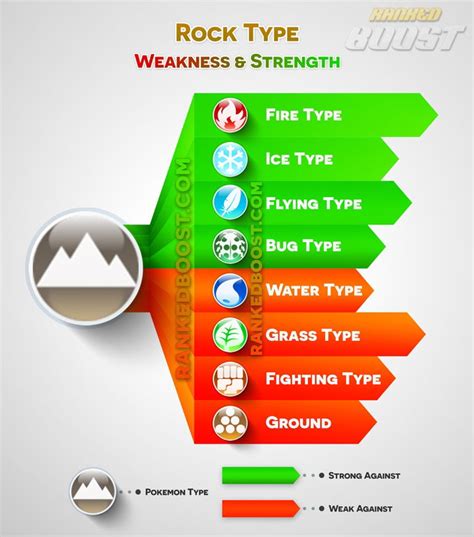
There are several causes of rock weakness, including weathering, erosion, and tectonic activity. Weathering refers to the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles through exposure to wind, water, ice, or temperature fluctuations. Erosion refers to the removal of rocks or soil through the action of wind, water, or ice. Tectonic activity refers to the movement of the Earth's crust, which can cause rocks to deform, fracture, or undergo metamorphism.
Weathering and Erosion
Weathering and erosion are two of the most significant causes of rock weakness. They can break down rocks into smaller particles, reducing their strength and stability. Weathering can occur through mechanical or chemical processes, including thermal expansion, freeze-thaw cycles, and chemical reactions with water or air. Erosion can occur through the action of wind, water, or ice, which can remove rocks or soil and transport them to new locations.5 Ways Rock Weak

Now that we have discussed the concept of rock weakness and its causes, let us explore five ways in which rocks can be weak. These include:
- Mechanical weakness due to structural defects or mineral composition
- Chemical weakness due to reaction with water or air
- Thermal weakness due to expansion or contraction
- Biological weakness due to the action of living organisms
- Geological weakness due to tectonic activity or metamorphism
Biological Weakness
Biological weakness refers to the susceptibility of rocks to the action of living organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms. This can occur through mechanical or chemical processes, including root growth, burrowing, or metabolic activity. Biological weakness can be significant in certain environments, such as soil or sediment, where living organisms are abundant and active.Implications of Rock Weakness

The implications of rock weakness are significant, and can affect various aspects of our lives, including construction, mining, and environmental science. In construction, rock weakness can affect the stability of buildings or infrastructure, leading to structural failure or collapse. In mining, rock weakness can affect the safety of mines, leading to accidents or injuries. In environmental science, rock weakness can affect the stability of soil or slopes, leading to landslides or erosion.
Environmental Implications
The environmental implications of rock weakness are significant, and can affect the stability of ecosystems and the health of living organisms. Rock weakness can lead to the release of pollutants or toxic substances, which can contaminate soil, water, or air. It can also affect the habitat of living organisms, leading to changes in population dynamics or community composition.Gallery of Rock Weakness
Rock Weakness Image Gallery


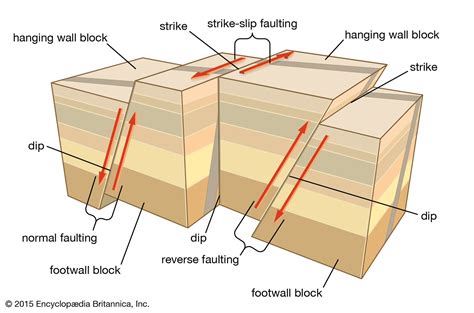

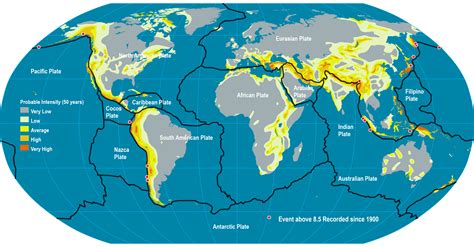
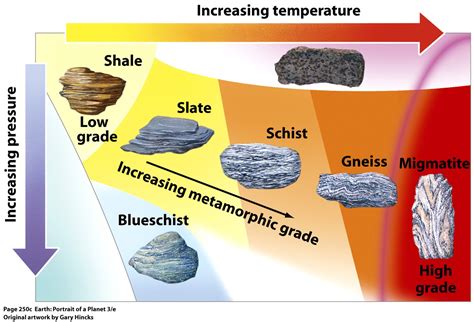
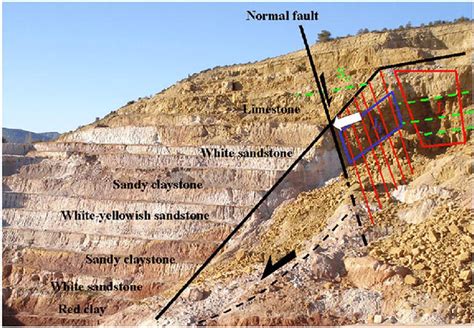

In conclusion, rock weakness is a complex and multifaceted concept that can have significant implications for construction, mining, and environmental science. By understanding the causes and types of rock weakness, we can develop strategies to mitigate their effects and promote stability and safety in our built environment. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of rock weakness and its implications, and we invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this topic. Please feel free to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about rock weakness and its significance.
