Intro
Unlock the power of Excel VBA with expert techniques for mastering sheet name manipulation. Learn how to automate tasks, optimize workflows, and boost productivity using VBA coding. Discover how to create dynamic sheet names, handle errors, and streamline your spreadsheet management with ease. Master Excel VBA sheet name techniques and take your skills to the next level.
Excel VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a powerful tool that can help you automate tasks, create custom functions, and manipulate data in your spreadsheets. One of the most fundamental aspects of working with Excel VBA is mastering sheet name techniques. In this article, we will delve into the world of sheet name VBA techniques, exploring the different methods, best practices, and examples to help you become proficient in this area.
The Importance of Sheet Name VBA Techniques
Sheet names are a crucial part of any Excel spreadsheet. They help you identify and organize your worksheets, making it easier to navigate and manage your data. However, working with sheet names in VBA can be tricky, especially when dealing with multiple sheets, renaming sheets, or referencing specific sheets in your code. Mastering sheet name VBA techniques will enable you to write more efficient, readable, and maintainable code.
Understanding Sheet Name VBA Syntax
Before we dive into the techniques, let's take a look at the basic syntax for referencing a sheet in VBA. The most common way to reference a sheet is by using the Worksheets collection, followed by the sheet name or index number.
Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1")
In this example, Worksheets is the collection of all worksheets in the active workbook, "Sheet1" is the name of the sheet, and Range("A1") is the specific range we want to reference.
Technique 1: Referencing Sheets by Name
Referencing sheets by name is a straightforward approach. Simply use the Worksheets collection and specify the sheet name in quotes.
Sub ReferenceSheetByName()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets("Sheet1")
ws.Range("A1").Value = "Hello World"
End Sub
Technique 2: Referencing Sheets by Index
Referencing sheets by index is useful when you don't know the sheet name or when working with multiple sheets. You can use the Worksheets collection and specify the index number of the sheet.
Sub ReferenceSheetByIndex()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets(1)
ws.Range("A1").Value = "Hello World"
End Sub
Technique 3: Referencing Sheets by CodeName
Each sheet in an Excel workbook has a unique code name that can be used to reference the sheet in VBA. The code name is not the same as the sheet name and is usually set to Sheet1, Sheet2, etc. when a new sheet is created.
Sub ReferenceSheetByCodeName()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Sheet1
ws.Range("A1").Value = "Hello World"
End Sub
Technique 4: Looping Through Sheets
Looping through sheets is a powerful technique that allows you to perform actions on multiple sheets. You can use the For Each loop to iterate through the Worksheets collection.
Sub LoopThroughSheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In Worksheets
ws.Range("A1").Value = "Hello World"
Next ws
End Sub
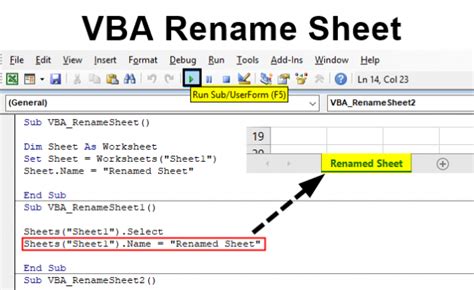
Technique 5: Renaming Sheets
Renaming sheets is a common task in Excel VBA. You can use the Name property to rename a sheet.
Sub RenameSheet()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Name = "MyNewSheet"
End Sub
Technique 6: Copying and Moving Sheets
Copying and moving sheets is another essential technique in Excel VBA. You can use the Copy and Move methods to perform these actions.
Sub CopyAndMoveSheets()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Copy Before:=Worksheets("Sheet2")
Worksheets("Sheet1").Move After:=Worksheets("Sheet3")
End Sub
Technique 7: Deleting Sheets
Deleting sheets is a straightforward technique that can be performed using the Delete method.
Sub DeleteSheet()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Delete
End Sub
Best Practices and Tips
- Always use the
Worksheetscollection to reference sheets, rather than theSheetscollection. - Use meaningful and descriptive sheet names to make your code easier to read and understand.
- Avoid using index numbers to reference sheets, as this can lead to errors if sheets are inserted or deleted.
- Use the
CodeNameproperty to reference sheets that have a unique code name. - Always test your code thoroughly before deploying it to a production environment.
Gallery of Sheet Name VBA Techniques
Sheet Name VBA Techniques Image Gallery





Conclusion
Mastering sheet name VBA techniques is essential for any Excel power user or developer. By following the techniques and best practices outlined in this article, you will be able to write more efficient, readable, and maintainable code. Remember to always test your code thoroughly and use meaningful and descriptive sheet names to make your code easier to read and understand. With practice and patience, you will become proficient in sheet name VBA techniques and take your Excel skills to the next level.
We hope this article has been informative and helpful. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us. Don't forget to share this article with your friends and colleagues who may benefit from it.
