Working with text files is a common task in various fields, and having an efficient way to open them can save a significant amount of time. VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a powerful tool that allows you to automate tasks in Microsoft Office applications, including Excel. In this article, we will explore how to create a VBA macro to open a text file easily.
Why Use VBA to Open a Text File?
Before we dive into the world of VBA macros, let's discuss why you might want to use VBA to open a text file in the first place. Here are a few reasons:
- Efficiency: Opening a text file manually can be a tedious task, especially if you need to open multiple files at once. A VBA macro can automate this process, saving you time and effort.
- Customization: With VBA, you can customize the way you open text files to suit your specific needs. For example, you can create a macro that opens a text file and performs certain actions, such as formatting the text or extracting specific data.
- Integration with Excel: If you work with Excel regularly, creating a VBA macro to open a text file can be a convenient way to integrate text data into your spreadsheets.
How to Create a VBA Macro to Open a Text File
Now that we've discussed the benefits of using VBA to open a text file, let's move on to the step-by-step process of creating a macro.
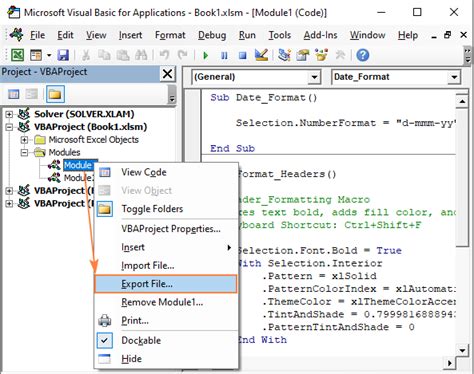
Step 1: Open the Visual Basic Editor
To create a VBA macro, you'll need to open the Visual Basic Editor in Excel. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open your Excel workbook.
- Press
Alt + F11to open the Visual Basic Editor. - Alternatively, you can navigate to
Developer>Visual Basicin the ribbon.
Step 2: Create a New Module
In the Visual Basic Editor, you'll need to create a new module to store your macro. Here's how:
- In the Visual Basic Editor, click
Insert>Modulein the ribbon. - This will create a new module in your workbook.
Step 3: Write the Macro Code
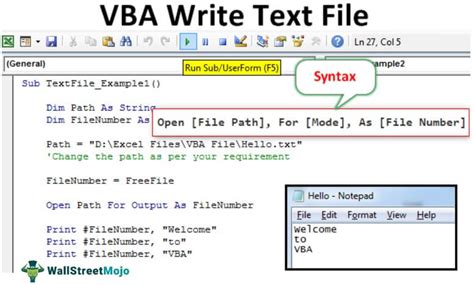
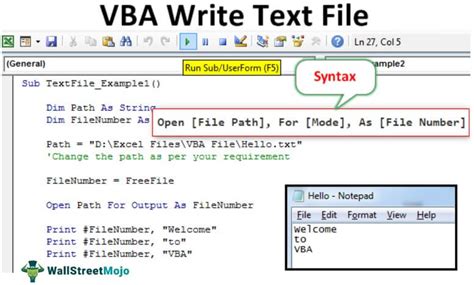
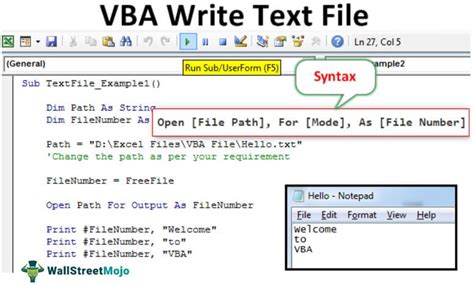
Now it's time to write the macro code. Here's an example code snippet that opens a text file:
Sub OpenTextFile()
Dim filePath As String
filePath = "C:\Path\To\Your\File.txt"
Workbooks.OpenText filePath
End Sub
In this code:
Sub OpenTextFile()declares a new subroutine calledOpenTextFile.Dim filePath As Stringdeclares a variable calledfilePathto store the file path.filePath = "C:\Path\To\Your\File.txt"sets the file path to the desired text file.Workbooks.OpenText filePathopens the text file using theWorkbooks.OpenTextmethod.
Step 4: Run the Macro
To run the macro, follow these steps:
- Click
Developer>Macrosin the ribbon. - Select the
OpenTextFilemacro from the list. - Click
Runto execute the macro.
The text file should now be open in Excel.
Customizing the Macro
The example code snippet above opens a text file using a hardcoded file path. However, you may want to customize the macro to prompt the user for a file path or perform additional actions after opening the file.
Here are some ideas for customizing the macro:
- Prompting the user for a file path: You can use the
Application.GetOpenFilenamemethod to prompt the user for a file path. - Performing additional actions: You can add additional code to the macro to perform actions such as formatting the text or extracting specific data.
Example Code Snippet: Prompting the User for a File Path
Here's an example code snippet that prompts the user for a file path:
Sub OpenTextFile()
Dim filePath As String
filePath = Application.GetOpenFilename("Text Files (*.txt), *.txt")
If filePath <> "" Then
Workbooks.OpenText filePath
Else
MsgBox "No file selected"
End If
End Sub
In this code:
Application.GetOpenFilename("Text Files (*.txt), *.txt")prompts the user to select a text file.If filePath <> "" Thenchecks if a file was selected.Workbooks.OpenText filePathopens the selected file.MsgBox "No file selected"displays a message box if no file was selected.
VBA Macro to Open a Text File Easily Image Gallery

Conclusion
In this article, we explored how to create a VBA macro to open a text file easily. We discussed the benefits of using VBA, the step-by-step process of creating a macro, and how to customize the macro to suit your specific needs. With this knowledge, you can automate tasks and increase efficiency in your work.
We hope this article has been informative and helpful. If you have any questions or need further assistance, please don't hesitate to ask.
