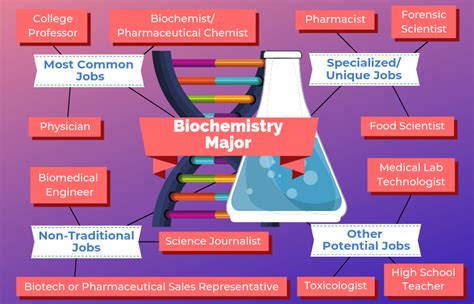
Unlock the molecular secrets of life with biochemists! Discover their key responsibilities, from analyzing biological samples to developing new medicines. Explore the crucial role biochemists play in advancing our understanding of lifes processes, from genetic engineering to forensic science, and uncover the impact of their work on human health and the environment.
As we continue to navigate the complexities of the human body and the world around us, the importance of biochemists in unlocking life's molecular secrets cannot be overstated. Biochemists play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of the intricate relationships between living organisms and their environment. From the intricate dance of molecular interactions to the development of new treatments for diseases, biochemists are at the forefront of some of the most significant scientific breakthroughs of our time.
The work of biochemists is multifaceted and far-reaching, with implications that extend from the smallest molecular structures to the most pressing global health concerns. Whether it's studying the molecular mechanisms underlying disease, developing new diagnostic tools, or exploring the vast potential of biofuels, biochemists are driving innovation and discovery in a wide range of fields. As we delve deeper into the world of biochemistry, it becomes clear that the key responsibilities of biochemists are not only fascinating but also essential to the advancement of human knowledge.
As we explore the intricacies of biochemistry, it's essential to understand the fundamental principles that underlie this field. Biochemistry is the study of the chemical processes that occur within living organisms, from the simplest bacteria to complex systems like the human body. Biochemists use a range of techniques, from molecular biology to analytical chemistry, to investigate the molecular mechanisms that govern life. By understanding these mechanisms, biochemists can identify new targets for disease treatment, develop more effective diagnostic tools, and uncover novel approaches to sustainable energy.
Key Responsibilities of Biochemists

Biochemists have a range of key responsibilities that are critical to advancing our understanding of the molecular world. Some of the most significant responsibilities of biochemists include:
- Conducting research: Biochemists design and conduct experiments to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying biological processes. This involves developing and testing hypotheses, collecting and analyzing data, and interpreting the results.
- Developing new treatments: Biochemists play a crucial role in the development of new treatments for diseases. By understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying disease, biochemists can identify new targets for treatment and develop more effective therapies.
- Analyzing data: Biochemists use a range of techniques, from computational modeling to analytical chemistry, to analyze data and draw conclusions about the molecular mechanisms underlying biological processes.
- Collaborating with other scientists: Biochemists often work in teams with other scientists, including biologists, chemists, and physicists, to advance our understanding of the molecular world.
- Communicating results: Biochemists must communicate their results effectively to other scientists, policymakers, and the general public. This involves writing papers, presenting at conferences, and engaging in public outreach and education.
Specializations within Biochemistry
Biochemistry is a diverse field that encompasses a range of specializations. Some of the most significant specializations within biochemistry include:
- Molecular biology: Molecular biologists study the structure and function of biological molecules, including DNA, RNA, and proteins.
- Biochemical engineering: Biochemical engineers apply the principles of biochemistry to develop new technologies and products, from biofuels to bioproducts.
- Nutritional biochemistry: Nutritional biochemists study the molecular mechanisms underlying nutrition and metabolism, with a focus on developing new approaches to preventing and treating disease.
- Toxicology: Toxicologists study the effects of toxins on living organisms, with a focus on developing new approaches to mitigating the risks associated with toxic substances.
Tools and Techniques of Biochemists

Biochemists use a range of tools and techniques to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying biological processes. Some of the most significant tools and techniques used by biochemists include:
- Spectroscopy: Spectroscopy involves the use of light to investigate the molecular structure of biological molecules.
- Chromatography: Chromatography involves the separation of biological molecules based on their size, charge, or other properties.
- Electrophoresis: Electrophoresis involves the separation of biological molecules based on their size and charge.
- Computational modeling: Computational modeling involves the use of computers to simulate the behavior of biological molecules and systems.
Applications of Biochemistry
Biochemistry has a wide range of applications, from medicine to agriculture to biofuels. Some of the most significant applications of biochemistry include:
- Developing new treatments for disease: Biochemists play a crucial role in the development of new treatments for disease, from antibiotics to vaccines.
- Improving crop yields: Biochemists can improve crop yields by developing new approaches to plant nutrition and disease resistance.
- Developing sustainable energy: Biochemists can develop new approaches to sustainable energy, from biofuels to bioelectricity.
- Monitoring environmental pollution: Biochemists can monitor environmental pollution by developing new approaches to detecting and measuring toxins.
Education and Training for Biochemists

Biochemists typically require a strong foundation in chemistry, biology, and mathematics. A bachelor's degree in biochemistry or a related field is often required for entry-level positions, while advanced degrees may be necessary for more senior roles.
- Bachelor's degree: A bachelor's degree in biochemistry or a related field typically takes four years to complete and provides a foundation in the principles of biochemistry.
- Master's degree: A master's degree in biochemistry or a related field typically takes two to three years to complete and provides advanced training in biochemistry.
- Ph.D.: A Ph.D. in biochemistry or a related field typically takes four to six years to complete and provides advanced training in biochemistry, as well as the opportunity to conduct original research.
Career Prospects for Biochemists
Biochemists have a wide range of career prospects, from academia to industry to government. Some of the most significant career prospects for biochemists include:
- Research scientist: Research scientists conduct experiments and gather data to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying biological processes.
- Clinical biochemist: Clinical biochemists work in hospitals and clinics to develop and implement new diagnostic tests and treatments.
- Biotechnology researcher: Biotechnology researchers develop new products and technologies, from biofuels to bioproducts.
- Science writer: Science writers communicate the results of scientific research to the general public through articles, blogs, and other media.
Challenges Facing Biochemists

Biochemists face a range of challenges, from funding constraints to public skepticism about the value of scientific research. Some of the most significant challenges facing biochemists include:
- Funding constraints: Biochemists often face funding constraints, which can limit the scope and duration of their research.
- Public skepticism: Biochemists may face public skepticism about the value of scientific research, which can make it difficult to secure funding and support.
- Complexity of biological systems: Biological systems are complex and dynamic, making it challenging to understand and predict their behavior.
- Ethical considerations: Biochemists may face ethical considerations, such as the potential risks and benefits of new technologies and treatments.
Future Directions for Biochemistry
Biochemistry is a rapidly evolving field, with new technologies and techniques emerging all the time. Some of the most significant future directions for biochemistry include:
- Synthetic biology: Synthetic biologists design and construct new biological systems, such as genetic circuits and synthetic genomes.
- Systems biology: Systems biologists study the behavior of complex biological systems, from cells to ecosystems.
- Personalized medicine: Personalized medicine involves the use of genetic and molecular information to develop tailored treatments for individual patients.
- Biofuels and bioproducts: Biochemists are developing new approaches to sustainable energy, from biofuels to bioelectricity.
Conclusion
Biochemists play a crucial role in unlocking life's molecular secrets, from the intricate dance of molecular interactions to the development of new treatments for diseases. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the human body and the world around us, the importance of biochemists in advancing our understanding of the molecular world cannot be overstated.
We hope you've enjoyed this article on biochemists and their key responsibilities. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. We'd love to hear from you!
Biochemistry Image Gallery