Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is a serious and complex condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a pattern of alcohol use that leads to significant impairment or distress, and is characterized by symptoms such as excessive drinking, withdrawal, and tolerance. As a healthcare professional, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of AUD, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.

AUD is a significant public health concern, as it can lead to a range of serious health problems, including liver disease, cardiovascular disease, and increased risk of certain cancers. Additionally, AUD can have a profound impact on an individual's relationships, employment, and overall quality of life.
Causes and Risk Factors of AUD
AUD is a complex condition, and there is no single cause or risk factor. However, research has identified several factors that can contribute to the development of AUD, including:
- Genetics: Individuals with a family history of AUD are more likely to develop the condition.
- Brain chemistry: Imbalances in neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin can contribute to AUD.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to trauma, stress, and social and cultural norms that promote drinking can increase the risk of AUD.
- Mental health: Individuals with mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety are more likely to develop AUD.

Genetic Factors
Research has identified several genetic variants that can increase the risk of AUD. For example, individuals with a variant of the DRD2 gene are more likely to develop AUD. Additionally, genetic studies have identified several genetic variants that are associated with an increased risk of AUD in certain populations.
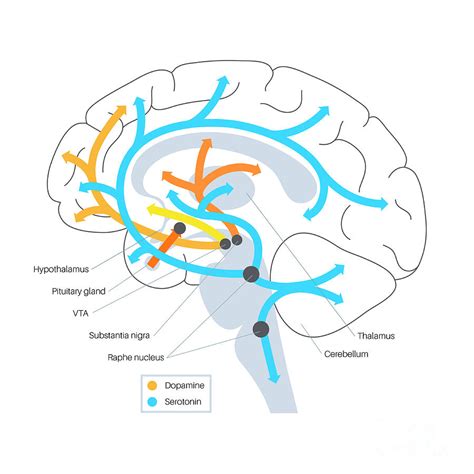
Brain Chemistry and AUD
Imbalances in neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin can contribute to AUD. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is involved in reward processing and motivation, and imbalances in dopamine can lead to increased craving and consumption of alcohol. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is involved in mood regulation, and imbalances in serotonin can lead to increased anxiety and depression.
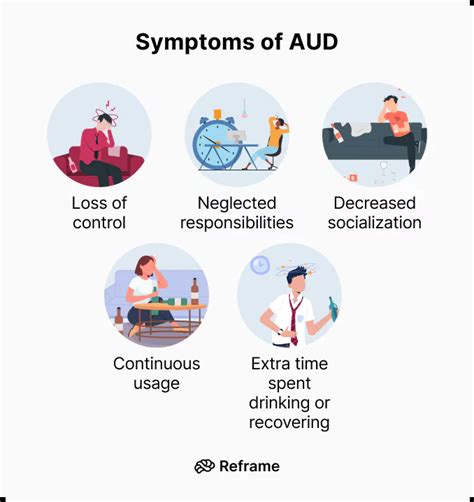
Symptoms of AUD
AUD is characterized by a range of symptoms, including:
- Excessive drinking: Drinking more than intended, or drinking more frequently than intended.
- Withdrawal: Experiencing symptoms such as anxiety, tremors, and seizures when attempting to stop or reduce drinking.
- Tolerance: Needing to drink more to achieve the same effects.
- Neglect of responsibilities: Neglecting responsibilities such as work, school, or family due to drinking.
- Continued use despite consequences: Continuing to drink despite physical or psychological problems.
Assessment and Diagnosis
AUD can be diagnosed using a range of assessment tools, including the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT). A comprehensive assessment should include a physical examination, laboratory tests, and a thorough medical and psychological history.
Treatment Options for AUD
AUD is a treatable condition, and there are several effective treatment options available, including:
- Medications: Medications such as naltrexone, acamprosate, and disulfiram can help to reduce craving and consumption of alcohol.
- Behavioral therapies: Behavioral therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational interviewing (MI) can help to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Support groups: Support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) can provide a sense of community and support for individuals in recovery.

Medications for AUD
Several medications have been approved for the treatment of AUD, including:
- Naltrexone: Naltrexone is a medication that works by blocking the opioid receptors in the brain, reducing the pleasurable effects of drinking.
- Acamprosate: Acamprosate is a medication that works by reducing the symptoms of withdrawal and reducing craving.
- Disulfiram: Disulfiram is a medication that works by causing an unpleasant reaction when alcohol is consumed.

Conclusion
AUD is a complex and serious condition that requires comprehensive treatment and support. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for AUD, healthcare professionals can provide effective care and support for individuals in recovery.
Gallery of AUD










We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of AUD, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. If you or a loved one is struggling with AUD, it is essential to seek professional help and support.
