Measuring vital signs is a fundamental nursing skill that provides essential information about a patient's overall health and well-being. As a nurse, it is crucial to master the techniques of measuring vital signs to accurately assess a patient's condition and make informed decisions about their care. In this article, we will discuss the 7 essential vital signs nursing skills to master.
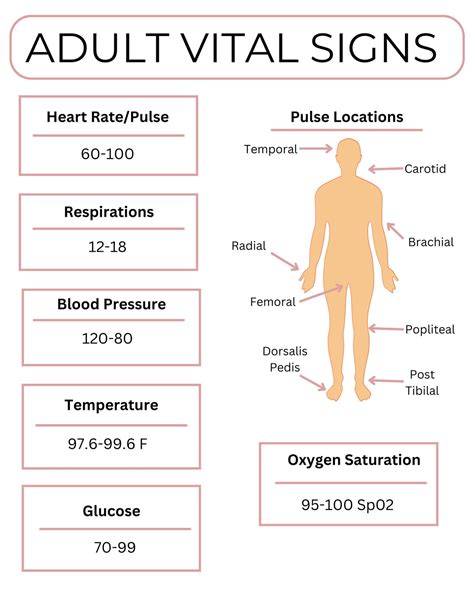
Understanding the Importance of Vital Signs
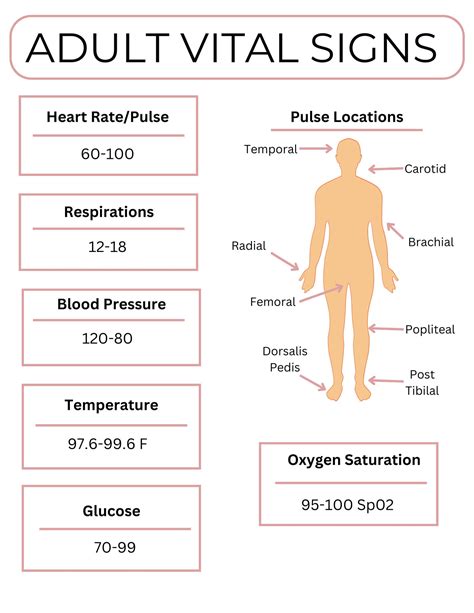
Vital signs are a set of measurements that provide critical information about a patient's physiological state. They are called "vital" because they are essential to life, and changes in these signs can indicate a life-threatening condition. The 7 essential vital signs nursing skills to master are:
1. Temperature Measurement

Temperature measurement is a critical vital sign that indicates the body's core temperature. It is measured using a thermometer, which can be oral, rectal, or tympanic (ear). Accurate temperature measurement is essential to diagnose fever, hypothermia, or other conditions that may affect the body's temperature regulation.
Best Practices for Temperature Measurement
- Use the correct type of thermometer for the patient's condition.
- Ensure the thermometer is calibrated and accurate.
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions for use.
- Take multiple readings to ensure accuracy.
2. Pulse Measurement

Pulse measurement is a vital sign that indicates the heart rate and rhythm. It is measured by palpating the radial artery or using a pulse oximeter. Accurate pulse measurement is essential to diagnose cardiovascular conditions, such as arrhythmias or cardiac arrest.
Best Practices for Pulse Measurement
- Use the correct technique to palpate the radial artery.
- Count the pulse for at least 15 seconds to ensure accuracy.
- Use a pulse oximeter to measure oxygen saturation and heart rate.
- Document any irregularities or abnormalities.
3. Blood Pressure Measurement
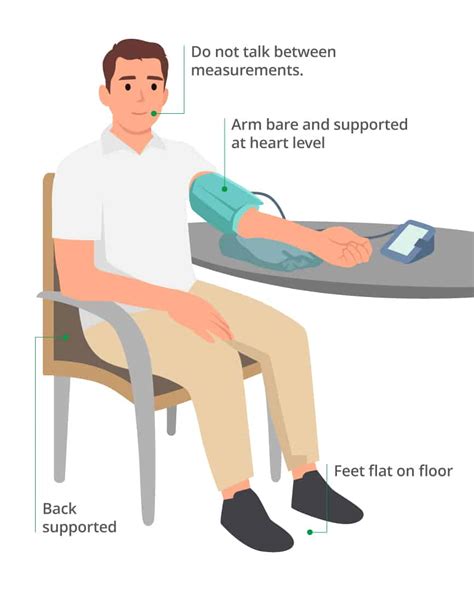
Blood pressure measurement is a vital sign that indicates the force of blood against the arterial walls. It is measured using a sphygmomanometer and a stethoscope. Accurate blood pressure measurement is essential to diagnose hypertension, hypotension, or other cardiovascular conditions.
Best Practices for Blood Pressure Measurement
- Use the correct technique to inflate and deflate the cuff.
- Use a calibrated sphygmomanometer to ensure accuracy.
- Take multiple readings to ensure accuracy.
- Document any irregularities or abnormalities.
4. Respiratory Rate Measurement
Respiratory rate measurement is a vital sign that indicates the number of breaths per minute. It is measured by counting the patient's breaths for a specified time. Accurate respiratory rate measurement is essential to diagnose respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Best Practices for Respiratory Rate Measurement
- Count the patient's breaths for at least 30 seconds to ensure accuracy.
- Use a timer to ensure accuracy.
- Document any irregularities or abnormalities.
- Consider using a pulse oximeter to measure oxygen saturation.
5. Oxygen Saturation Measurement

Oxygen saturation measurement is a vital sign that indicates the amount of oxygen in the blood. It is measured using a pulse oximeter. Accurate oxygen saturation measurement is essential to diagnose respiratory conditions, such as asthma or COPD.
Best Practices for Oxygen Saturation Measurement
- Use a calibrated pulse oximeter to ensure accuracy.
- Take multiple readings to ensure accuracy.
- Document any irregularities or abnormalities.
- Consider using a pulse oximeter with a built-in heart rate monitor.
6. Pain Assessment
Pain assessment is a vital sign that indicates the patient's level of pain or discomfort. It is measured using a standardized pain scale, such as the numeric rating scale (NRS) or the faces pain scale (FPS). Accurate pain assessment is essential to diagnose and manage pain effectively.
Best Practices for Pain Assessment
- Use a standardized pain scale to ensure accuracy.
- Ask the patient to rate their pain on a scale of 0-10.
- Consider using a pain assessment tool, such as a pain questionnaire.
- Document any irregularities or abnormalities.
7. Level of Consciousness Assessment

Level of consciousness assessment is a vital sign that indicates the patient's level of alertness and responsiveness. It is measured using a standardized scale, such as the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). Accurate level of consciousness assessment is essential to diagnose and manage neurological conditions, such as stroke or traumatic brain injury.
Best Practices for Level of Consciousness Assessment
- Use a standardized scale, such as the GCS.
- Assess the patient's eye opening, verbal response, and motor response.
- Document any irregularities or abnormalities.
- Consider using a neurological assessment tool, such as a neurological examination.
Gallery of Vital Signs Nursing Skills
Vital Signs Nursing Skills Image Gallery







Final Thoughts
Mastering the 7 essential vital signs nursing skills is crucial to providing high-quality patient care. By following the best practices outlined in this article, nurses can ensure accurate and reliable vital sign measurements that inform patient care decisions. Remember to practice regularly and seek guidance from experienced nurses or mentors to refine your skills. With dedication and practice, you can become proficient in measuring vital signs and provide exceptional care to your patients.
