Intro
Conducting a thorough physical examination is a crucial aspect of medical practice, allowing healthcare professionals to assess a patient's overall health and identify potential issues. The musculoskeletal (MSK) physical exam is a specialized examination that focuses on the musculoskeletal system, which includes the muscles, bones, joints, and associated structures. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to the MSK physical exam template, including its importance, key components, and step-by-step instructions.
Importance of MSK Physical Exam
The MSK physical exam is an essential tool for healthcare professionals to evaluate and diagnose musculoskeletal disorders, injuries, and conditions. It helps to identify areas of pain, limited mobility, and other abnormalities that may indicate underlying musculoskeletal issues. By conducting a thorough MSK physical exam, healthcare professionals can:
- Develop an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan
- Identify potential causes of pain and discomfort
- Assess the effectiveness of treatment and rehabilitation programs
- Prevent further injury or deterioration of musculoskeletal conditions
MSK Physical Exam Template
The MSK physical exam template typically includes the following key components:
- Patient History: A comprehensive review of the patient's medical history, including previous injuries, surgeries, and medical conditions.
- Visual Inspection: A visual examination of the patient's posture, alignment, and movement patterns.
- Palpation: A hands-on examination of the patient's muscles, bones, and joints to assess for tenderness, swelling, and abnormalities.
- Range of Motion: An assessment of the patient's joint mobility and flexibility.
- Strength Testing: An evaluation of the patient's muscle strength and function.
- Special Tests: A series of specialized tests to assess for specific musculoskeletal conditions or injuries.

Step-by-Step Guide to MSK Physical Exam
The following is a step-by-step guide to conducting a comprehensive MSK physical exam:
Step 1: Patient History
- Review the patient's medical history, including previous injuries, surgeries, and medical conditions.
- Ask the patient to describe their symptoms, including the location, severity, and duration of pain or discomfort.
- Inquire about the patient's occupational and recreational activities to identify potential risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries or conditions.
Key Questions to Ask During Patient History
- What is your chief complaint?
- How long have you been experiencing symptoms?
- What activities exacerbate or relieve your symptoms?
- Have you had any previous injuries or surgeries?

Step 2: Visual Inspection
- Observe the patient's posture, alignment, and movement patterns.
- Look for any visible signs of injury or abnormality, such as swelling, bruising, or deformity.
- Assess the patient's gait and balance.
Key Observations During Visual Inspection
- Posture: Is the patient's posture symmetrical and aligned?
- Alignment: Are the patient's joints and limbs properly aligned?
- Movement patterns: Are the patient's movement patterns smooth and coordinated?

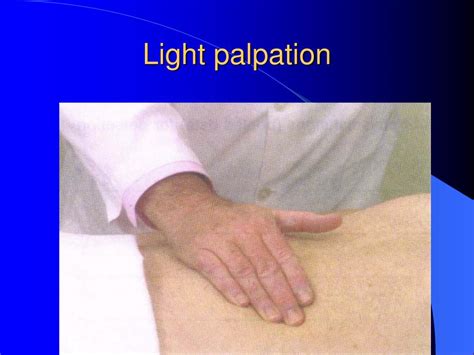
Step 3: Palpation
- Perform a hands-on examination of the patient's muscles, bones, and joints to assess for tenderness, swelling, and abnormalities.
- Use your fingertips to apply gentle pressure to specific areas.
Key Areas to Palpate
- Muscles: Assess for tenderness, spasms, or weakness.
- Bones: Assess for tenderness, swelling, or deformity.
- Joints: Assess for tenderness, swelling, or limited mobility.

Step 4: Range of Motion
- Assess the patient's joint mobility and flexibility.
- Use a goniometer to measure the range of motion in specific joints.
Key Joints to Assess
- Shoulder: Assess flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation.
- Elbow: Assess flexion, extension, and rotation.
- Wrist: Assess flexion, extension, and rotation.

Step 5: Strength Testing
- Evaluate the patient's muscle strength and function.
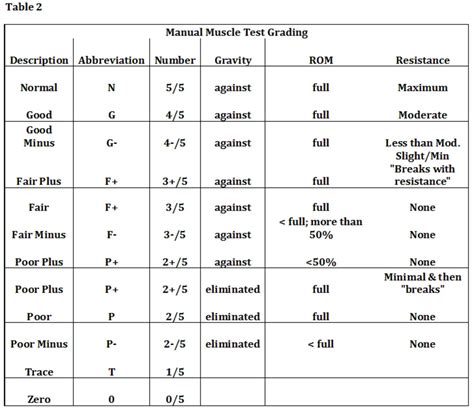
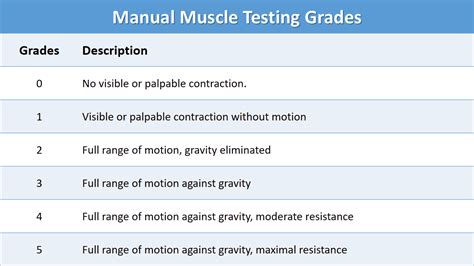
- Use manual muscle testing or dynamometry to assess muscle strength.
Key Muscles to Test
- Shoulder: Assess deltoid, rotator cuff, and scapular muscles.
- Elbow: Assess biceps, triceps, and forearm muscles.
- Wrist: Assess flexor, extensor, and rotational muscles.
Step 6: Special Tests
- Perform specialized tests to assess for specific musculoskeletal conditions or injuries.
- Use tests such as the Lachman test, anterior drawer test, or McMurray test to assess for ligamentous instability or meniscal injuries.
Key Special Tests
- Lachman test: Assess for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) integrity.
- Anterior drawer test: Assess for anterior tibial translation.
- McMurray test: Assess for meniscal injuries.

Gallery of MSK Physical Exam Images
MSK Physical Exam Image Gallery







We hope this comprehensive guide to the MSK physical exam template has been informative and helpful. Remember to always follow a systematic approach when conducting a physical examination, and don't hesitate to ask for help or clarification when needed. By mastering the MSK physical exam, you'll be better equipped to diagnose and treat musculoskeletal disorders, injuries, and conditions.
Call to Action
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with the MSK physical exam template in the comments section below. Have you used this template in your practice? What challenges or successes have you encountered? Your feedback and insights will help us improve and refine this guide for the benefit of all healthcare professionals.
