Intro
Unlock the power of Excel with the Private Sub WorksheetChange event. Learn how to automatically trigger VBA macros when changes occur in a worksheet, improving productivity and streamlining workflows. Discover how to harness this event to detect changes, update values, and more, with expert guidance on Excel VBA programming.
Excel is an incredibly powerful tool for data analysis and manipulation, and one of its most useful features is the ability to create custom macros and event-driven code. One of the most popular and versatile events in Excel is the WorksheetChange event, which allows you to write code that responds to changes made to a worksheet. In this article, we'll take an in-depth look at the WorksheetChange event, how it works, and how you can use it to automate tasks and improve your productivity in Excel.
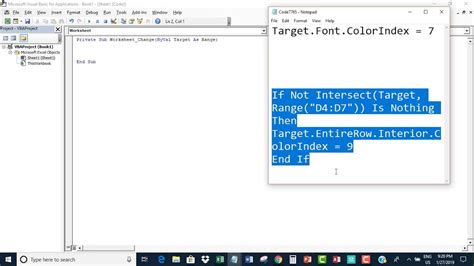
What is the WorksheetChange Event?
The WorksheetChange event is a built-in Excel event that triggers when a change is made to a worksheet. This can include changes to cell values, formatting, or even the insertion or deletion of rows or columns. When the WorksheetChange event is triggered, it runs a macro that can perform a wide range of tasks, from simple formatting changes to complex data analysis and manipulation.
How Does the WorksheetChange Event Work?
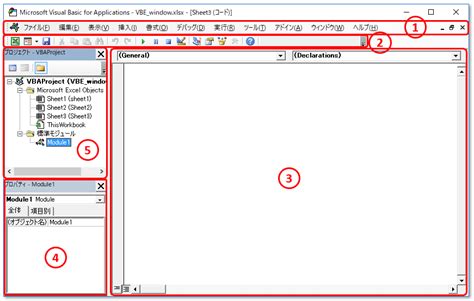
The WorksheetChange event is triggered by changes made to a worksheet, and it runs a macro that is stored in the worksheet's code module. To access the code module, you'll need to open the Visual Basic Editor (VBE) by pressing Alt + F11 or by navigating to the Developer tab in the Excel ribbon.
Once you're in the VBE, you'll see a list of modules and worksheets. To create a WorksheetChange event, you'll need to insert a new module and add the following code:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
' Your code goes here
End Sub
This code sets up the WorksheetChange event and defines the Target range as the cells that were changed. You can then add your own code to the Worksheet_Change event to perform tasks such as formatting changes, data validation, or even sending emails.
Benefits of Using the WorksheetChange Event
The WorksheetChange event offers a wide range of benefits, including:
- Automation: The
WorksheetChangeevent allows you to automate tasks and workflows, freeing up time for more important tasks. - Data validation: You can use the
WorksheetChangeevent to validate data entry and ensure that data is accurate and consistent. - Formatting: The
WorksheetChangeevent can be used to apply formatting changes to cells and ranges, making it easier to visualize data. - Data analysis: You can use the
WorksheetChangeevent to perform complex data analysis and manipulation, such as calculating sums and averages.
Common Uses of the WorksheetChange Event
The WorksheetChange event is commonly used in a wide range of scenarios, including:
- Data entry validation: Use the
WorksheetChangeevent to validate data entry and ensure that data is accurate and consistent. - Automating workflows: Use the
WorksheetChangeevent to automate tasks and workflows, freeing up time for more important tasks. - Formatting changes: Use the
WorksheetChangeevent to apply formatting changes to cells and ranges, making it easier to visualize data. - Data analysis: Use the
WorksheetChangeevent to perform complex data analysis and manipulation, such as calculating sums and averages.

Examples of WorksheetChange Event Code
Here are some examples of WorksheetChange event code:
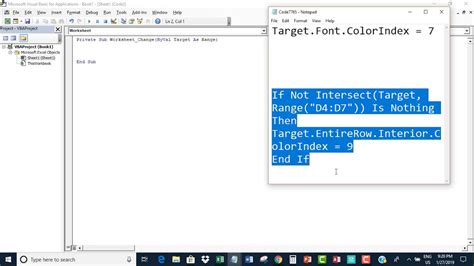
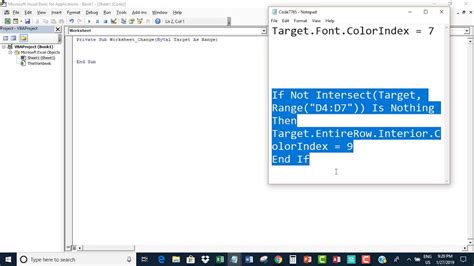
- Simple formatting change:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
If Target.Count = 1 Then
If Target.Value > 10 Then
Target.Font.Color = vbRed
Else
Target.Font.Color = vbBlack
End If
End If
End Sub
- Data validation:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
If Target.Count = 1 Then
If Target.Value < 0 Then
MsgBox "Invalid value", vbExclamation
Target.ClearContents
End If
End If
End Sub
- Automating workflows:
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
If Target.Count = 1 Then
If Target.Value = "Complete" Then
' Send email to manager
Dim olApp As Object
Set olApp = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Dim olMail As Object
Set olMail = olApp.CreateItem(0)
With olMail
.To = "manager@example.com"
.Subject = "Task Complete"
.Body = "Task complete"
.Send
End With
Set olMail = Nothing
Set olApp = Nothing
End If
End If
End Sub
WorksheetChange Event Image Gallery

Conclusion
In conclusion, the WorksheetChange event is a powerful tool in Excel that allows you to automate tasks and workflows, validate data entry, and perform complex data analysis and manipulation. By using the WorksheetChange event, you can improve your productivity and efficiency in Excel, and take your data analysis and manipulation skills to the next level. Whether you're a beginner or an advanced user, the WorksheetChange event is an essential tool to have in your Excel toolkit.
We hope this article has been helpful in explaining the WorksheetChange event and how it can be used in Excel. If you have any questions or need further assistance, please don't hesitate to ask. Happy coding!
