Intro
Unlock the secrets of DNA replication with ATPs unwinding power. Discover the crucial role of enzymes in unwinding DNA templates, enabling genetic material to be accessed and copied. Learn how ATP hydrolysis fuels this process, and explore the intricate mechanisms driving DNA unwinding, helicase activity, and replication initiation.
The process of DNA replication is a complex and highly regulated mechanism that involves the coordinated effort of multiple enzymes. One of the most crucial enzymes involved in this process is ATP (Adenosine triphosphate), which plays a central role in unwinding the DNA template. In this article, we will delve into the world of DNA replication and explore the enzymes crucial role in unwinding the DNA template.
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. This process is essential for the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. The DNA molecule is a double-stranded helix, with each strand composed of nucleotides that are linked together by phosphodiester bonds. The process of DNA replication involves the unwinding of the double helix, followed by the synthesis of new nucleotides to form a complementary copy of the original DNA molecule.
ATP's Role in DNA Replication
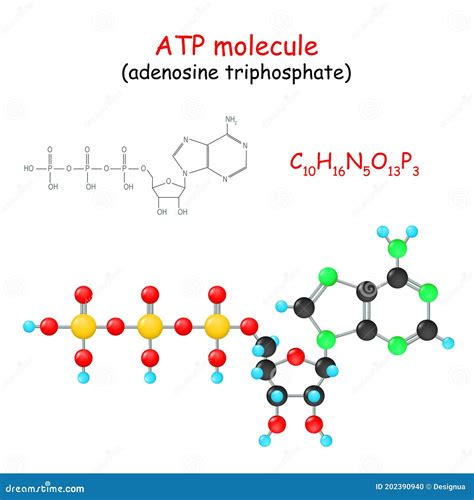
ATP is a molecule that plays a central role in the process of DNA replication. It is a high-energy molecule that is produced during cellular respiration and is used to drive many of the energy-requiring processes that occur within the cell. In the context of DNA replication, ATP is used to provide the energy required to unwind the DNA template.
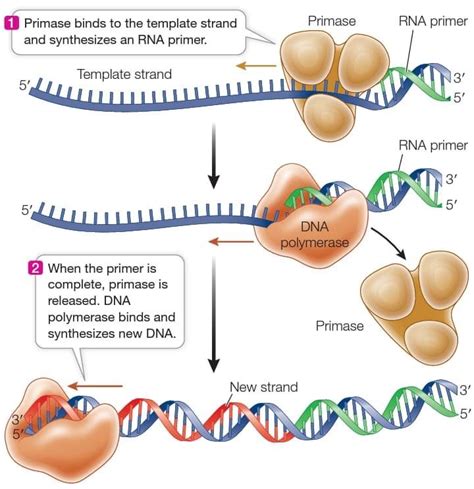
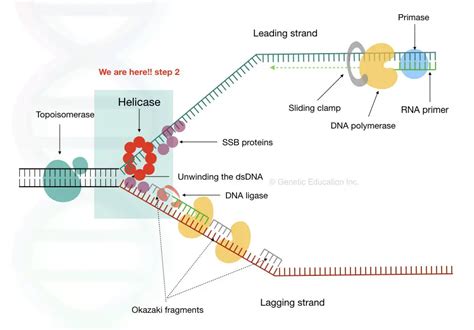
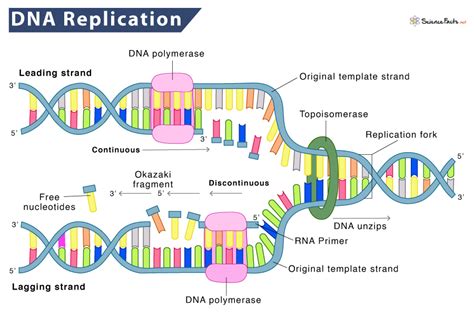
The process of unwinding the DNA template is initiated by an enzyme called helicase. Helicase is an ATP-dependent enzyme that uses the energy from ATP to unwind the double helix. As the helicase enzyme moves along the DNA molecule, it uses the energy from ATP to break the hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides, causing the double helix to unwind.
Helicase Enzyme
The helicase enzyme is a crucial component of the DNA replication process. It is responsible for unwinding the DNA template, allowing the replication machinery to access the template strands. The helicase enzyme is a complex molecule that consists of multiple subunits, each of which plays a specific role in the unwinding process.
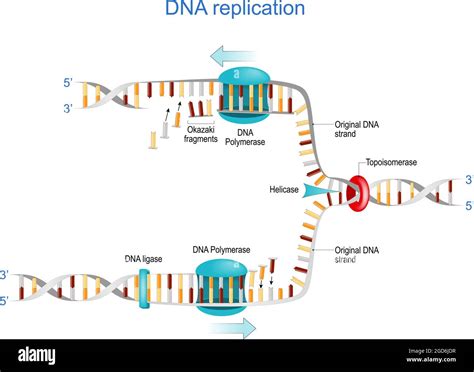
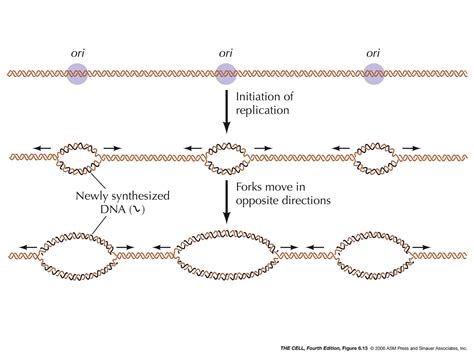
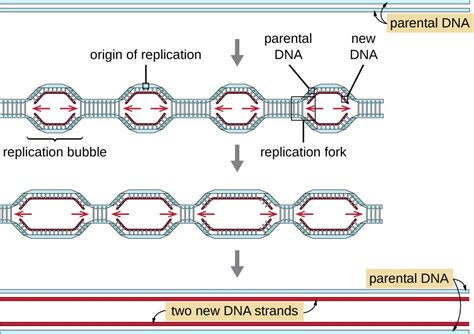
The helicase enzyme uses the energy from ATP to drive the unwinding process. As the enzyme moves along the DNA molecule, it uses the energy from ATP to break the hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides, causing the double helix to unwind. The unwinding process is initiated at a specific region of the DNA molecule known as the origin of replication.
Origin of Replication
The origin of replication is a specific region of the DNA molecule that serves as the starting point for DNA replication. This region is characterized by a unique sequence of nucleotides that is recognized by the replication machinery. The origin of replication is where the helicase enzyme binds to the DNA molecule, initiating the unwinding process.
Once the helicase enzyme has unwound the DNA template, the replication machinery can access the template strands. The replication machinery consists of a complex of enzymes and proteins that work together to synthesize new nucleotides to form a complementary copy of the original DNA molecule.
Replication Machinery
The replication machinery is a complex of enzymes and proteins that work together to synthesize new nucleotides to form a complementary copy of the original DNA molecule. This machinery includes enzymes such as DNA polymerase, which is responsible for synthesizing new nucleotides, and RNA primase, which is responsible for synthesizing RNA primers.
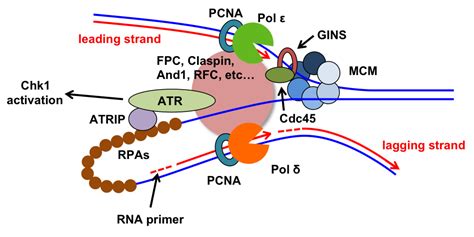
The replication machinery uses the energy from ATP to drive the synthesis of new nucleotides. As the replication machinery moves along the DNA molecule, it uses the energy from ATP to synthesize new nucleotides to form a complementary copy of the original DNA molecule.
Importance of ATP in DNA Replication
ATP plays a crucial role in the process of DNA replication. It provides the energy required to unwind the DNA template, allowing the replication machinery to access the template strands. Without ATP, the DNA replication process would not be possible.
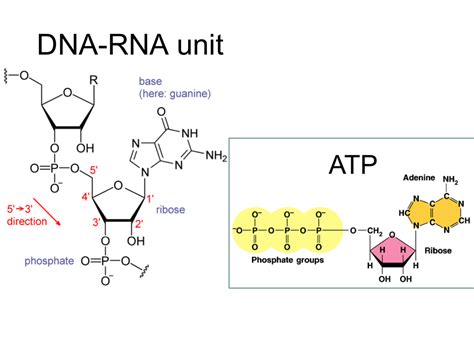
In addition to its role in unwinding the DNA template, ATP is also required for the synthesis of new nucleotides. The replication machinery uses the energy from ATP to synthesize new nucleotides to form a complementary copy of the original DNA molecule.
Energy Requirements of DNA Replication
The process of DNA replication requires a significant amount of energy. This energy is provided by ATP, which is produced during cellular respiration. The energy from ATP is used to drive the unwinding of the DNA template, as well as the synthesis of new nucleotides.
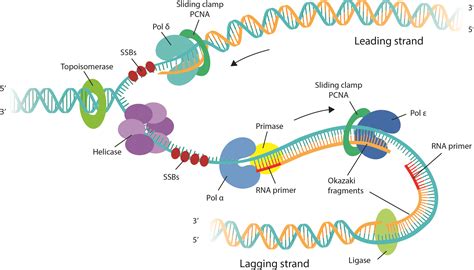
In conclusion, ATP plays a crucial role in the process of DNA replication. It provides the energy required to unwind the DNA template, allowing the replication machinery to access the template strands. The helicase enzyme uses the energy from ATP to unwind the DNA template, while the replication machinery uses the energy from ATP to synthesize new nucleotides to form a complementary copy of the original DNA molecule.
Gallery of DNA Replication
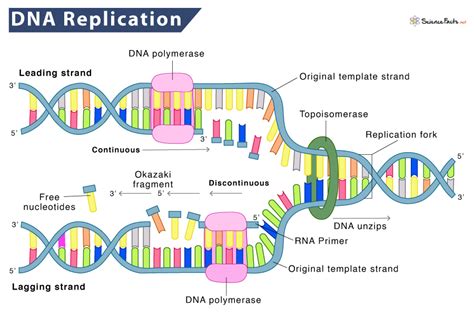
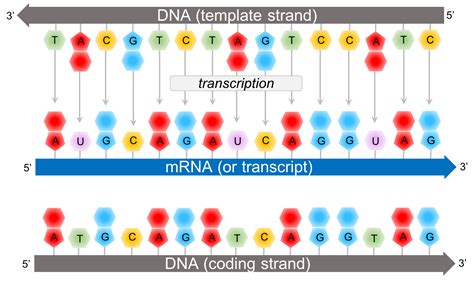
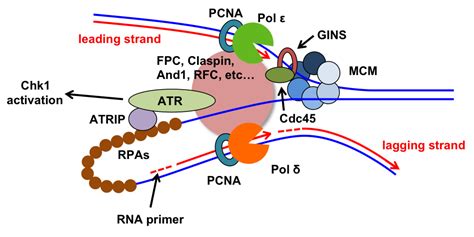
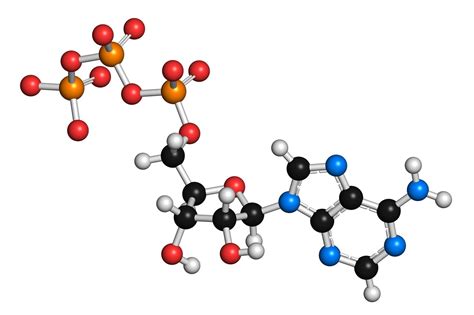
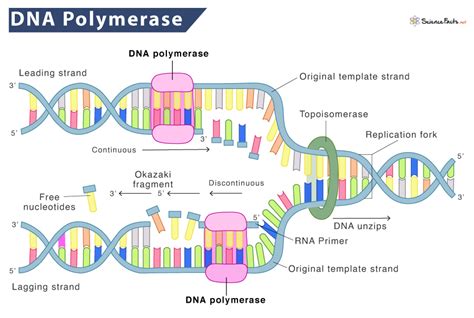
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the role of ATP in DNA replication. If you have any questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please don't hesitate to ask. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about DNA replication and the crucial role that ATP plays in this process.
