Intro
Discover the Aircraft Controller Job Description and Requirements. Learn about the role of air traffic controllers, their responsibilities, and skills needed to succeed. Explore education, training, and certification requirements for a career in air traffic control, including FAA regulations and radar technology expertise.
The role of an aircraft controller, also known as an air traffic controller, is a highly specialized and critical position in the aviation industry. These professionals are responsible for ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft through the National Airspace System (NAS). The job requires a unique blend of technical skills, situational awareness, and decision-making abilities.
Aircraft controllers work in a fast-paced, dynamic environment, often under intense pressure. They must be able to multitask, prioritize, and make quick decisions to prevent collisions, minimize delays, and optimize air traffic flow. The importance of their role cannot be overstated, as the safety of thousands of passengers, crew members, and aircraft depend on their expertise and judgment.
Key Responsibilities
Aircraft controllers are responsible for:
- Coordinating the movement of aircraft on the ground and in the air
- Issuing clearances, instructions, and advisories to pilots
- Separating aircraft to prevent collisions and maintain safe distances
- Providing weather information, navigation assistance, and other critical information to pilots
- Managing air traffic flow to minimize delays and optimize efficiency
- Responding to emergency situations, such as aircraft emergencies or severe weather events
Requirements and Qualifications
To become an aircraft controller, an individual must meet certain requirements and qualifications, including:
- Being at least 18 years old
- Being a U.S. citizen
- Passing a physical examination and a background investigation
- Scoring well on the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) pre-employment test
- Completing an FAA-approved training program at the Federal Aviation Administration Academy
- Gaining practical experience through on-the-job training
Education and Training
Aircraft controllers typically hold a bachelor's degree in a field such as air traffic control, aviation, or a related field. However, the FAA does not require a specific degree for this position. Instead, candidates must complete an FAA-approved training program, which includes both classroom instruction and practical training.

Skills and Abilities
Aircraft controllers must possess a range of skills and abilities, including:
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Strong problem-solving and decision-making abilities
- Ability to multitask and prioritize tasks
- Strong situational awareness and spatial reasoning
- Ability to work well under pressure and manage stress
- Familiarity with air traffic control procedures and regulations
Certification and Licensing
Aircraft controllers must obtain certification from the FAA, which involves passing a written examination and a practical skills test. Controllers must also meet the FAA's medical standards and undergo regular medical evaluations to maintain their certification.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Aircraft controllers can advance to a range of positions, including:
- Supervisor or manager
- Traffic management coordinator
- Air traffic control specialist
- Aviation safety inspector
Salary and Benefits
The salary range for aircraft controllers varies depending on the location, experience, and level of certification. However, median salaries range from $60,000 to over $170,000 per year. Controllers also receive a range of benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.
Challenges and Opportunities
The role of an aircraft controller is both challenging and rewarding. Controllers must work in a fast-paced, dynamic environment, often under intense pressure. However, they also have the opportunity to make a critical contribution to the safety and efficiency of the aviation industry.
Aircraft Controller Salary and Benefits
Aircraft controllers are among the highest-paid professionals in the aviation industry. Their salaries vary depending on the location, experience, and level of certification.

Median Salary Range
The median salary range for aircraft controllers is:
- Developmental controllers: $60,000 - $80,000 per year
- Certified professional controllers: $80,000 - $120,000 per year
- Executive controllers: $120,000 - $170,000 per year
Benefits
Aircraft controllers receive a range of benefits, including:
- Health insurance
- Retirement plans
- Paid time off
- Life insurance
- Disability insurance
Aircraft Controller Work Environment
Aircraft controllers work in a fast-paced, dynamic environment, often under intense pressure.

Air Traffic Control Towers
Aircraft controllers work in air traffic control towers, which are typically located at airports or other aviation facilities. The towers are equipped with sophisticated radar and communication systems, which allow controllers to track and coordinate the movement of aircraft.
Shift Work
Aircraft controllers typically work rotating shifts, including night shifts, weekends, and holidays. They may also be required to work overtime, especially during periods of high air traffic volume.
Stress and Pressure
The role of an aircraft controller is highly stressful, as controllers must make quick decisions to prevent collisions and minimize delays. They must also work well under pressure, often in emergency situations.
Aircraft Controller Training and Certification
Aircraft controllers must complete an FAA-approved training program and obtain certification from the FAA.

FAA Academy
The FAA Academy is the primary training facility for aircraft controllers. The academy provides a comprehensive training program, which includes both classroom instruction and practical training.
Certification Requirements
To become certified, aircraft controllers must pass a written examination and a practical skills test. They must also meet the FAA's medical standards and undergo regular medical evaluations to maintain their certification.
Aircraft Controller Career Path
Aircraft controllers can advance to a range of positions, including supervisor or manager, traffic management coordinator, air traffic control specialist, and aviation safety inspector.

Supervisor or Manager
Aircraft controllers can advance to supervisory or management positions, where they oversee the work of other controllers and coordinate air traffic flow.
Traffic Management Coordinator
Traffic management coordinators are responsible for planning and coordinating air traffic flow, often in response to changing weather conditions or other factors.
Air Traffic Control Specialist
Air traffic control specialists work in a range of roles, including air traffic control, aviation safety, and air traffic management.
Aviation Safety Inspector
Aviation safety inspectors are responsible for ensuring that aircraft and aviation facilities meet safety standards and regulations.
Gallery of Aircraft Controller Images
Aircraft Controller Image Gallery




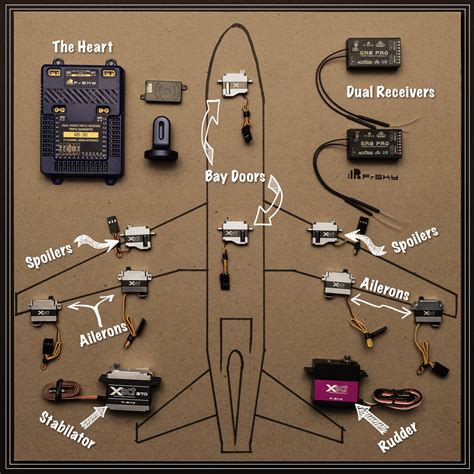




We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the role of an aircraft controller. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
