Intro
Unlock the power of Excel VBA by mastering the Active Worksheet. Learn how to efficiently interact with the active worksheet, manipulate data, and automate tasks using VBA coding. Discover essential methods, properties, and techniques for working with the active worksheet, including selecting cells, formatting, and data manipulation, to boost your Excel productivity.
When it comes to working with Excel VBA, understanding how to interact with the active worksheet is essential. The active worksheet is the worksheet that is currently being displayed and edited in the Excel application. In this article, we will explore the different ways to work with the active worksheet in Excel VBA, including how to select cells, ranges, and worksheets, as well as how to perform common tasks such as formatting and data manipulation.
Understanding the Active Worksheet
The active worksheet is the worksheet that is currently being displayed in the Excel application. It is the worksheet that is currently being edited and manipulated by the user. In VBA, the active worksheet can be referred to using the ActiveSheet property. This property returns a Worksheet object that represents the active worksheet.
Referencing the Active Worksheet
To reference the active worksheet in VBA, you can use the ActiveSheet property. For example:
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = ActiveSheet
This code sets the ws variable to the active worksheet. You can then use the ws variable to refer to the active worksheet in your code.
Selecting Cells and Ranges
To select cells and ranges in the active worksheet, you can use the Range property. This property returns a Range object that represents a range of cells in the worksheet.
Selecting a Single Cell
To select a single cell in the active worksheet, you can use the Range property and specify the address of the cell. For example:
Dim cell As Range
Set cell = Range("A1")
This code sets the cell variable to the cell at address A1 in the active worksheet.
Selecting a Range of Cells
To select a range of cells in the active worksheet, you can use the Range property and specify the address of the range. For example:
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Range("A1:C10")
This code sets the rng variable to the range of cells from A1 to C10 in the active worksheet.
Performing Common Tasks

Once you have selected cells and ranges in the active worksheet, you can perform common tasks such as formatting and data manipulation.
Formatting Cells
To format cells in the active worksheet, you can use the Font, Interior, and Borders properties of the Range object. For example:
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Range("A1:C10")
rng.Font.Bold = True
rng.Interior.Color = vbYellow
rng.Borders.LineStyle = xlContinuous
This code sets the font of the range to bold, sets the interior color to yellow, and sets the border style to continuous.
Data Manipulation
To perform data manipulation in the active worksheet, you can use the Value property of the Range object. For example:
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Range("A1:C10")
rng.Value = 10
This code sets the value of the range to 10.
Working with Multiple Worksheets
In addition to working with the active worksheet, you can also work with multiple worksheets in a workbook.
Selecting Multiple Worksheets
To select multiple worksheets in a workbook, you can use the Worksheets collection and specify the indexes of the worksheets. For example:
Dim ws1 As Worksheet
Dim ws2 As Worksheet
Set ws1 = Worksheets(1)
Set ws2 = Worksheets(2)
This code sets the ws1 variable to the first worksheet in the workbook and the ws2 variable to the second worksheet in the workbook.
COPYING AND PASTING DATA BETWEEN WORKSHEETS
To copy and paste data between worksheets, you can use the Copy and Paste methods of the Range object. For example:
Dim ws1 As Worksheet
Dim ws2 As Worksheet
Set ws1 = Worksheets(1)
Set ws2 = Worksheets(2)
ws1.Range("A1:C10").Copy
ws2.Range("A1").Paste
This code copies the range of cells from A1 to C10 in the first worksheet and pastes it into the range of cells starting at A1 in the second worksheet.
Gallery of Mastering Excel VBA
Mastering Excel VBA Image Gallery
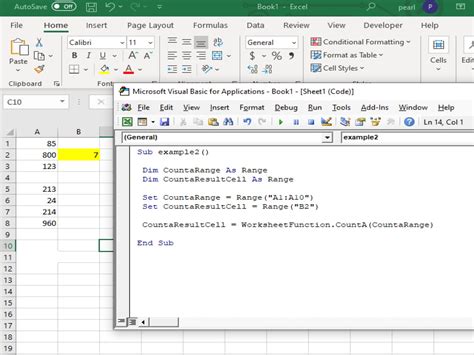

In conclusion, mastering Excel VBA requires a deep understanding of how to work with the active worksheet, including selecting cells and ranges, performing common tasks, and working with multiple worksheets. By following the tips and techniques outlined in this article, you can improve your skills and become more proficient in using Excel VBA to automate tasks and manipulate data.
