Intro
Section 8 Housing and Food Stamps are two vital programs designed to support low-income individuals and families in the United States. The Section 8 Housing Choice Voucher Program helps participants pay rent, while the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), also known as Food Stamps, assists with food purchases. Both programs aim to improve the overall quality of life for those struggling financially.
The Section 8 Housing Choice Voucher Program, administered by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), provides rental assistance to eligible low-income families, the elderly, and people with disabilities. The program's primary goal is to help participants find safe, decent, and affordable housing in the private market. Section 8 vouchers enable families to pay a reduced rent amount, making it possible for them to afford housing that might otherwise be unaffordable.

In contrast, the SNAP program, also known as Food Stamps, is a federal program administered by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). SNAP provides assistance to eligible low-income individuals and families to purchase food. The program aims to reduce hunger and malnutrition among vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and people with disabilities.
Eligibility and Application Process
To be eligible for Section 8 Housing and Food Stamps, applicants must meet specific income and eligibility requirements. For Section 8, the applicant's income must not exceed 50% of the area median income, adjusted for family size. Additionally, applicants must be U.S. citizens or have eligible immigration status.

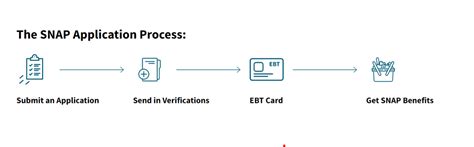
To apply for Section 8, applicants typically need to submit an application to their local public housing agency (PHA). The PHA will review the application, verify income and eligibility, and place the applicant on a waiting list if eligible.
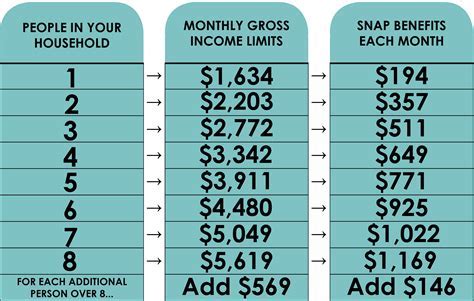
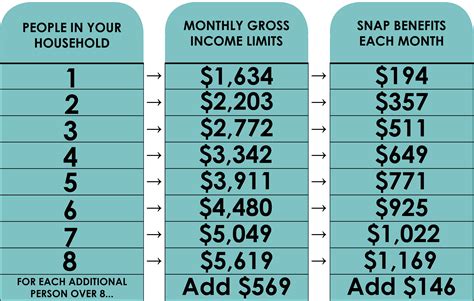
For SNAP, applicants must also meet income and eligibility requirements, which vary depending on the state and household size. Applicants typically need to submit an application to their local social services department or SNAP office.
Benefits of Section 8 Housing
The Section 8 Housing Choice Voucher Program offers several benefits to participants, including:
- Affordable housing: Section 8 vouchers enable participants to pay a reduced rent amount, making it possible to afford housing that might otherwise be unaffordable.
- Increased mobility: Participants can choose from a wide range of housing options, including single-family homes, apartments, and townhouses.
- Improved living conditions: Section 8 vouchers can help participants access safer, more decent housing.

Benefits of Food Stamps
The SNAP program offers several benefits to participants, including:
- Food assistance: SNAP benefits enable participants to purchase food, reducing the risk of hunger and malnutrition.
- Flexibility: Participants can use their SNAP benefits to purchase a wide range of food items, including fresh produce, meat, dairy products, and household staples.
- Convenience: SNAP benefits can be used at most grocery stores, supermarkets, and farmers' markets.

Challenges and Limitations
While Section 8 Housing and Food Stamps provide essential support to low-income individuals and families, both programs face challenges and limitations.
For Section 8, some of the challenges include:
- Limited funding: Section 8 funding is limited, resulting in long waiting lists for vouchers.
- Insufficient affordable housing: The availability of affordable housing units is often insufficient, making it difficult for participants to find suitable housing.

For SNAP, some of the challenges include:
- Stigma: Some participants may experience stigma associated with receiving SNAP benefits.
- Limited benefits: SNAP benefits may not be sufficient to cover the full cost of food, leaving participants with limited purchasing power.

Conclusion and Future Directions
Section 8 Housing and Food Stamps are vital programs that provide essential support to low-income individuals and families. While both programs face challenges and limitations, they remain critical components of the social safety net. To address the challenges and limitations, policymakers and administrators can explore strategies such as increasing funding, improving program administration, and expanding eligibility.
As the landscape of poverty and housing continues to evolve, it is essential to revisit and refine these programs to ensure they remain effective and responsive to the needs of vulnerable populations.
Section 8 Housing and Food Stamps Image Gallery






If you or someone you know is struggling with poverty and housing, there are resources available to help. We encourage you to reach out to your local social services department or non-profit organizations that provide assistance with housing and food. By working together, we can build a more supportive and inclusive community for all.
