Intro
Executing Access queries using VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a powerful way to automate and customize tasks within Microsoft Access. This approach allows you to leverage the flexibility of VBA to run queries under specific conditions, at scheduled times, or as part of a larger automation process. In this article, we will delve into the details of running Access queries with VBA, covering the basics, practical examples, and optimization techniques.
Understanding Access Queries and VBA
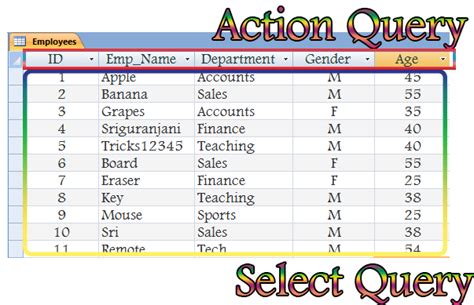
Before we dive into the specifics of running Access queries with VBA, it's essential to understand the basics of both Access queries and VBA. Access queries are used to retrieve, manipulate, and analyze data stored in your Access database. VBA, on the other hand, is a programming language used for creating and automating tasks within Microsoft Office applications, including Access.
Why Use VBA to Run Access Queries?
Using VBA to run Access queries offers several advantages:
- Automation: VBA allows you to automate repetitive tasks, such as running queries at specific times or when certain conditions are met.
- Flexibility: You can dynamically change query parameters, tables, or even the query itself based on your needs.
- Integration: VBA can interact with other Access objects, such as forms and reports, enabling more complex workflows.
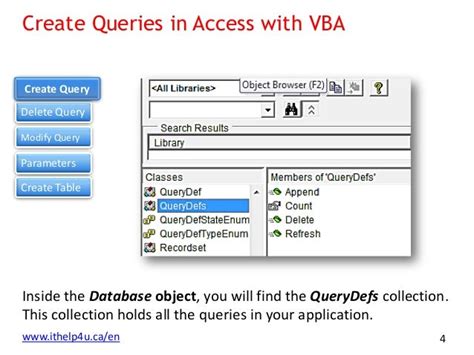
Running Access Queries with VBA

To run an Access query using VBA, you can use the DoCmd.OpenQuery method. Here's a basic example:
Sub RunQuery()
DoCmd.OpenQuery "YourQueryName"
End Sub
Replace "YourQueryName" with the actual name of your query.
Parameters and Criteria
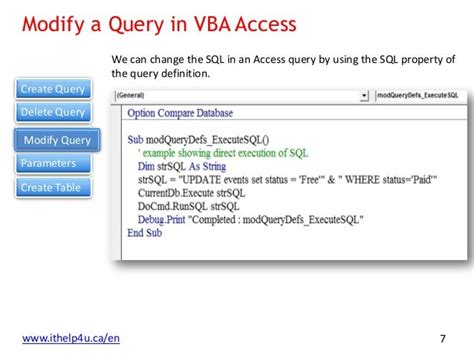
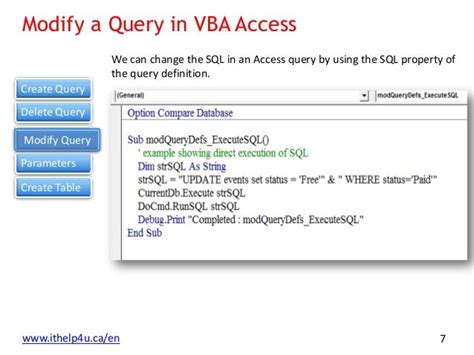
For queries that require parameters or criteria, you can modify the query object itself or use the DoCmd.OpenQuery method with parameters. Here's an example of how to set a parameter:
Sub RunQueryWithParameter()
Dim qry As DAO.QueryDef
Set qry = CurrentDb.QueryDefs("YourQueryName")
qry.Parameters("ParameterName").Value = "ParameterValue"
qry.Execute
Set qry = Nothing
End Sub
Practical Examples
- Daily Data Update: Use VBA to run a query that updates your database with new data from another source on a daily basis.
- Automated Reporting: Run queries that feed into reports, and then use VBA to automatically generate and email these reports to stakeholders.
Optimization Techniques
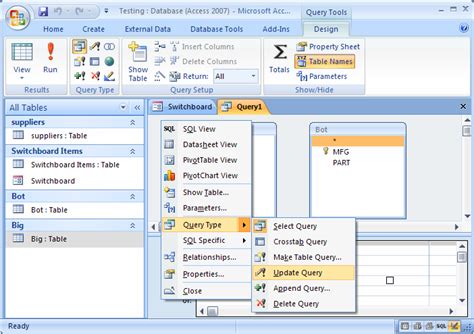
- Use Indexes: Proper indexing can significantly speed up your queries.
- Optimize Query Design: Ensure your queries are designed to retrieve only necessary data.
- Avoid Unnecessary Operations: Minimize the number of times a query is run by caching results when appropriate.
Common Issues and Solutions
- Error Handling: Use
On Errorstatements to gracefully handle errors and provide useful feedback. - Performance Issues: Monitor database size and query complexity to prevent slowdowns.
Conclusion
Running Access queries with VBA opens up a world of automation and customization possibilities within your database. By understanding how to leverage VBA to execute queries dynamically, you can streamline tasks, improve data analysis, and enhance overall database performance.
Gallery of Access Queries with VBA
Access Queries with VBA Gallery
We invite you to share your experiences and tips on using VBA to run Access queries in the comments section below. Don't forget to subscribe for more in-depth articles on Access, VBA, and database management.
