Intro
Discover the most efficient ways to calculate heat loss and optimize your buildings energy efficiency. Learn how to identify heat loss sources, conduct heat loss calculations, and implement cost-effective solutions. Master the art of heat loss calculation methods, including U-factor, R-value, and ASHRAE standards, to minimize energy waste and reduce heating costs.
Heat loss is a critical factor in building design and energy efficiency. Understanding how to calculate heat loss efficiently is essential for architects, engineers, and builders to create buildings that are not only comfortable but also energy-efficient. In this article, we will explore seven ways to calculate heat loss efficiently, providing you with a comprehensive guide to help you optimize your building's energy performance.
Understanding Heat Loss
Before we dive into the calculation methods, it's essential to understand what heat loss is and how it affects buildings. Heat loss occurs when warm air escapes from a building, and cold air enters, causing a temperature difference. This temperature difference can lead to energy losses, increased energy bills, and a reduced level of comfort for occupants.
Method 1: U-Value Calculation
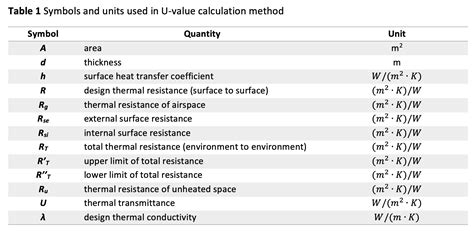
The U-value calculation is a widely used method to determine heat loss through building elements such as walls, floors, and roofs. The U-value is a measure of the thermal transmittance of a material, and it's usually expressed in watts per square meter per degree Kelvin (W/m²K). To calculate the U-value, you need to know the thermal conductivity of the material, its thickness, and the temperature difference between the inside and outside environments.
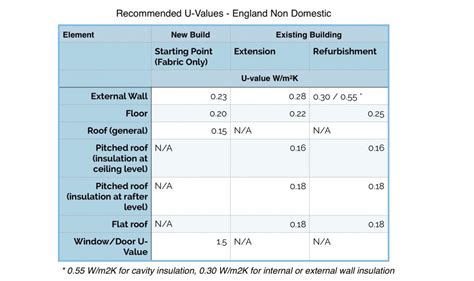
Method 2: ASHRAE Calculation
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) provides a calculation method to determine heat loss through building envelopes. This method takes into account various factors, including the building's location, climate, and envelope characteristics. The ASHRAE calculation is more comprehensive than the U-value method and provides a more accurate estimate of heat loss.
ASHRAE Calculation Formula
- Q = (U * A * ΔT) + (L * ΔT)
Where:
- Q = heat loss (W)
- U = U-value (W/m²K)
- A = surface area (m²)
- ΔT = temperature difference (K)
- L = length of the building element (m)
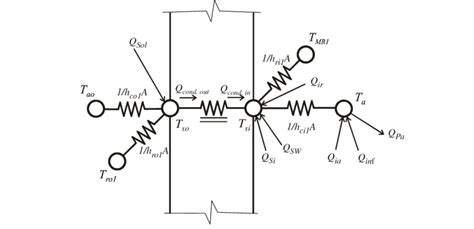
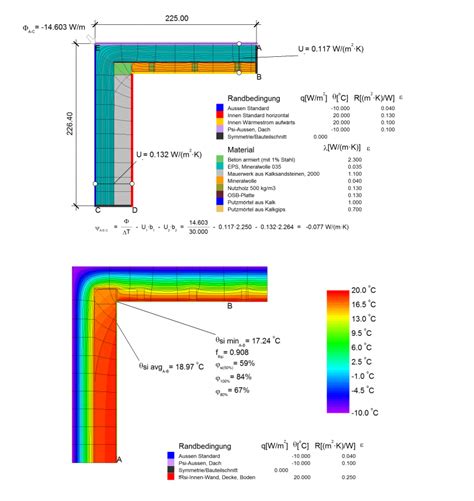
Method 3: Thermal Bridging Calculation
Thermal bridging occurs when there is a gap or a discontinuity in the building envelope, allowing heat to escape. This method calculates the heat loss through thermal bridges, which can be significant in buildings with complex geometries or construction details.
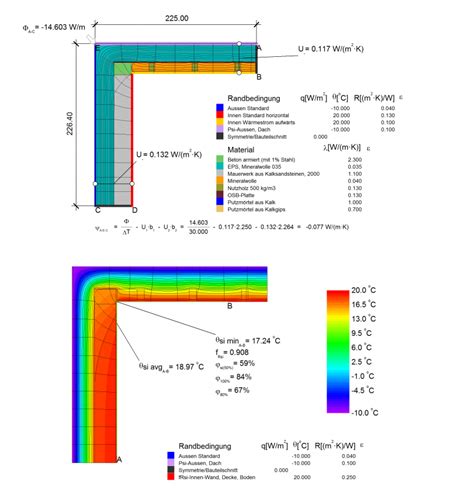
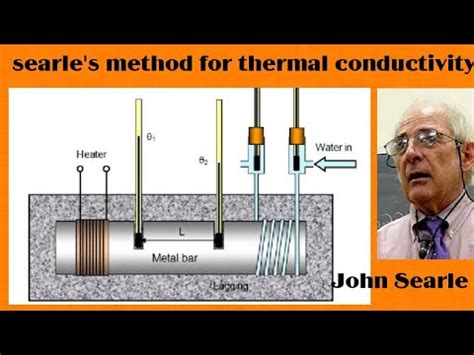
Method 4: Conduction Calculation
Conduction is the transfer of heat through a solid material. This method calculates the heat loss through conduction, taking into account the thermal conductivity of the material, its thickness, and the temperature difference between the inside and outside environments.
Conduction Calculation Formula
- Q = (k * A * ΔT) / d
Where:
- Q = heat loss (W)
- k = thermal conductivity (W/mK)
- A = surface area (m²)
- ΔT = temperature difference (K)
- d = thickness of the material (m)
Method 5: Radiation Calculation
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. This method calculates the heat loss through radiation, taking into account the surface temperature, emissivity, and the temperature difference between the inside and outside environments.

Method 6: Infiltration Calculation
Infiltration is the entry of outside air into a building through gaps and cracks. This method calculates the heat loss through infiltration, taking into account the air leakage rate, the temperature difference between the inside and outside environments, and the building's volume.
Infiltration Calculation Formula
- Q = (L * ΔT * V)
Where:
- Q = heat loss (W)
- L = air leakage rate (m³/h)
- ΔT = temperature difference (K)
- V = building volume (m³)
Method 7: Building Simulation
Building simulation is a comprehensive method that takes into account various factors, including the building's geometry, materials, climate, and occupancy. This method uses software tools to simulate the building's energy performance and calculate heat loss.
Gallery of Heat Loss Calculation Methods
Heat Loss Calculation Methods Image Gallery



Conclusion
Calculating heat loss efficiently is crucial for building designers and energy efficiency experts. By using the seven methods outlined in this article, you can optimize your building's energy performance and reduce heat loss. Remember to consider various factors, including the building's geometry, materials, climate, and occupancy, to get an accurate estimate of heat loss. By doing so, you can create buildings that are not only comfortable but also energy-efficient and sustainable.
What's your experience with heat loss calculation methods? Share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below!
